أدوات قطع كربيد التنغستن are trusted across many industries for their strength, precision, and long-lasting performance. But even the toughest tools wear out over time.
For decision-makers in machining and manufacturing companies, reducing tool wear isn’t just a technical challenge—it’s a smart business move. Less wear means lower costs, better productivity, and fewer interruptions.
In this article, we’ll explain the best ways to reduce tool wear using tungsten carbide cutting tools.
سواء كنت في الفضاء الجوي, السيارات, medical device manufacturing, or general machining, these tips will help your team make better decisions, cut smarter, and improve output.
1. Understand What Causes Tool Wear
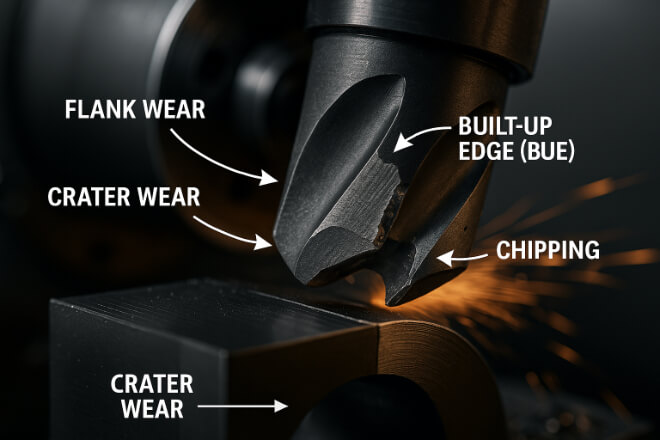
Before you reduce tool wear, you need to know what causes it. Tool wear can happen for many reasons:
Heat – High temperatures from fast cutting can break down the tool’s surface.
Friction – Poor lubrication or incorrect speeds cause rubbing that dulls the tool.
Vibration – Instability in the machine setup creates chatter, damaging tool edges.
Material hardness – Some workpieces, like titanium or stainless steel, are harder to cut and wear tools faster.
There are also different types of wear: flank wear (on the side), crater wear (on the face), built-up edge (material sticking to the tool), and chipping.
Understanding these patterns helps you take action before serious problems occur.
2. Use the Right Tool Grade and Geometry
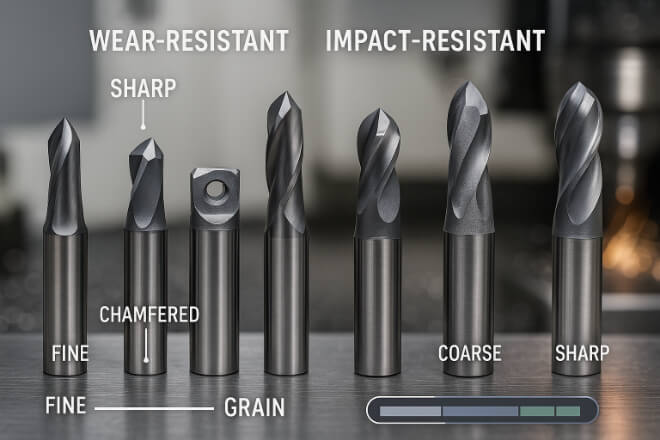

