In modern industry, machines are expected to run faster, longer, and under more demanding conditions than ever before. Reliability and uptime directly affect productivity and profitability.
One small but essential component that makes this possible is the tungsten carbide bushing. These precision-made rings or sleeves are used to support shafts, reduce friction, and protect more expensive machine parts from wear.
In this article, we’ll explain how tungsten carbide bushings help improve machine performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
We’ll also look at why their unique material properties make them superior to conventional metals or plastics in high-duty applications.
What Is a Tungsten Carbide Bushing?
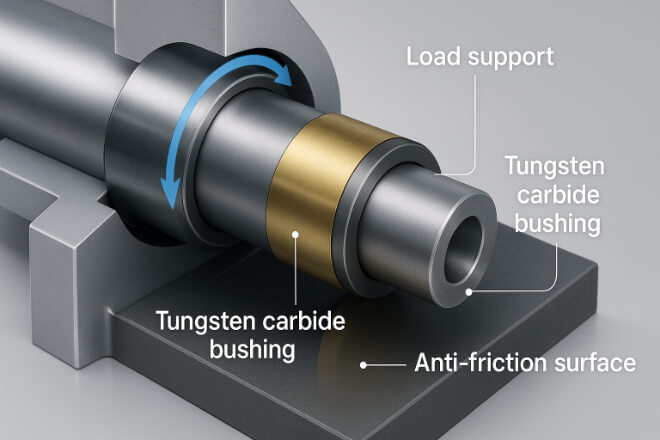
A tungsten carbide bushing is a cylindrical component made from tungsten carbide (WC) combined with a small amount of a metallic binder such as cobalt (Co) or nickel (Ni).
They are used in machines to support rotating shafts or sleeves, acting as a bearing surface between moving parts.
Their role is to prevent direct metal-to-metal contact, reduce wear, and maintain proper shaft alignment.
Tungsten carbide’s exceptional dureza (about 90 HRA) and strength make these bushings ideal for heavy-load and abrasive environments.
Why Material Matters: Properties of Tungsten Carbide
| Propiedad | Descripción | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dureza | 88–92 HRA (very high) | Excelente resistencia al desgaste |
| Resistencia a la compresión | Up to 6,000 MPa | Handles heavy loads |
| Conductividad térmica | High (good heat transfer) | Prevents overheating |
| Resistencia a la corrosión | Excellent (especially Ni-bonded) | Ideal for chemical or wet environments |
| Estabilidad dimensional | Low thermal expansion | Maintains precision at high temperature |
These properties make tungsten carbide bushings suitable for continuous high-speed rotation, abrasive media, and high-pressure environments.
Reduced Friction and Improved Efficiency

One of the main reasons machines lose energy is friction between moving parts.
Tungsten carbide bushings reduce friction by maintaining a smooth, stable contact surface with the shaft.
Esto significa:
Less heat generation during operation
Lower energy consumption
Reduced wear on both bushing and shaft
Longer maintenance intervals
When paired with proper lubrication, tungsten carbide bushings can run with almost no measurable wear for thousands of operating hours.
Dimensional Accuracy and Alignment
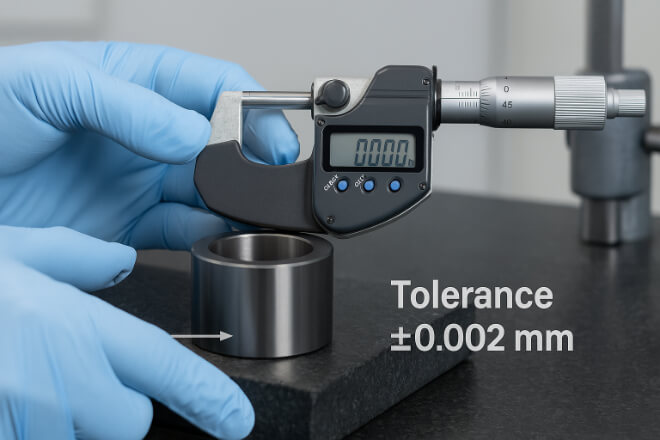

