In pumps, turbines, and compressors, seal rings are essential. They stop leaks, protect equipment, and keep operations safe.
But not all anillos de sellado de carburo de tungsteno are the same. They come in different grades, each designed for a specific condition.
For decision-makers, choosing the correct grade can make the difference between smooth performance and costly breakdowns.
This guide explains how to select the right tungsten carbide seal ring grade based on environment, binder type, pressure, and chemical exposure.
What Is a Tungsten Carbide Seal Ring Grade?
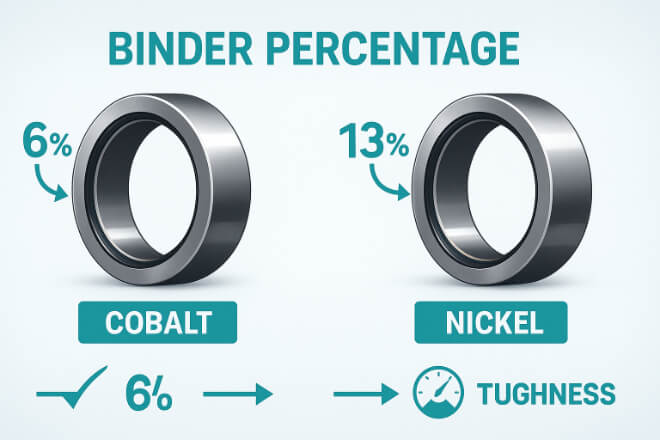
A grade refers to the specific formula of tungsten carbide and binder used to make the seal ring.
By changing binder type or percentage, the ring’s properties also change.
Aglutinante de cobalto → higher tenacidad
Aglutinante de níquel → better Resistencia a la corrosión
Mixed or coated grades → designed for special conditions
Selecting the right grade ensures longer life and better performance.
Why Grade Selection Matters
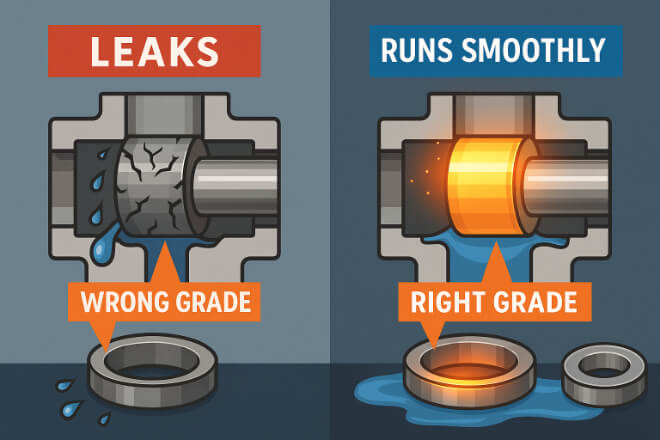
The wrong grade can lead to:
Cracks or wear under high load
Fast corrosion in chemical plants
Seal failure in high-temperature systems
Increased replacement costs
The correct grade matches environment, fluid type, and load conditions, giving decision-makers peace of mind and cost savings.
Binder Choice: Nickel vs Cobalt

