In industries where parts must survive heavy wear, heat, and corrosion, choosing the right material is critical.
Three of the most popular materials for أجزاء التآكل are tungsten carbide, ceramic, and Stellite. Each material has unique properties, strengths, and weaknesses.
For decision-makers in manufacturing, التعدين, النفط والغاز, and other heavy industries, the choice between these materials can greatly affect production costs, downtime, and product performance.
This guide compares tungsten carbide, ceramic, and Stellite wear parts in detail so you can make informed choices for your operations.
ما هو كربيد التنغستن؟

Tungsten carbide is a compound made of tungsten and carbon atoms.
It is one of the hardest materials used in industry, ranking about 8.5–9 on the Mohs hardness scale.
Key Properties:
Extremely high صلابة — harder than steel and most metals.
ممتاز مقاومة التآكل — ideal for abrasive conditions.
High heat resistance — retains hardness even at high temperatures.
معتدل صلابة — more brittle than steel but stronger than most ceramics.
Common Applications: Cutting tools, mining drills, wear-resistant dies, pump and valve components, and nozzles.
What Are Ceramic Wear Parts?
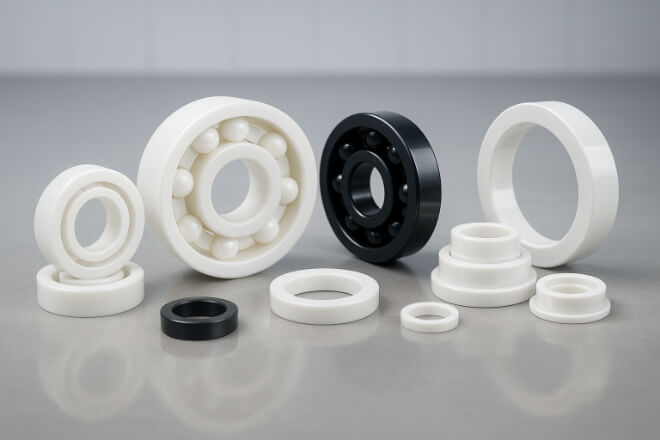

Ceramics are non-metallic, inorganic materials made from compounds such as alumina, zirconia, or silicon nitride.
Key Properties:
عالية جدًا صلابة — can be as hard as or harder than tungsten carbide.
Excellent corrosion resistance — does not rust or oxidize.
Lightweight — less dense than metal-based wear parts.
قليل صلابة — very brittle, prone to cracking under impact.
Common Applications: Bearings, seals, cutting blades for very fine finishes, and high-temperature components in chemical processing.
What Is Stellite?
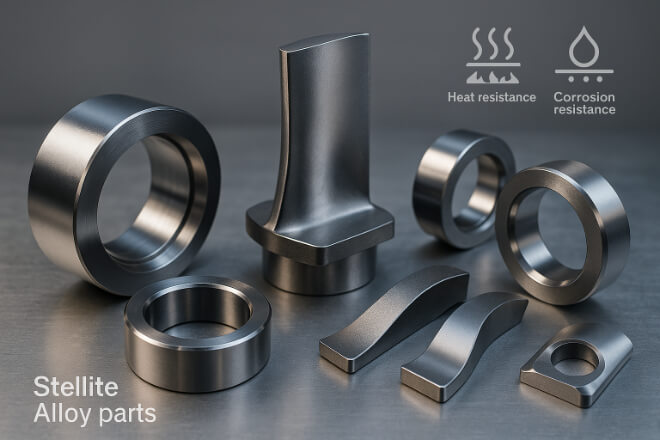

