Cuando se trata de herramientas de corte, el carburo de tungsteno es el material preferido por los profesionales que necesitan resistencia, velocidad y confiabilidad.
Pero no todas las herramientas de carburo son iguales. El grado de carburo de tungsteno que elija puede afectar considerablemente el rendimiento de su herramienta y su vida útil.
Ya sea que esté cortando aluminio, acero o compuestos, utilizar el grado de carburo correcto es clave para lograr los mejores resultados.
Esta guía le ayuda a comprender qué significan los grados de carburo, por qué son importantes y cómo elegir el mejor grado para su trabajo.
1. ¿Cuáles son los grados de carburo de tungsteno?

Los grados de carburo de tungsteno se refieren a diferentes mezclas de carburo de tungsteno y otros materiales (como el cobalto), que afectan la herramienta. dureza, fuerza, tenacidad y resistencia al desgaste.
Piénselo como elegir el tipo de acero adecuado: algunos son excelentes por su resistencia, otros por su flexibilidad. Con el carburo de tungsteno, la mezcla determina el comportamiento de la herramienta.
Ingredientes básicos:
Carburo de tungsteno (WC): Las partículas duras
Cobalto (Co): El aglutinante que mantiene unidas las partículas.
Diferentes proporciones y tamaños de grano crean diferentes calidades: algunas mejores para trabajos difíciles, otras mejores para un acabado preciso.
2. ¿Por qué importan las calificaciones?

El uso de una calificación incorrecta puede provocar:
Rotura de herramientas
Desgaste prematuro
Mal acabado superficial
Baja productividad
Costos más altos
Por otro lado, la calificación correcta significa:
Mayor vida útil de la herramienta
Mejor calidad de la superficie
Velocidades de mecanizado más rápidas
Precisión dimensional mejorada
Es por eso que seleccionar el grado correcto de carburo de tungsteno es fundamental en cualquier operación de mecanizado.
3. Cómo se clasifican las calificaciones
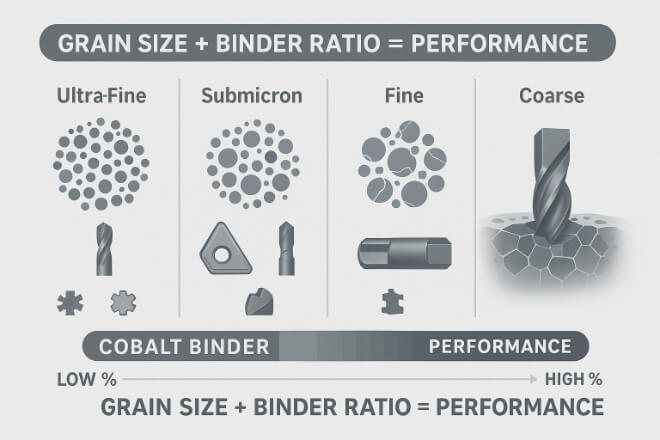
Los grados de carburo de tungsteno no siguen un código universal, pero la mayoría de los fabricantes utilizan sistemas basados en el tamaño del grano, el porcentaje de aglutinante y la categoría de aplicación. A continuación, se detallan:
1) Tamaño del grano (microestructura)
Ultrafino (<0,5 µm): ideal para herramientas afiladas, alta resistencia al desgaste, y terminando
Fino (0,5–1,0 µm): bueno para un desgaste moderado y un equilibrio de resistencia.
Medio (1–2 µm): uso general, adecuado para muchos trabajos
Grueso (>2 µm): mejor tenacidad, menor resistencia al desgaste
2) Contenido de aglutinante (cobalto %):
6–10% Co: Superior dureza, menor tenacidad (mejor para materiales duros)
10–20% Co: Mayor tenacidad, mejor resistencia a los golpes
3) Clasificación ISO (para insertos):
Grado P: acero
Grado M: acero inoxidable
Grado K: Hierro fundido
Grado N: No ferrosos (aluminio, cobre)
Grado S: Aleaciones de alta temperatura (Inconel, titanio)
Grado H: Materiales endurecidos
4. Grados comunes de carburo de tungsteno y sus usos
A continuación se muestra una tabla de referencia simplificada que muestra los grados de carburo típicos y para qué sirven:
| Tipo de grado | Tamaño del grano | Cobalto % | Mejor para |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrafino (UF) | <0,5 µm | 6–10% | Acabados, cantos afilados, aluminio, plásticos. |
| Grano fino (F) | 0,5–1 µm | 6–12% | Uso general, acero ligero, cobre. |
| Grano medio (M) | 1–2 µm | 10–15% | Acero, fundición, aplicaciones versátiles. |
| Grano grueso (C) | > 2 µm | 15–20% | Cortes interrumpidos de alta resistencia y resistencia al impacto. |
5. Cómo elegir el grado adecuado para su aplicación