1). Cobalt-Bonded Grades
Tougher and stronger under heavy pressure
Less resistant to acids and seawater
2). Nickel-Bonded Grades
Excelente Resistencia a la corrosión
Safer in chemical and marine applications
Un poco más abajo tenacidad than cobalt grades
Tip for buyers: If corrosion is the main risk → choose nickel. If load and shock are higher → choose cobalt.
Operating Conditions That Affect Grade Selection
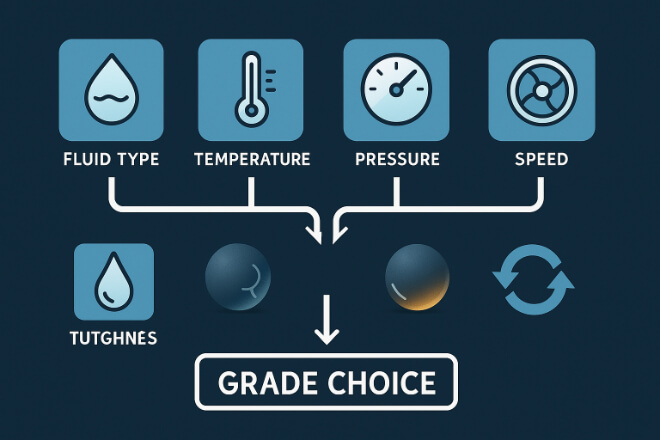
1) Tipo de fluido
Acids, solvents, seawater → nickel-bonded grades
Abrasive slurry or drilling mud → cobalt-bonded grades
2). Temperature
Standard tungsten carbide works in hot environments
Thermal shock grades are better for systems with sudden heat changes
3). Pressure
High-pressure pumps and turbines → cobalt binder preferred
Moderate pressure with corrosive media → nickel binder
4). Speed
- High-speed compressors and mixers need smoother, low-friction grades
Special Coatings and Composite Grades

In some cases, standard nickel or cobalt grades are not enough.
Diamond-like coatings (DLC): extra protection against friction
Composite grades: tungsten carbide mixed with ceramics for unique needs
Polished surfaces: reduce heat and wear in high-speed systems
Decision-makers should ask suppliers if coated or composite grades are needed for special applications.
Industry Examples of Grade Selection

1). Petróleo y gas
Cobalt-bonded grades are used in downhole pumps and compressors because they resist impact and abrasion.
2) Plantas químicas
Nickel-bonded grades are preferred for acids and corrosive solvents.
3) Marina y Offshore
Nickel-bonded grades perform better in seawater, preventing premature failures.
4) Generación de energía
Cobalt-bonded grades work in turbines and steam systems, where pressure and heat are very high.
Steps to Select the Right Grade

1). Identify the Environment
Is it corrosive, abrasive, or clean?
2). Check Temperature and Pressure
High stress → cobalt grades
Corrosive + moderate stress → nickel grades
3). Consider Speed and Friction
Fast-moving systems may need polished or coated grades
4). Review Industry Standards
Follow ISO and safety requirements
5). Work With Trusted Suppliers
Ask for recommendations based on proven case studies
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Choosing based on cost alone
Ignoring chemical compatibility
Forgetting to plan for maintenance cycles
Not checking supplier certifications
Correct grade choice lowers lifetime cost, even if initial price is higher.
Maintenance and Replacement Planning
Even with the right grade, regular care is needed.
Inspection: Every few weeks in critical systems
Warning Signs: Leaks, noise, cracks, or corrosion marks
Replacement: Always match the original grade and dimensions
Recycling: Old tungsten carbide rings can be recycled, saving money
Cost and ROI of Correct Grade Selection
The upfront cost of nickel-bonded or cobalt-bonded grades is higher than steel or graphite. But for decision-makers, the return is clear:
5–10x longer lifespan
Fewer failures and shutdowns
Safer operations in critical plants
Stronger long-term savings
Estudios de caso
1). Offshore Pump Manufacturer
Switched from cobalt to nickel-bonded grades for seawater pumps. Result: longer service life, lower warranty claims.
2) Compresor de yacimientos petrolíferos
Used cobalt grades for high-pressure drilling. Result: fewer cracks and better uptime.
3) Planta química
Replaced stainless steel seals with nickel-bonded tungsten carbide. Result: reduced corrosion failures and safer operations.
How to Source the Right Grade

When buying tungsten carbide seal rings:
Confirm binder type (nickel or cobalt)
Ask for grade recommendations based on your fluid and pressure
Check ISO and industry certifications
Choose suppliers with local stock for quick delivery
Conclusión
Choosing the right tungsten carbide seal ring grade is not just technical—it’s a business decision.
Unido con níquel → Mejor para la resistencia a la corrosión
Unido con cobalto → better for toughness and load
By matching grade to operating conditions, decision-makers can improve reliability, reduce downtime, and secure stronger long-term ROI.
Si desea conocer más detalles sobre alguna empresa, no dude en contactarnos. Contáctanos.