Stellite is a cobalt-based alloy containing chromium, tungsten, and other metals.
It was designed for exceptional wear and corrosion resistance, especially at high temperatures.
Key Properties:
عالي مقاومة التآكل — especially in sliding and galling conditions.
Good corrosion resistance — suitable for chemical and marine environments.
عالي صلابة — resists impact better than tungsten carbide and ceramics.
أدنى صلابة than tungsten carbide — but often enough for many industrial uses.
Common Applications: Valve seats, cutting edges, turbine blades, and wear-resistant coatings.
Material Property Comparison Table
Here is a side-by-side comparison of the three materials:
| ملكية | كربيد التنغستن | سيراميك | Stellite |
|---|---|---|---|
| صلابة | 8.5–9 Mohs | 8–9.5 Mohs | 4–6 Mohs |
| مقاومة التآكل | ممتاز | ممتاز | جيد |
| مقاومة الحرارة | عالية جدًا | عالية جدًا | عالي |
| مقاومة التآكل | عالي | ممتاز | عالي |
| صلابة | معتدل | قليل | عالي |
| كثافة | عالية جدًا | Low to medium | واسطة |
| يكلف | عالي | عالي | Medium to high |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Material
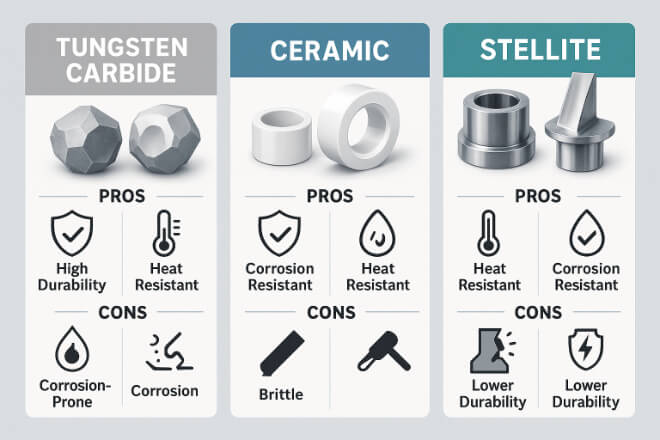
1). Tungsten Carbide
1.1). Pros:
ممتاز مقاومة التآكل in abrasive environments.
Performs well in high-heat applications.
Long service life reduces downtime.
1.2). Cons:
Can chip or break under very high impact.
More expensive than many steels.
2). Ceramic
2.1). Pros:
Extremely hard and corrosion-proof.
Lightweight — ideal for applications where weight matters.
Can operate in extremely high temperatures.
2.2). Cons:
Brittle — can fracture easily under shock or bending loads.
Can be expensive for large or complex parts.
3). Stellite
3.1). Pros:
ممتاز صلابة — handles shock and vibration well.
Good wear and corrosion resistance.
Can be welded or coated onto other parts.
3.2). Cons:
Lower hardness compared to tungsten carbide and ceramics.
May wear faster in abrasive environments.
Best Material by Application Type
| طلب | Best Choice | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| التعدين والحفر | كربيد التنغستن | Exceptional wear resistance in abrasive rock and soil. |
| المعالجة الكيميائية | سيراميك | Superior corrosion resistance and high heat capability. |
| Valve Seats in Oil & Gas | Stellite | High toughness to resist impact and vibration. |
| أدوات القطع عالية السرعة | كربيد التنغستن | Maintains sharpness and hardness at high speeds. |
| High-Temperature Bearings | سيراميك | Lightweight and stable under extreme heat. |
Choosing the Right Material
When deciding between tungsten carbide, ceramic, and Stellite, consider the following:
Type of Wear: For abrasion, tungsten carbide and ceramics are top choices. For impact and galling, Stellite is better.
Operating Temperature: All three handle heat well, but ceramics excel in extreme heat.
Corrosion Risk: Ceramics offer the best corrosion protection, followed by Stellite and tungsten carbide.
Budget: Stellite often costs less than ceramics and tungsten carbide for similar part sizes.
Cost vs. Performance
While ceramics and tungsten carbide can last longer, Stellite can be more cost-effective for certain jobs.
Always calculate total cost of ownership — not just purchase price. Factors like downtime, replacement intervals, and machining costs matter.
خاتمة
Tungsten carbide, ceramic, and Stellite are all excellent wear materials — but they excel in different ways.
Choose tungsten carbide for extreme abrasion and heat resistance.
Choose ceramic for corrosion-proof and lightweight applications.
Choose Stellite when toughness and impact resistance are most important.
For decision-makers, the right choice depends on your operating environment, budget, and performance goals.
A careful comparison of these materials can save your company money and improve equipment reliability.
إذا كنت تريد معرفة المزيد من التفاصيل حول أي شركة، فلا تتردد في اتصل بنا.