Not all carbide tools are the same. Choosing the right grade and geometry can make a big difference in wear resistance.
Grades: Fine-grain carbide grades are better for precision and wear resistance. For tougher jobs, a tougher binder content helps resist breakage.
Geometry: The shape of the cutting edge affects tool life. For example, sharper edges cut better but wear faster, while stronger edges last longer but may produce more heat.
Work with your supplier to match the tool to your material, cutting method, and machine capabilities.
3. Optimize Cutting Speeds and Feeds
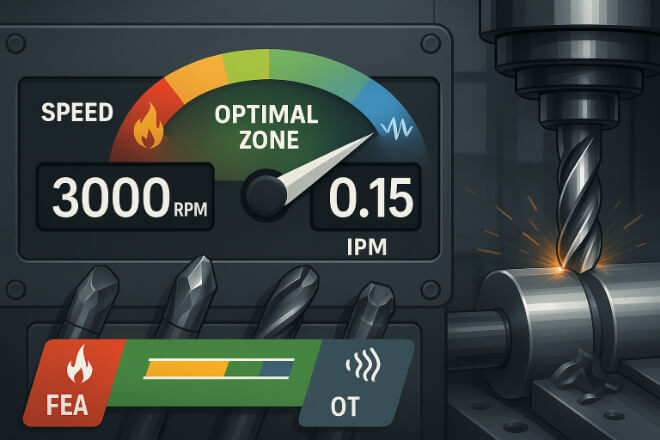
One of the most common causes of wear is using incorrect speeds and feeds.
Too fast and you generate too much heat, which leads to early tool failure.
Too slow and the tool may rub instead of cut, leading to poor surface finish and wear.
Use manufacturer recommendations as a baseline, and monitor tool life data to fine-tune performance.
Investing in a CAM system or digital feed/speed calculators can help teams stay consistent.
4. Apply Proper Coolant and Lubrication
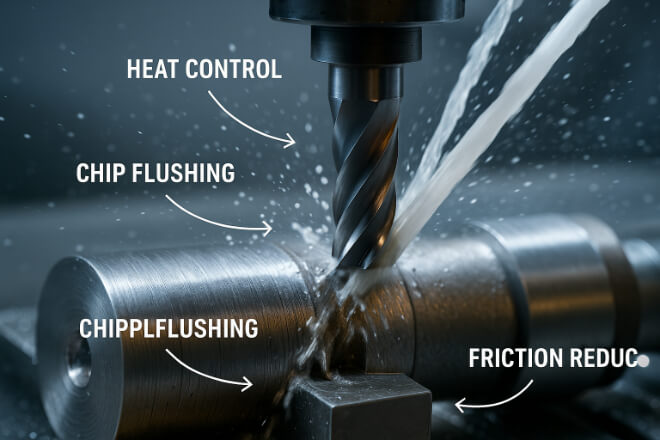
Heat is the enemy of tool life. A good coolant strategy can greatly extend carbide tool performance.
Use flood coolant for materials like steel or titanium.
Use mist or air blast for dry machining and chip removal.
Make sure the coolant reaches the cutting zone.
Also, consider high-pressure coolant systems for deep-hole drilling or tough metals. These reduce heat and flush chips away effectively.
5. Maintain Tool Holders and Setup Rigidity
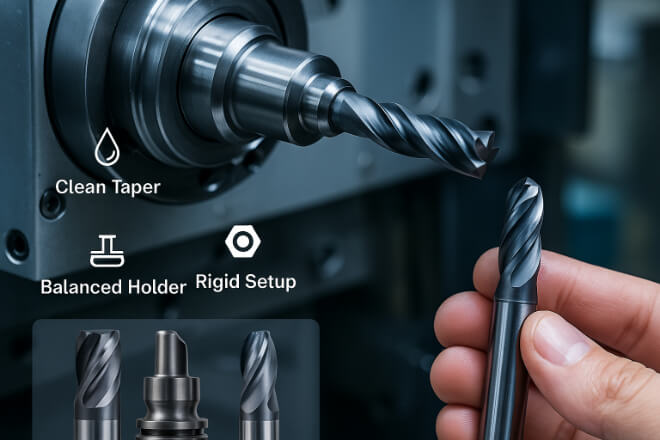

Tool wear isn’t always about the tool itself. Poor fixturing and worn holders cause runout and vibration, which damage tools over time.
Inspect tool holders regularly for wear, corrosion, or imbalance.
Keep spindle tapers and tool holder surfaces clean.
Use shrink-fit, hydraulic, or precision collet holders for high-precision work.
When the setup is stable, the tool works more efficiently and wears more evenly.
6. Choose the Right Coating

Coatings are like armor for your cutting tools. They reduce friction, manage heat, and prevent material from sticking.
Popular coatings for carbide tools include:
TiAlN / AlTiN – Great for dry cutting and high temperatures.
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) – Ideal for aluminum and sticky materials.
CVD Diamond – For composites and abrasive work.
The right coating can double or even triple your tool’s lifespan.
7. Monitor Tool Wear with Smart Sensors or Scheduled Checks

Regular inspection helps catch wear before it affects your parts. Modern monitoring systems can alert operators to tool changes.
Options include:
Manual checks under magnification
Software-based wear tracking
Vibration or acoustic sensors in advanced CNCs
Logging tool life and replacement intervals can help you predict failure before it happens.
8. Use Regrinding and Tool Recycling Services

Many carbide tools don’t need to be thrown away—they can be reground and recoated. This cuts costs and improves sustainability.
Use a trusted regrinding service with precision equipment.
Recoat tools after sharpening to regain performance.
Track regrind cycles to know when a tool is truly worn out.
It’s more cost-effective than buying new tools too often.
9. Train Operators and Standardize Processes

Even the best tools wear out fast in the wrong hands. Operator error is a hidden cause of tool failure.
Train staff on proper speeds, feeds, and setup techniques.
Use checklists for tool selection, installation, and inspection.
Document best practices across the shop floor.
Consistent knowledge leads to consistent results—and lower tool costs.
10. Work with Reliable Tool Suppliers

Partnering with a good supplier makes it easier to get the right tools for your job, and their technical teams can help solve wear issues.
Ask for tool trials or wear audits
Use supplier data to set benchmarks
Buy from brands known for carbide performance and regrind options
Final Thoughts: Reducing Wear, Increasing Profits
Tool wear will always happen—but how fast it happens is up to you. Using tungsten carbide tools is a great start. Applying the best practices listed here will help you:
Cut more parts per tool
Reduce tool change downtime
Improve part accuracy and finish
Lower overall machining costs
For decision-makers, investing in wear prevention is investing in long-term productivity. Make your tools last—and your bottom line stronger.
Ready to upgrade your tooling strategy? Explore wear-resistant solutions at ريتوبز.
