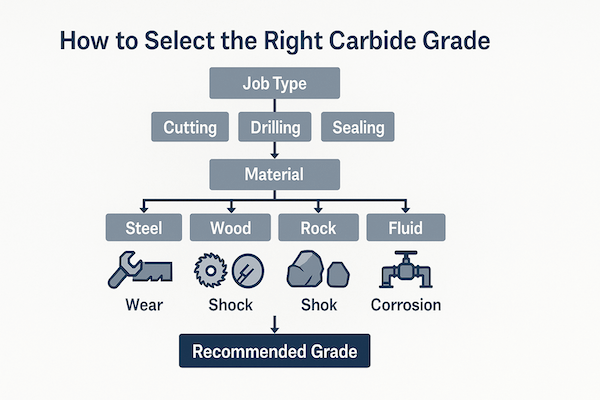
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Tungsten Carbide Grade
Learn how to choose the perfect tungsten carbide grade for your tools — based on hardness, toughness, and job performance.
What is a Carbide Grade?
Tungsten carbide grades are like “recipes” — they mix tungsten carbide grains with a metal binder (usually cobalt) in different ways.
Some grades are harder, some are tougher, and each is made for a different kind of job.
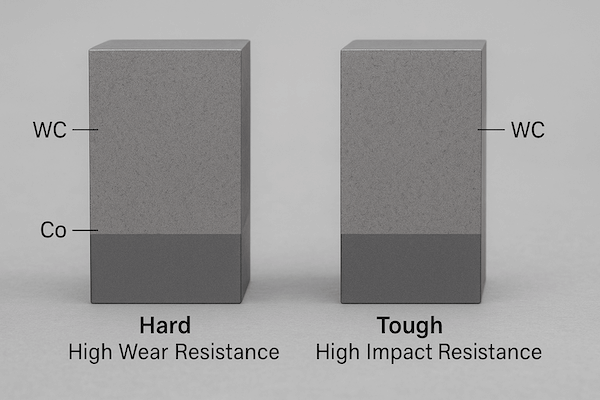
It’s about the mix of hard and tough
Carbide is made from tungsten carbide grains (WC) and a metal binder like cobalt. More WC means higher hardness. More binder means better toughness. Each grade has a different mix for different jobs.
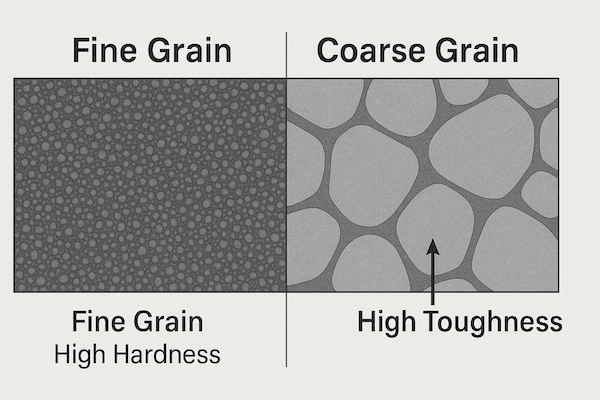
Grain size changes how it behaves
Smaller grains make the material harder and better for fine cutting. Larger grains make it tougher and better for impact work. Grain size affects sharpness and durability.

The code tells you what it’s made for
Grades like YG6 or K20 follow a naming system. YG6 = 6% cobalt. K20 = for cutting wood or plastic. The code helps match the right grade to the right job.
Grade Comparison: Hardness vs Toughness
Hard grades resist wear but can crack under shock. Tough grades survive impact but wear faster. Most jobs need a balance.
| Grade | ISO Grade | Hardness (HRA) | Toughness | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YG3 | K01 | 92.5 | Very Low | Precision wear parts |
| YG6X | K10 | 92.0 | Low | Metal cutting with high wear |
| YG6 | K20 | 91.5 | Low | Dry cutting steel |
| YG8 | K20–K30 | 90.5 | Medium | General-purpose tools |
| YG10 | K40 | 89.0 | High | Impact-resistant tooling |
| YG10X | K40 | 90.0 | High | High strength + cutting |
| YG15 | K30 | 88.5 | Very High | Mining and drilling bits |
| YG20 | K30 | 85.5 | Extreme | Heavy-duty impact tools |
Application-Based Carbide Grade Guide
Choose the right tungsten carbide grade based on the industry and usage scenario.
This table shows common grades matched with real-world applications.
| Industry | Common Grade | Why This Grade Works |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Cutting | YG6, YG10 | Wear-resistant, high hardness |
| Mining/Construction | YG15, YG20 | Tough for impact and rock shock |
| Woodworking | K05, K20 | Sharp edge + medium toughness |
| Fluid Sealing | YG8, YG13X | Good balance + corrosion resistant |
FAQ: Common Mistakes in Grade Selection
Learn about frequent errors in choosing tungsten carbide grades and how to avoid poor performance, premature wear, or tool failure by understanding material behavior and application needs.
Q1: Is a harder carbide grade always better?
No. Harder grades wear slowly but are more brittle. In applications with impact or vibration, they can crack or chip.
Q2: Can one grade work for all materials?
Not effectively. For example, a grade used for cutting wood may fail quickly on steel or stone. Each material needs a different balance of hardness and toughness.
Q3: What happens if I choose too soft a grade?
The tool may wear out quickly or lose its sharp edge. This leads to poor surface finish, lower precision, and more frequent replacements.
Q4: What if I use a grade with too much binder?
A high binder content increases toughness but lowers hardness. If wear resistance is critical (e.g. high-speed cutting), the tool may dull too fast.
Q5: Does coating fix a wrong grade choice?
No. Coatings can improve surface performance, but they can’t fix poor base properties. A weak grade underneath still limits tool life.
Q6: How do I know if the grade I chose is wrong?
Signs include chipping, cracking, rapid wear, or unexpected tool failure. Reviewing tool performance and working conditions can help identify mismatches.