Bushings are essential parts in any system with rotating shafts — they guide, support, and reduce friction between moving components.
In high-performance machinery, the type of bushing material you choose can determine the system’s reliability and lifespan.
Two common types used in demanding industries are coated bushings and solid bujes de carburo de tungsteno.
Both aim to reduce wear and improve durability, but they perform very differently in practice.
This article explains how coated bushings compare to solid tungsten carbide bushings in terms of dureza, resistencia al desgaste, corrosion protection, and cost-effectiveness — helping decision-makers select the best option for long-term performance.
What Are Coated Bushings?
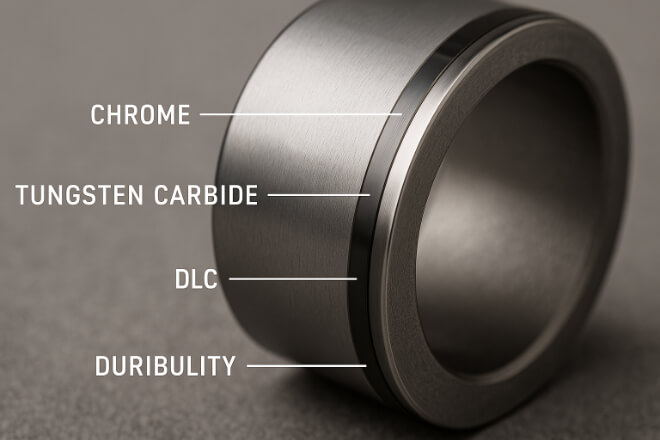
Coated bushings are usually made from steel, bronze, or alloy substrates covered with a thin surface layer designed to improve wear resistance.
Common coating types include:
Tungsten Carbide Coatings (HVOF)
Chrome Plating
Nickel-Phosphorus Coatings
Ceramic or DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) Layers
These coatings are typically 20–200 microns thick and applied by spraying, electroplating, or chemical vapor deposition.
Their goal is to give cheaper base metals the wear and Resistencia a la corrosión of hard materials.
However, since the coating is only a thin surface layer, once it wears through, the softer metal underneath is exposed — reducing the lifespan drastically.
What Are Solid Tungsten Carbide Bushings?

Solid bujes de carburo de tungsteno are made entirely from a sintered tungsten-carbon compound, often bonded with cobalt or nickel.
They are solid, dense, and hard all the way through, meaning that even after years of wear, their performance remains consistent.
These bushings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and drilling equipment where extreme pressure, heat, or abrasive media would quickly destroy coated or metal bushings.
In short, coated bushings imitate the surface dureza of carbide, but solid carbide bushings deliver it throughout their structure.
Key Material Comparison
| Propiedad | Coated Bushing | Solid Tungsten Carbide Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| Dureza (HRA) | 60–80 (coating only) | 88–92 (throughout) |
| Coating Thickness | 20–200 µm | N/A (solid body) |
| Resistencia a la compresión (MPa) | 500–1200 | 4000+ |
| Resistencia al desgaste | Moderate to Good | Excelente |
| Resistencia a la corrosión | Depends on coating material | Excellent (Nickel-bonded) |
From this table, solid bujes de carburo de tungsteno clearly provide more consistent mechanical performance and long-term reliability than coated bushings.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
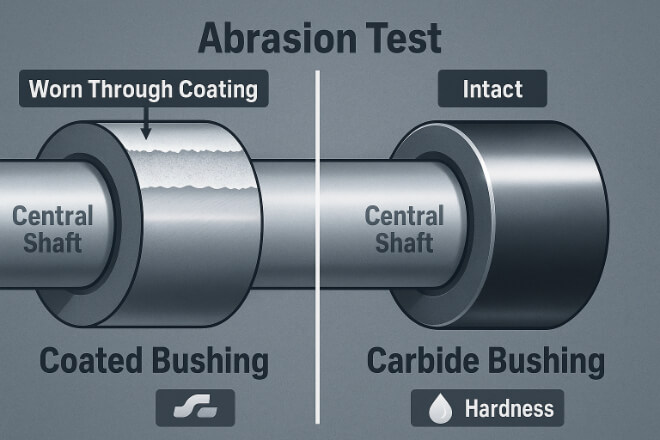
Coated bushings offer good short-term protection, especially when the coating is properly applied and used in mild conditions.
However, in high-load or abrasive situations, coatings can chip, peel, or crack. Once the coating layer is gone, the underlying metal wears quickly.
Solid tungsten carbide, in contrast, maintains its properties across the entire volume — meaning wear is slow and uniform, not catastrophic.
In most industrial applications, solid tungsten carbide bushings last 5–10 times longer than coated ones.
Thermal and Pressure Stability
| Factor | Coated Bushing | Solid Tungsten Carbide Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperatura máxima de funcionamiento | 300–500°C (depends on coating) | Up to 1000°C |
| Thermal Expansion | Moderate to High | Muy bajo |
| Resistencia a la presión | Limited by base metal | Excellent (40 MPa+) |
Solid tungsten carbide bushings perform much better in extreme temperature or pressure environments because their structure is homogeneous.
Coated bushings rely on the bond between the coating and base metal — which can weaken under repeated thermal cycling or mechanical stress.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
At first, coated bushings appear cheaper due to lower material costs.
But over time, frequent replacements, downtime, and coating failures add up.
Solid tungsten carbide bushings, while more expensive initially, require far less maintenance and replacement.
| Parámetro | Coated Bushings | Solid Tungsten Carbide Bushings |
|---|---|---|
| Costo inicial | Bajo | Alto |
| Vida útil | Short (1–2 years typical) | Long (5–10 years typical) |
| Maintenance Frequency | Alto | Bajo |
| Total Cost of Ownership | High (due to replacements) | Lower over time |
For continuous-operation industries like petróleo y gas, power generation, or mining, the ROI of solid carbide bushings is often realized within one maintenance cycle.
Applications and Best Use Cases

