Tungsten carbide is one of the hardest and most durable materials used in modern industry. When shaped into wear parts, it offers resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and extreme pressure.
These properties make tungsten carbide wear parts critical in industries where machines and tools are exposed to high levels of friction and stress.
For decision-makers, understanding what tungsten carbide wear parts are used for is essential to make better choices in procurement, cost reduction, and equipment reliability.
This article explains the applications, benefits, and key markets where tungsten carbide wear parts deliver the most value.
What Are Tungsten Carbide Wear Parts?

Tungsten carbide wear parts are engineered components made from a composite of tungsten carbide grains and a metal binder, usually cobalt or nickel.
These parts are designed to resist:
Friction and abrasion
High pressure and impact
Corrosion and chemical attack
Extreme temperatures
Common examples of tungsten carbide wear parts include:
Inserts
Custom-made wear parts
They are widely used because they offer longer service life, less downtime, and lower maintenance costs compared to steel or ceramic parts.
Why Industries Choose Tungsten Carbide Wear Parts
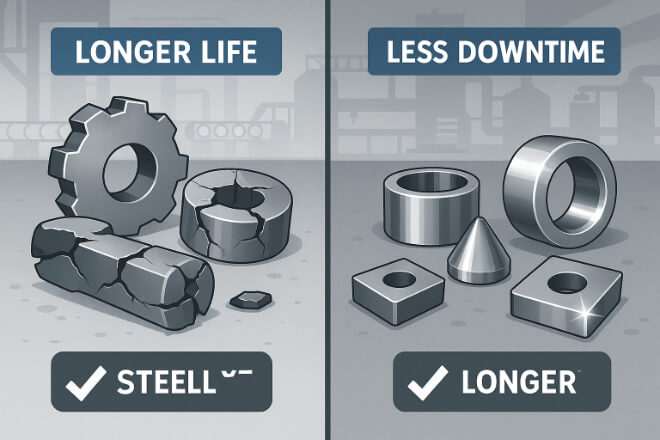
Decision-makers prefer tungsten carbide wear parts because they help improve productivity and cost efficiency. The key benefits are:
Longer lifespan – parts last 5–10 times longer than steel.
Lower downtime – fewer replacements and repairs.
Improved performance – machines run at higher speeds with less wear.
Better safety – reduced risk of part failure in critical systems.
Cost savings – lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
For industries with heavy-duty operations, investing in tungsten carbide wear parts is not only about saving money but also about ensuring reliability and safety.
Applications in the Oil and Gas Industry
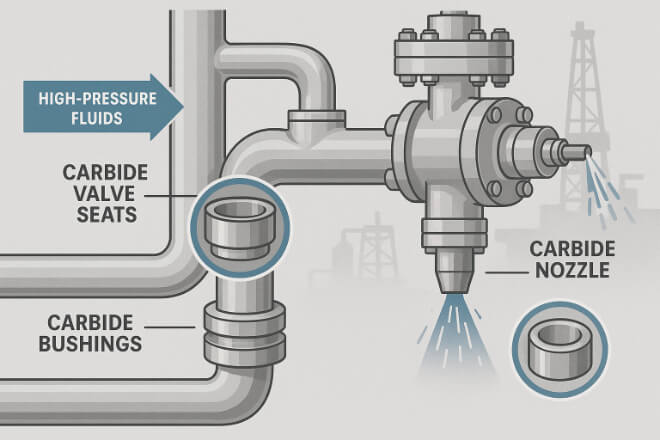
In oil and gas drilling, equipment faces sand erosion, high-pressure fluids, and corrosive chemicals. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Valve seats and poppets – to resist erosion and maintain tight sealing under pressure.
Flow control nozzles – to handle abrasive fluids.
Pump sleeves and bushings – to extend pump life and reduce downtime.
Without tungsten carbide, equipment would fail quickly, leading to costly shutdowns and safety risks.
Applications in the Mining and Construction Industry
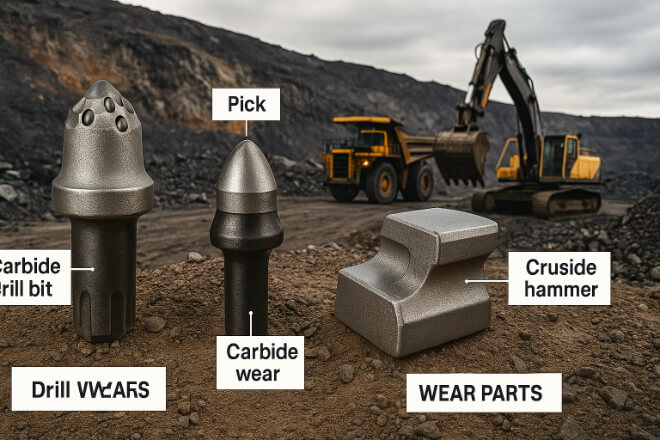

