Tungsten carbide balls are small, but they play a very big role in modern industries. Known for their dureza, strength, and ability to last longer than steel, these balls are used in everything from bearings and valves to grinding media.
Para los tomadores de decisiones en el sector manufacturero, minería, petróleo y gas, and precision engineering, understanding the value of tungsten carbide balls helps in planning for both performance and cost efficiency.
In this article, we will look at six key facts about tungsten carbide balls, explain how they are used, and show why they are such a strong choice in demanding applications.
Tungsten Carbide Balls Are Extremely Hard
The first fact about tungsten carbide balls is their dureza.
Tungsten carbide is about twice as hard as steel, with a Rockwell hardness rating of 90+ HRA. This makes them wear resistant, abrasion, and deformation.
Hardness matters most in applications where constant stress or friction would normally damage steel balls. For example:
In bearings, they keep rolling smoothly even under heavy load.
In grinding and milling, their hardness allows them to crush and refine materials efficiently.
En petróleo y gas válvulas, they resist erosion from sand, fluids, and pressure.
This hardness is one of the main reasons industries choose tungsten carbide over steel.
They Can Handle Heat and Pressure
Another fact is that tungsten carbide balls can work under high heat and high pressure.
Unlike steel, which may lose strength at high temperatures, carbide balls keep their properties even at 800°C or higher.
This makes them essential in:
Aeroespacial applications, where parts must perform under heat and stress.
Oil drilling equipment, where downhole tools face extreme pressure.
Industrial pumps and valves, where fluids can be hot, corrosive, or abrasive.
The ability to resist heat and pressure extends their working life and reduces downtime.
They Are Used in Bearings, Valves, and Ball Screws
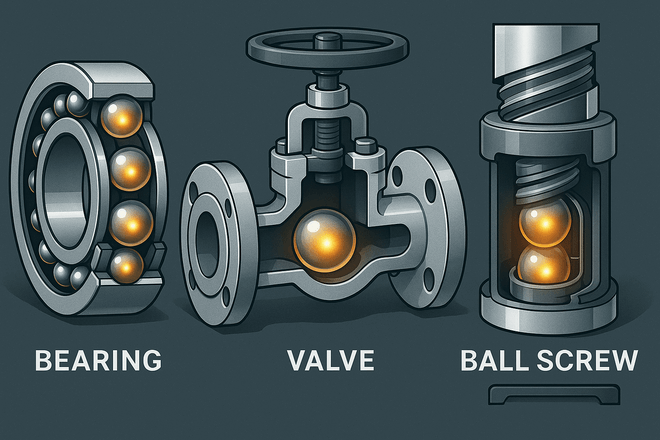
One of the most common uses of tungsten carbide balls is in bearings, valves, and ball screws. Their strength and precision help machines move smoothly and reliably.
Bearings: In heavy machinery, they reduce friction and last longer than steel bearings.
Valves: They provide tight sealing, preventing leaks in oil, gas, and chemical industries.
Ball screws: Used in CNC machines and robotics, carbide balls ensure smooth, accurate movement.
Because they resist wear, these balls mean fewer replacements and more consistent performance.
They Perform Well as Grinding and Milling Media
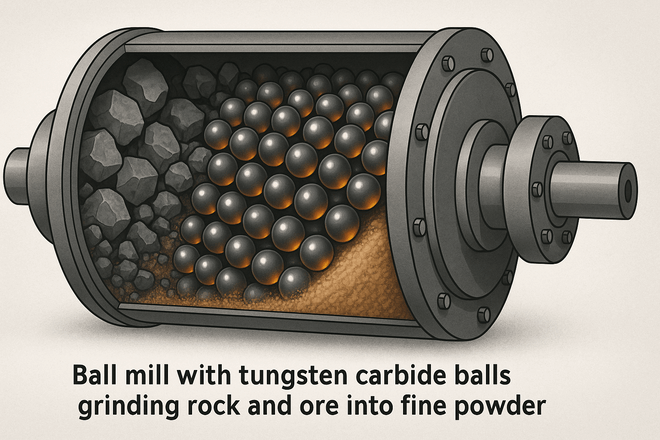
Tungsten carbide balls are widely used in grinding and milling operations.
When used as media in ball mills, they crush hard materials like ceramics, minerals, and alloys.
Compared to steel media, carbide balls:
Provide finer grinding results
Last much longer before needing replacement
Reduce contamination of milled materials
This is why industries such as mining, cement, and chemical processing rely on tungsten carbide balls to improve output and reduce cost per ton.
They Can Be Recycled and Reused
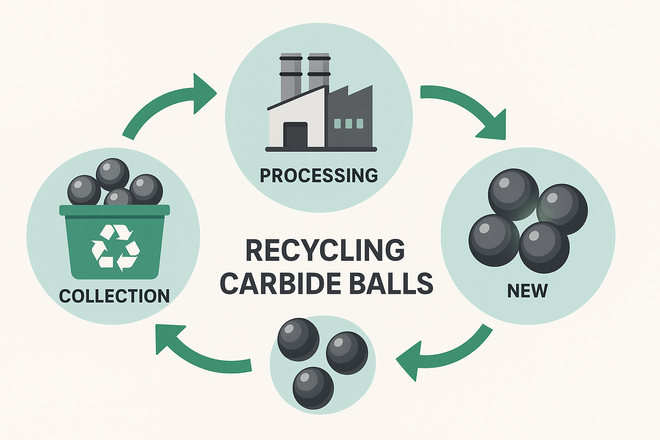
Sustainability is an important factor today, and tungsten carbide balls have an advantage: they are highly recyclable. Up to 95% of scrap tungsten carbide can be recovered and turned into new balls or tools.
The recycling process saves energy compared to mining new tungsten and cobalt, reduces environmental impact, and lowers costs.
Many suppliers now run carbide recycling programs, giving industries both an economic and environmental benefit.
They Offer Long-Term Value in High-Stress Environments
The last key fact is their long-term value. While tungsten carbide balls are more expensive than steel at the time of purchase, their durability, wear resistance, and longer service life save money in the long run.
Companies benefit through:
Lower replacement costs
Less downtime from failures
Higher machine reliability
Mejor calidad del producto
For decision-makers, the cost-per-part calculation clearly shows carbide balls deliver more value over time compared to steel or other materials.
Example Comparison Table
Here’s a quick look at how tungsten carbide balls compare to steel balls:
| Propiedad | Bolas de carburo de tungsteno | Bolas de acero |
|---|---|---|
| Dureza | 90+ HRA (very high) | ~60 HRC (lower) |
| Resistencia al desgaste | Excellent – resists abrasion | Moderate – wears faster |
| Resistencia al calor | Performs at 800°C+ | Weakens at high heat |
| Costo | Mayor pago inicial | Adelante más bajo |
| Vida útil | Muy largo | Más corto |
Reflexiones finales
Tungsten carbide balls are a small but powerful part of industrial systems. Their hardness, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions make them better than steel in most high-stress applications.
While the upfront cost is higher, the long-term savings, performance, and recyclability make them a smart investment for industries.
For decision-makers looking at efficiency, sustainability, and cost management, tungsten carbide balls are not just an option—they are a necessity.
Si desea conocer más detalles sobre alguna empresa, no dude en contactarnos. Contáctanos.