Coated Bushings are suitable for:
Low to medium load conditions
Clean or lubricated environments
Short-term or budget-sensitive applications
Solid Tungsten Carbide Bushings are ideal for:
High pressure and speed equipment
Slurry, sand, or chemical exposure
Offshore, minería, and chemical plants
| Industria | Preferred Bushing Type | Razón |
|---|---|---|
| Procesamiento químico | Solid Tungsten Carbide | Excellent corrosion and wear resistance |
| Hydraulic Systems | Coated Bushings | Cost-effective for moderate pressure |
| Oil and Gas Equipment | Solid Tungsten Carbide | Handles vibration, heat, and abrasives |
| General Machinery | Coated Bushings | Good balance of cost and performance |
Environmental and Operational Advantages

Solid tungsten carbide bushings not only extend service life but also reduce environmental impact by minimizing:
Waste from frequent replacements
Energy consumption from frictional losses
Maintenance downtime and lubricant waste
For operations aiming at sustainability and energy efficiency, solid tungsten carbide bushings support both technical and environmental goals.
Final Verdict
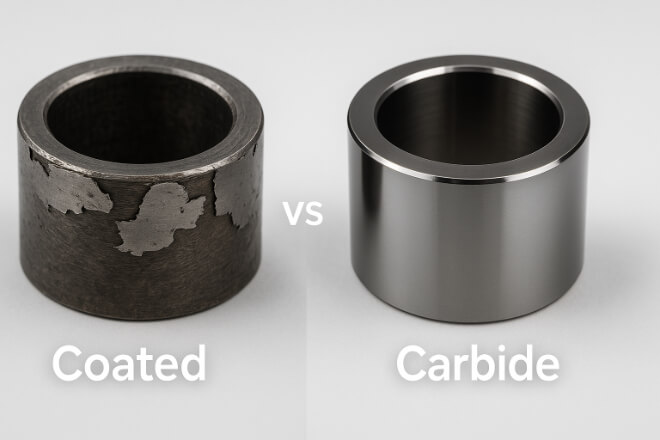

While coated bushings offer a temporary improvement over traditional metals, they cannot match the durability, precision, or long-term value of solid tungsten carbide bushings.
If your machines operate under abrasion, pressure, heat, or chemical stress, solid carbide is the smarter investment.
For budget-sensitive or short-cycle machinery, coated bushings may still serve a purpose — but only as an interim solution.
Conclusión
Choosing the right bushing type depends on your operating environment, lifespan expectations, and maintenance strategy.
Coated bushings: Good for moderate conditions and cost control.
Solid tungsten carbide bushings: Best for harsh, continuous, and critical industrial systems.
For most modern industries, upgrading to solid tungsten carbide bushings translates directly into greater uptime, reliability, and lifecycle savings.
Si desea conocer más detalles sobre alguna empresa, no dude en contactarnos. Contáctanos.