Machine performance depends on precise shaft alignment. Even a small deviation can cause vibration, imbalance, and premature seal failure.
Tungsten carbide bushings are ground and polished to micron-level tolerances, often achieving roundness within 0.002 mm.
This extreme accuracy allows the rotating shaft to remain perfectly aligned under heavy load.
Their rigid structure also minimizes deformation under pressure, which is critical for consistent operation in pumps and compressors.
Resistance to Wear and Erosion
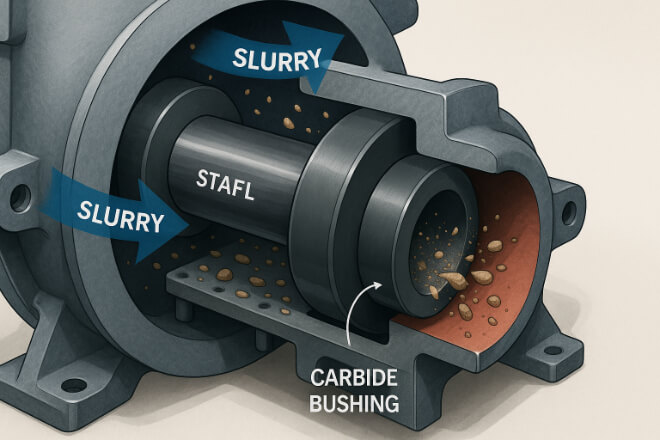
In many industries, machines handle abrasive fluids such as sand, slurry, or corrosive chemicals.
In such environments, soft metal bushings wear quickly, causing leakage and equipment damage.
Tungsten carbide bushings resist abrasive wear far better than bronze or steel. They also handle erosion from particles suspended in liquids, making them ideal for:
Slurry pumps
Dredging equipment
Oilfield tools
Paper and pulp processing
Over time, this durability translates into less downtime, fewer replacements, and better cost control.
Superior Thermal Stability
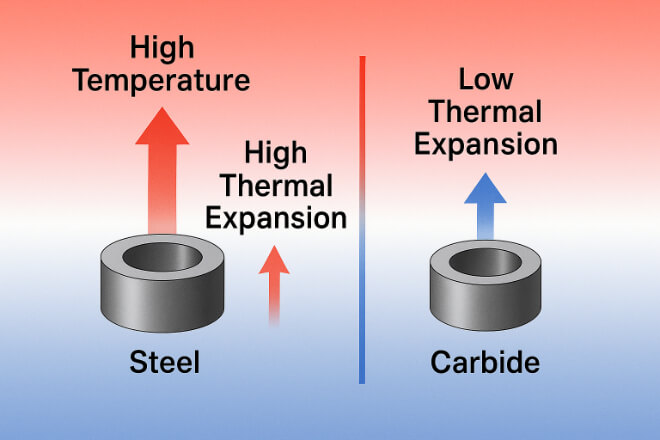
When a machine runs at high speed, friction and pressure generate heat. Most metals expand when heated, which can lead to misalignment and failure.
Tungsten carbide has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it maintains its size and shape even when temperatures rise.
This thermal stability ensures:
Steady clearances between parts
Minimal thermal distortion
Reliable operation in hot environments (up to 500°C for some grades)
Corrosión y resistencia química
| Material | Resistencia a la corrosión | Aplicación típica |
|---|---|---|
| Bronce | Bajo | General lubrication only |
| Stainless Steel | Medio | Mild chemical contact |
| Carburo unido con níquel | Excelente | Acids, seawater, chemical pumps |
Nickel-bonded tungsten carbide grades perform exceptionally well in acidic or alkaline media, where other materials would quickly corrode.
This property is especially valuable in the chemical processing, desalination, and marine industries.
Longer Service Life and ROI
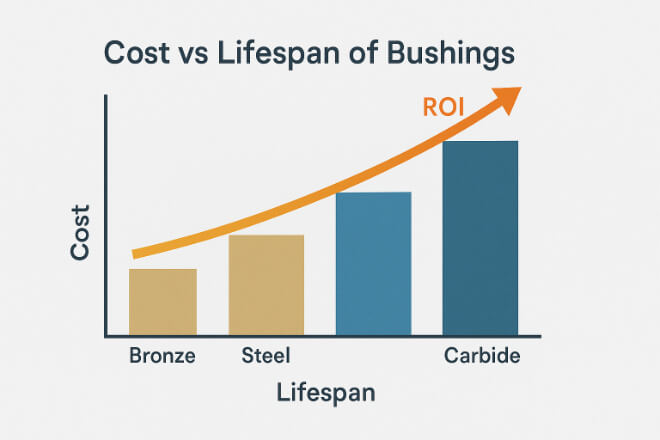
Because tungsten carbide bushings resist wear, corrosion, and heat, they last significantly longer than conventional bushings. This translates directly to:
Costos de mantenimiento más bajos
Tiempo de inactividad reducido
Improved return on investment (ROI)
Even though tungsten carbide components are more expensive initially, their longer life and reduced failure rates make them more economical over time.
1). Typical Service Life Comparison
| Material | Estimated Lifespan (Hours) | Relative Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Bronce | 2,000–3,000 | Bajo |
| Acero endurecido | 5,000–8,000 | Moderado |
| Carburo de tungsteno | 20,000–40,000+ | Muy alto |
Aplicaciones industriales
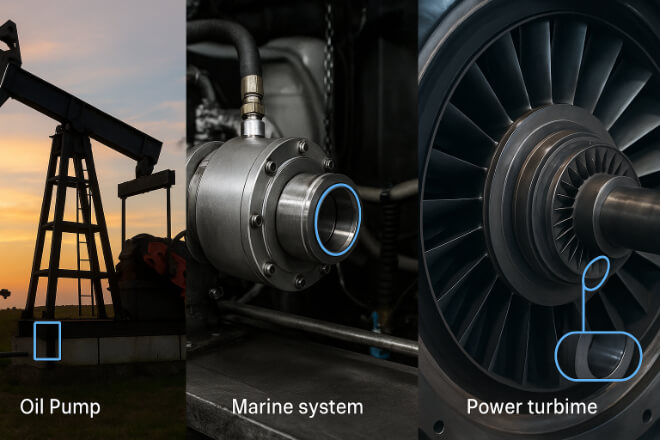

Tungsten carbide bushings are found across a wide range of industries where reliability is critical:
Petróleo y gas: Drilling tools, pumps, compressors
Minería: Slurry transport systems
Marine: Seawater pumps and propulsion systems
Power Generation: Turbines and cooling systems
Chemical Processing: Reactors, agitators, and corrosive pumps
Their combination of resistencia al desgaste, strength, and dimensional stability ensures consistent machine performance in all of these environments.
Conclusión
Machine performance is only as strong as its weakest component.
Tungsten carbide bushings enhance overall efficiency by reducing friction, maintaining precision alignment, and resisting both wear and corrosion.
For decision-makers, investing in tungsten carbide means more than durability — it means lower life-cycle cost, less downtime, and greater reliability in every operation.
Si desea conocer más detalles sobre alguna empresa, no dude en contactarnos. Contáctanos.