A continuación se explica cómo elegir el grado de carburo adecuado según el material que esté mecanizando:
1)Aluminio y materiales no ferrosos
Utilice carburo de grano ultrafino con estrías pulidas
Menor contenido de cobalto para bordes más afilados
Ideal para altas RPM y acabados limpios.
2)Acero (dulce, aleado)
Elija carburo de grano medio con aglutinante moderado
Busque recubrimientos como TiAlN o AlCrN para resistencia al calor.
3). Acero inoxidable
Necesita un equilibrio entre dureza y tenacidad.
Vaya con grano fino, 10–15% cobalto
Evite las esquinas afiladas: utilice perfiles redondeados
4)Hierro fundido
Utilice calidades más duras, de grano medio o fino.
Las herramientas afiladas son menos efectivas: opte por la resistencia del borde
5)Titanio y aleaciones de alta temperatura
Requiere carburo ultrafino con recubrimientos fuertes
Evite la soldadura de viruta con recubrimientos DLC o TiAlN
6)Acero endurecido
Necesita carburo de alta dureza y bajo contenido de cobalto.
A menudo se combina con puntas de cerámica o PCD.
6. Los recubrimientos también importan
Incluso el mejor grado de carburo necesita el recubrimiento adecuado para funcionar bien.
A continuación se muestran algunos tipos de recubrimiento populares utilizados en herramientas de carburo:
| Revestimiento | Mejor para | Beneficios clave |
|---|---|---|
| Estaño | Uso general | Mayor dureza |
| TiAlN | Acero, aleaciones de alta temperatura | Resistencia al calor, larga vida útil de la herramienta. |
| AlTiN | Aceros endurecidos | Fuerte a altas temperaturas, corte en seco. |
| Contenido descargable | Aluminio, plásticos | Reduce la adherencia y proporciona un corte suave. |
Consejo: La combinación correcta de grado y recubrimiento es lo que distingue los buenos resultados de los excelentes.
7. Por qué usar el grado correcto le ahorra dinero

Muchos talleres eligen herramientas basándose únicamente en el precio. Pero usar la calidad incorrecta conlleva:
Desgaste más rápido de la herramienta
Reemplazos frecuentes
Mala calidad de la superficie
Más tiempo de inactividad y reelaboración
Por otro lado, el grado de carburo adecuado le ayuda a:
Correr a velocidades más altas
Consiga mejores acabados
Reducir la rotura de herramientas
Menor costo por pieza
Aumente la eficiencia de su CNC
Si bien las herramientas de primera calidad pueden costar más al principio, a largo plazo le permitirán ahorrar más.
8. Ejemplos de industrias reales
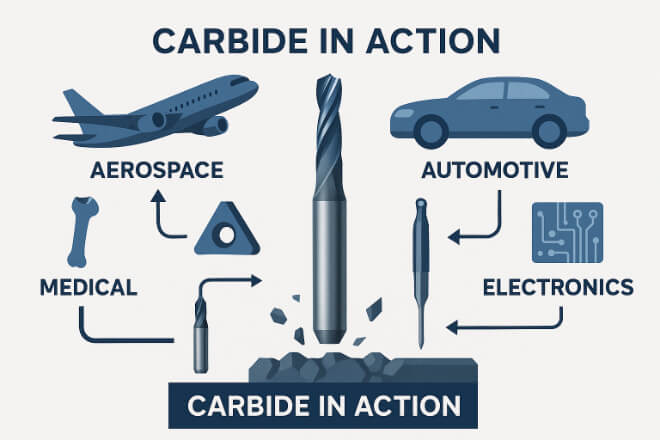
Veamos cómo las diferentes industrias se benefician del uso de los grados de carburo adecuados:
1). Aeroespacial
Mecanizado de titanio e Inconel con calidades ultrafinas
Larga vida útil de la herramienta incluso bajo calor extremo
2). Automotor
Herramientas de grano grueso para desbastar bloques de motor
Grano fino para agujeros de precisión y acabado superficial.
3). Médico
Microherramientas que utilizan carburo ultrafino para implantes óseos
Alta nitidez para cortes sin rebabas
4) Electrónica
Acabado de cobre y plásticos con herramientas de grano fino recubiertas de DLC
Control de rebabas y alta precisión
9. Lista de verificación final: Qué preguntar antes de elegir

Antes de comprar su próxima herramienta de corte, pregunte:
¿Qué material estoy cortando?
¿Qué operación estoy realizando (desbaste, acabado, taladrado)?
¿Qué nivel de calor y desgaste enfrentará la herramienta?
¿Necesito resistencia a los golpes (para cortes interrumpidos)?
¿Qué acabado de superficie espero?
Reflexiones finales
Las herramientas de carburo de tungsteno son potentes, pero solo si elige el grado adecuado para su aplicación.
Al comprender el tamaño del grano, el contenido de aglutinante y los recubrimientos, puede lograr una mayor vida útil de la herramienta, acabados más suaves y un mecanizado más rápido.
No se limite a comprar herramientas: adáptelas a sus necesidades.
Si desea conocer más detalles sobre alguna empresa, no dude en contactarnos. Contáctanos.