Mining and construction require tools that can withstand rock, concrete, and heavy impact. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Drill bits and inserts – for rock drilling and tunnel boring.
Crusher hammers and picks – for crushing and grinding rocks.
Wear plates and strips – for earth-moving equipment.
By using carbide, machines can operate longer in harsh environments, reducing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Applications in the Metalworking Industry
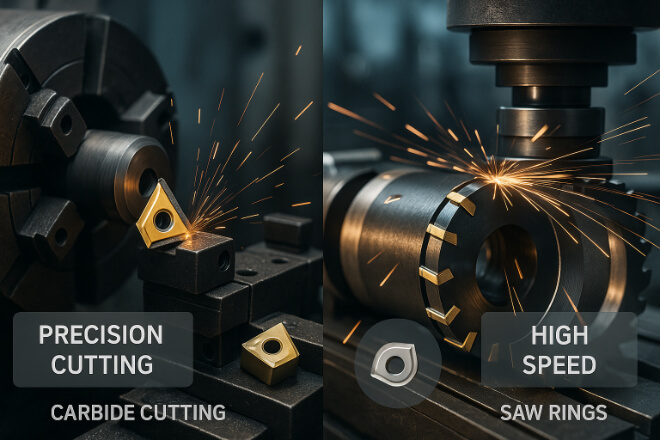
Metal cutting and machining depend on tools that can cut hard materials at high speeds. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Cutting inserts – for turning, milling, and drilling.
Saw tips – for cutting steel, aluminum, and alloys.
Forming dies – for stamping and shaping metals.
Carbide tools provide higher cutting speeds, better precision, and longer life compared to traditional steel tools.
Applications in the Woodworking and Paper Industry

In woodworking and paper cutting, tools face continuous friction and cutting stress. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Wood inserts and saw blades – for clean, precise wood cutting.
Paper knives and trimmer blades – for high-speed paper cutting machines.
Rotary cutters – for long production runs without tool failure.
These parts reduce the need for frequent sharpening and replacement, saving time and cost.
Applications in the Aerospace and Automotive Industry
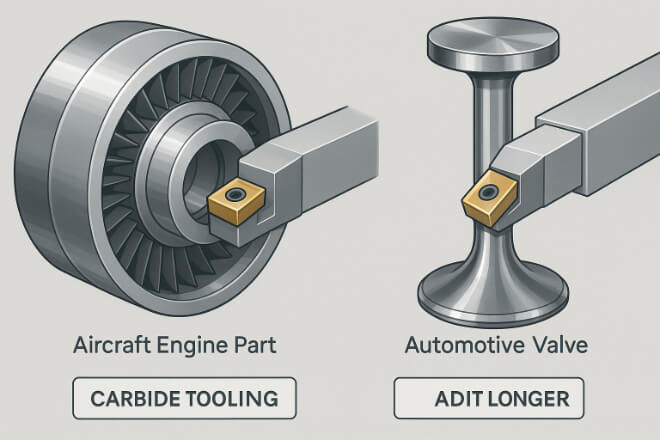
Both aerospace and automotive industries demand precision and reliability. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Precision cutting tools – for machining engine components.
Valve components – for high-pressure systems.
Seals and bearings – to handle extreme loads and temperatures.
These industries depend on carbide wear parts to ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term performance.
Applications in the Electronics Industry
The electronics sector requires micron-level precision. Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in:
Micro drills and cutting tools – for printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Punches and dies – for forming small electronic components.
Wire drawing dies – for producing ultra-fine wires.
Here, carbide ensures high accuracy and long tool life in mass production.
Custom Carbide Wear Parts for Special Applications
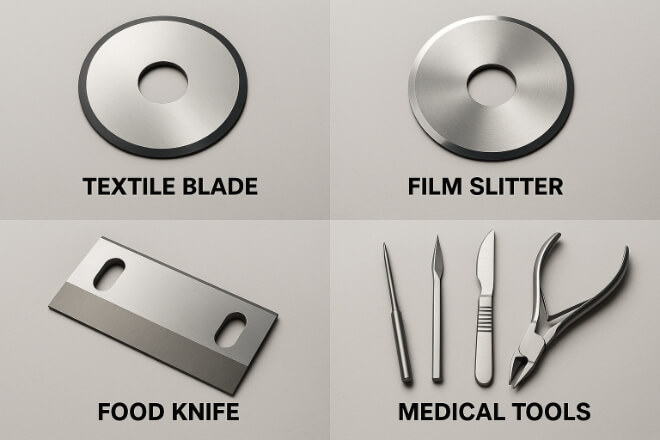

Not all industries use standard parts. Many require custom carbide solutions. Examples include:
Textile cutting blades
Film and packaging slitters
Food processing knives
Medical precision tools
Custom carbide wear parts are designed based on application requirements, ensuring performance and durability in niche markets.
The Business Value of Choosing Carbide Wear Parts
For decision-makers, the choice of carbide wear parts is a strategic investment. Benefits include:
Reduced operational costs by lowering replacement frequency.
Improved production efficiency with less downtime.
Better return on investment (ROI) compared to cheaper, short-life alternatives.
Competitive advantage in industries where reliability is critical.
By choosing carbide wear parts, companies secure long-term efficiency and sustainability in their operations.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide wear parts are used in almost every heavy-duty industry, from oil and gas to mining, from woodworking to electronics.
Their wear resistance, hardness, and durability make them essential for companies that want to reduce costs, increase reliability, and protect valuable machines.
For decision-makers, investing in tungsten carbide wear parts is not just about replacing steel – it is about choosing long-term performance, safety, and efficiency.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
