Refinery charge and bottoms pumps work in tough conditions. They handle high pressure, high temperature, and aggressive fluids.
Choosing the right carbide seal rings is critical for safe operation, lower maintenance costs, and longer pump life.
This guide uses simple words and clear steps to help refinery decision-makers choose the best seal rings.
Why Carbide Seal Rings Matter
Carbide seal rings are made from very hard materials like tungsten carbide or silicon carbide.
These materials resist wear, heat, and chemical attack better than steel or ceramic. In refinery charge and bottoms pumps, good seals help to:
Prevent dangerous leaks of hydrocarbons
Reduce pump downtime and repair costs
Improve pump efficiency and reliability
Protect workers and the environment
Types of Carbide Materials
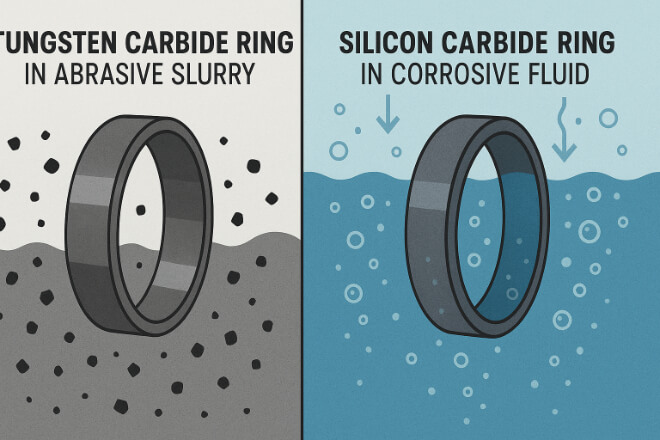
1). Tungsten Carbide (WC)
Extremely hard and strong
Works well with abrasive fluids and heavy loads
Usually contains cobalt or nickel binders for toughness or corrosion resistance
2). Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Excellent chemical resistance
Lighter weight, reducing shaft load
More brittle, so less suited to shock loads
3). Binder Options
Cobalt Binder: Tough and handles shock well but can corrode in sour service
Nickel Binder: Better corrosion resistance for acidic or aggressive fluids
Key Factors for Selection
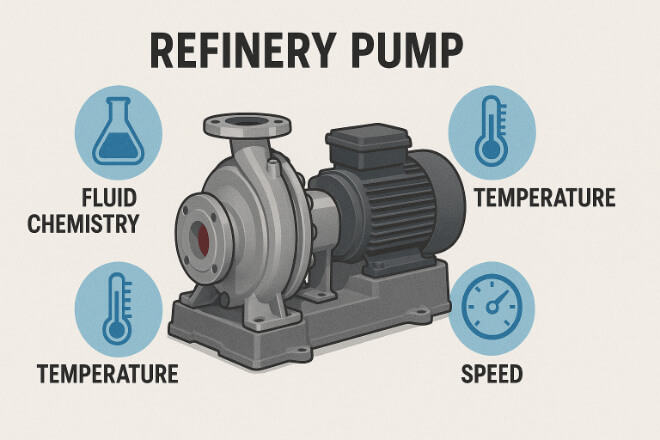
1). Fluid Chemistry
Heavy bottoms or light hydrocarbons?
Sour or acidic fluids?
Abrasive slurries or solids?
Choose silicon carbide for high corrosion risk. Use tungsten carbide for abrasive fluids.
2). Temperature and Pressure
Refinery pumps may face over 400 °F (200 °C) and very high pressures. Tungsten carbide works well under extreme stress.
Silicon carbide can handle heat but must be protected from thermal shock.
3). Pump Speed and Load
Higher shaft speeds create more frictional heat. Pick ring grades with strong wear resistance. Tungsten carbide’s strength is ideal for heavy loads.
4). Mechanical Seal Design
Decide between balanced or unbalanced seals
Check face pairings: carbide vs. carbon or carbide vs. carbide
Include flush or cooling systems to avoid dry running
5). Standards and Compliance
Follow API 682 or other refinery standards. Choose suppliers with ISO 9001 or similar certifications.
Common Errors to Avoid
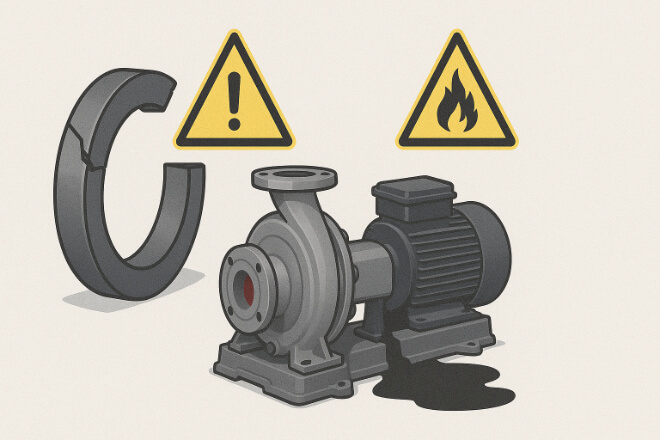
Selecting cobalt binder in corrosive sour service
Ignoring thermal shock limits for silicon carbide
Skipping flush systems, leading to dry running and wear
Choosing suppliers without refinery experience or fast support
Cost vs. Long-Term Value
Carbide seal rings are more expensive upfront but cheaper over time. They:
Reduce unplanned shutdowns
Extend pump and seal life
Lower environmental and safety risks
Considering total cost of ownership can help justify the higher initial price.
Supplier Selection Tips

Pick suppliers with proven refinery experience
Ask for engineering support and local inventory
Verify that material grades are traceable and genuine
Check case studies or references
| Binder Type | Main Advantage | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt | High toughness and shock resistance | Abrasive slurries and high mechanical stress |
| Nickel | Excellent corrosion resistance | Sour service and aggressive chemicals |
Maintenance Best Practices

Inspect seal faces during planned shutdowns
Use clean flush water or compatible process fluid
Replace rings before cracks or scoring appear
Train staff on proper installation torque and alignment
Environmental and Safety Benefits
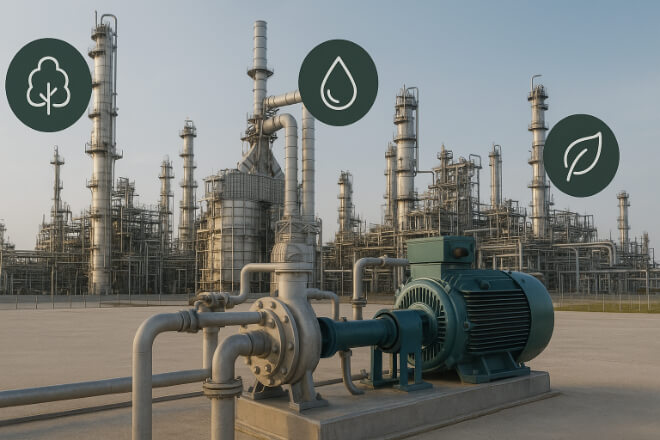

Leaks in refinery pumps can cause fire, emissions, or injury.
Correct carbide seal ring selection prevents spills and supports environmental compliance.
Investing in high-quality rings protects both people and equipment.
Conclusion
Selecting the right carbide seal rings for refinery charge and bottoms pumps is about more than price.
Decision-makers should look at fluid chemistry, temperature, binder type, standards, and supplier support. Using high-quality carbide rings ensures pump reliability, safety, and lower lifetime costs.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
