Coatings for Tungsten Carbide Tools: What You Need to Know
Simple guide to help you choose the best surface treatment for better wear, heat, and corrosion resistance.
Why Do Tungsten Carbide Tools Need Coatings?
Tungsten carbide is strong, but coatings make it even better. Coatings help the tool last longer, work better at high speeds, and resist rust and heat.
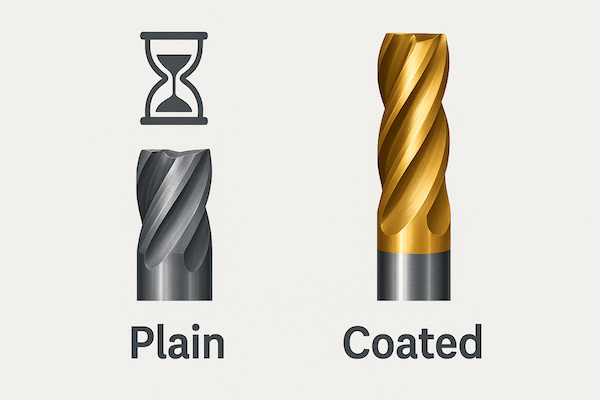
Longer Tool Life
Tungsten carbide is already hard, but coatings protect it from wearing out too fast. A coated tool can last 2 to 10 times longer than a plain one. This means fewer tool changes and lower costs over time.
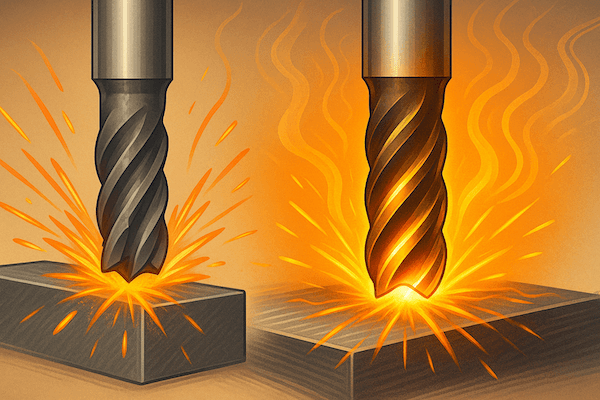
Better Performance at High Speeds
When tools spin fast or cut tough metals, they get very hot. Some coatings, like TiAlN, help tools stay cool and strong under heat. This keeps the cutting edge sharp and reduces tool damage.
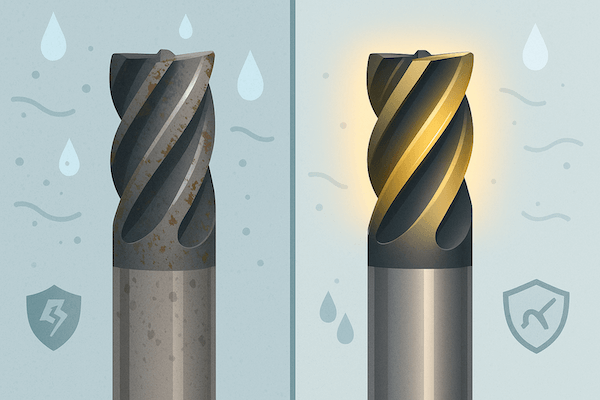
Protection from Rust and Corrosion
In wet or dirty environments, carbide tools without coating can rust or break down. Coatings like CrN act as a shield, stopping moisture and chemicals from attacking the tool surface.
When Do You Need a Coated Tool?
Not always. If the job is simple, a plain tool may be enough. But for cutting fast, working with hard metals, or in wet, hot, or dirty places — coatings help a lot.
High-Speed Cutting
When tools spin or cut very fast, they generate a lot of heat. Without coating, the tool may get soft or dull quickly. Coatings like TiAlN or AlTiN help tools stay cool and sharp during high-speed cutting.
Cutting Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is strong and sticky. It causes friction and can wear tools quickly. Coatings like TiCN or TiAlN reduce friction and make cutting stainless steel easier and smoother.

Wet or Corrosive Working Environments
In areas with water, coolants, or chemicals, uncoated tools can rust or corrode. CrN or DLC coatings add a protective shield to prevent damage in wet, dirty, or chemical-heavy conditions.
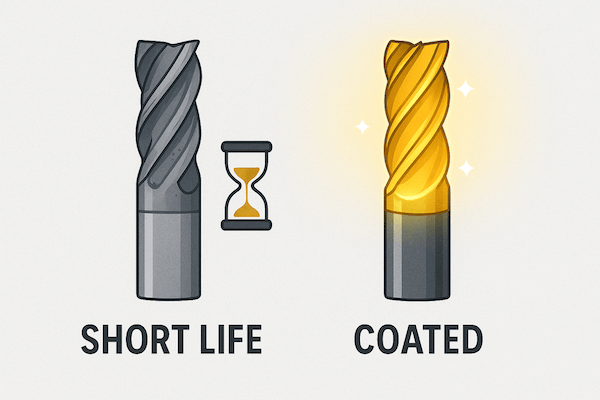
Long Tool Life Needed
If you want to reduce tool changes, save time, or cut harder materials for a long time — coated tools are a smart choice. Coatings reduce wear, meaning longer use and fewer replacements.
Coating vs. No Coating – What’s the Difference?
Adding a coating makes tungsten carbide tools last longer, resist heat better, and reduce wear. Here’s how they compare side by side:
| Feature | No Coating | With Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Life | Shorter | 2–10x Longer |
| Heat Resistance | Low | High |
| Surface Friction | High | Low |
| Wear Rate | Fast | Slow |
How Are Coatings Applied to Carbide Tools?
Most coatings are added using PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition). These methods form a thin, hard layer on the surface without changing the size or shape of the tool.
Step 1: Clean the Tool
Before coating, the carbide tool must be cleaned carefully. Any dust, oil, or metal chips left on the tool can ruin the coating. Cleaning is done using ultrasonic washing, alcohol, or plasma cleaning to ensure the surface is 100% clean.
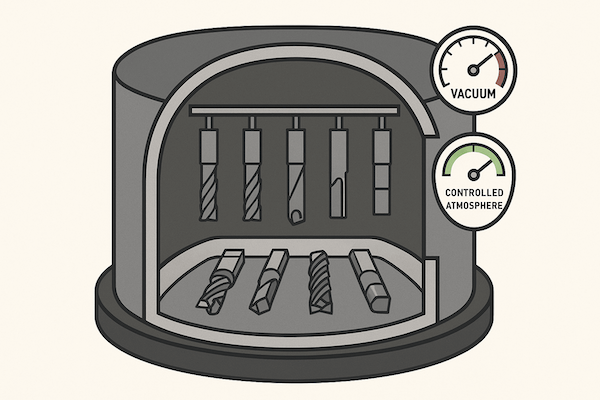
Step 2: Place in Coating Chamber
After cleaning, the tool is placed into a sealed chamber. This chamber is where the coating happens. The machine sets the right vacuum, temperature, and gas levels to prepare for PVD or CVD coating.
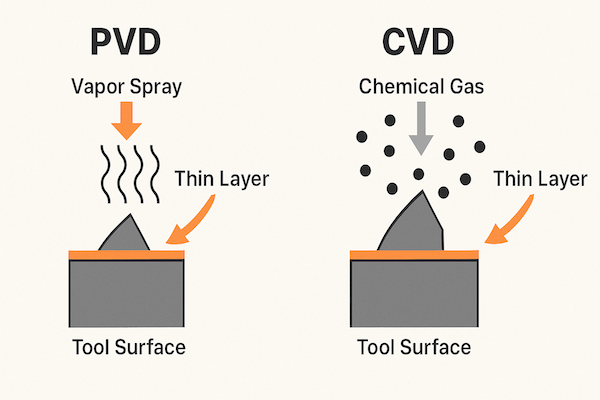
Step 3: Apply Coating (PVD or CVD)
This is the key step. In PVD, a vapor of metal (like Ti or Cr) is sprayed onto the tool and sticks to it as a hard, thin film. In CVD, a chemical reaction in gas form deposits the coating. Both methods make a strong, even layer.
Step 4: Cool and Inspect
Once coating is done, the tools cool down slowly to prevent cracks. Then each tool is inspected for coating quality — using microscopes, thickness tests, or scratch tests — to ensure the surface is perfect and ready to use.
How to Choose the Right Coating?
Different coatings work best for different materials and conditions. Use this guide to match your carbide tool with the right surface treatment.
| Application | Recommended Coating |
|---|---|
| High-speed steel cutting | TiAlN |
| Non-ferrous metal cutting | DLC |
| Corrosive environment | CrN |
| Stainless steel | TiCN |
| Heavy wear | TiN or TiAlN |
FAQs About Carbide Tool Coatings
Have questions about tool coatings? Here are clear, quick answers to help you understand when and why to use coated carbide tools.
Q1: Will coating make my tool more expensive?
A bit, but it lasts much longer — so it saves money overall.
Q2: Can I recoat my old carbide tools?
Yes, many tools can be recoated after sharpening.
Q3: Is black coating always TiAlN?
Often, but not always. Ask your supplier to confirm.
Q4: Do coatings affect the size or shape of the tool?
No. Most coatings are very thin (just a few microns) and do not change the tool’s dimensions.
Q5: Which coating is best for cutting aluminum?
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) is a great choice because it has low friction and avoids material sticking.
Q6: How do I know if I need a coating?
If you’re cutting hard metals, working in hot or wet environments, or need long tool life — a coating is usually a good idea.
