Dans les industries où les machines sont confrontées à la friction, à la pression et à l’abrasion, le choix du matériau fait toute la différence.
Pièces d'usure en carbure, en particulier ceux fabriqués avec du carbure de tungstène, sont connus pour leur résistance, dureté, et la durabilité.
Ces pièces se retrouvent dans les foreuses minières, les vannes de champs pétrolifères, les outils d’usinage, les lames de travail du bois et même dans les équipements de transformation des aliments.
Pour les décideurs, comprendre les caractéristiques et les applications des pièces d’usure en carbure n’est pas seulement une question technique : cela affecte directement l’efficacité, les coûts et la compétitivité à long terme.
Caractéristiques principales des pièces d'usure en carbure
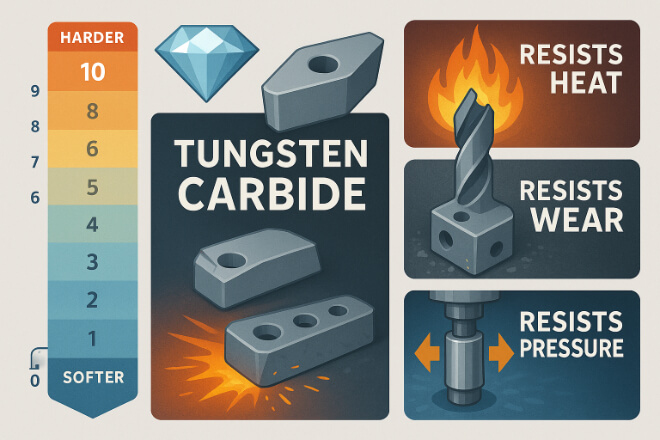
Les pièces d'usure en carbure se distinguent par leur combinaison unique de propriétés matérielles.
Contrairement à l’acier ou à la céramique seuls, le carbure est fabriqué en combinant poudre de carbure de tungstène avec un liant métallique tel que le cobalt ou le nickel.
Cet équilibre offre à la fois dureté et ténacité.
Exceptionnel Dureté:Le carbure de tungstène est presque aussi dur que le diamant, ce qui le rend résistant à l'usure et aux rayures.
Haut Résistance à l'usure:Le carbure dure beaucoup plus longtemps que l'acier dans des conditions abrasives.
Résistance à la chaleur : le carbure conserve sa résistance à des températures d'usinage élevées.
Qualités personnalisables : Différents rapports de liant et tailles de grains permettent d'adapter le carbure à des travaux spécifiques.
Durée de vie plus longue : des remplacements moins fréquents réduisent les temps d'arrêt et les coûts d'exploitation.
Ces caractéristiques expliquent pourquoi le carbure est le choix privilégié dans les industries où la longévité et la fiabilité sont essentielles.
Applications minières et de construction
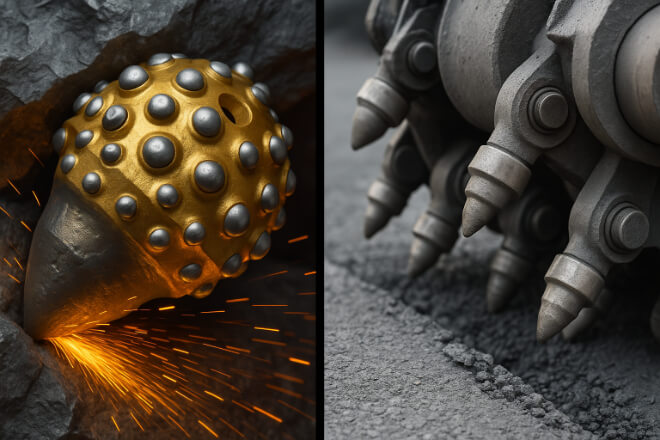

Exploitation minière L'industrie sidérurgique est l'un des environnements les plus exigeants pour les équipements. Les pièces d'usure en carbure sont essentielles dans les domaines suivants :
Forets pour l'excavation de roches dures.
Dents de coupe pour tunneliers.
Broyeur plaques d'usure pour gérer les impacts constants.
Dans la construction, le carbure est utilisé pour le creusement de tranchées, le fraisage de routes et la découpe de béton.
Le résultat est une réduction des changements d’outils et une productivité accrue, ce qui profite directement aux entreprises qui gèrent des opérations à grande échelle.
Applications de l'industrie pétrolière et gazière
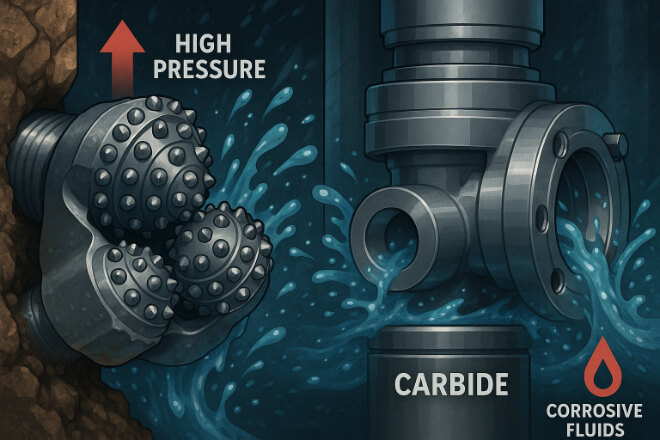
Le pétrole et gaz Le secteur dépend des pièces d'usure en carbure pour faire face aux environnements extrêmes :
Sièges de soupape et des manchons résistants à la corrosion.
Pistons et chemises de pompe qui survivent à un frottement constant.
Inserts de foret pour forage de fond de trou.
Ces applications nécessitent des matériaux résistants à la pression, à la chaleur et aux attaques chimiques, et le carbure est la solution éprouvée. En réduisant les défaillances imprévues, il évite aux entreprises des temps d'arrêt coûteux.
Applications de travail des métaux et d'usinage
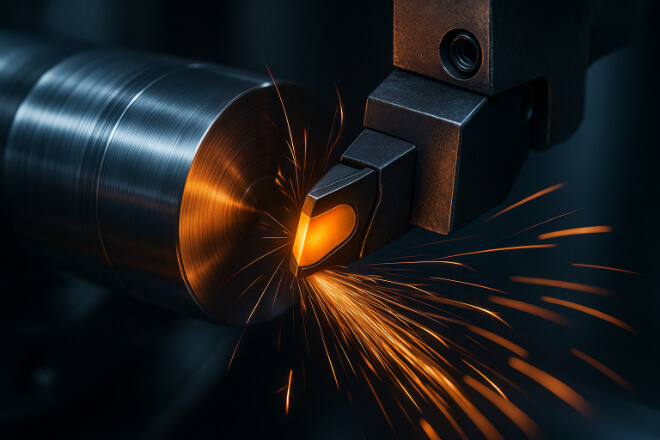

L'utilisation la plus courante des pièces d'usure en carbure est probablement celle des outils de coupe des métaux.
Les plaquettes, forets et fraises en carbure sont essentiels pour l'usinage de composants automobiles, aérospatiaux et industriels.
Les outils en carbure permettent :
Découpe à grande vitesse.
Usinage de précision avec des tolérances serrées.
Finition de surface améliorée.
Intervalles plus longs entre les changements d'outils.
Cela réduit directement les coûts et le temps de production, faisant des outils en carbure l'épine dorsale de l'usinage moderne.
Applications automobiles et aérospatiales
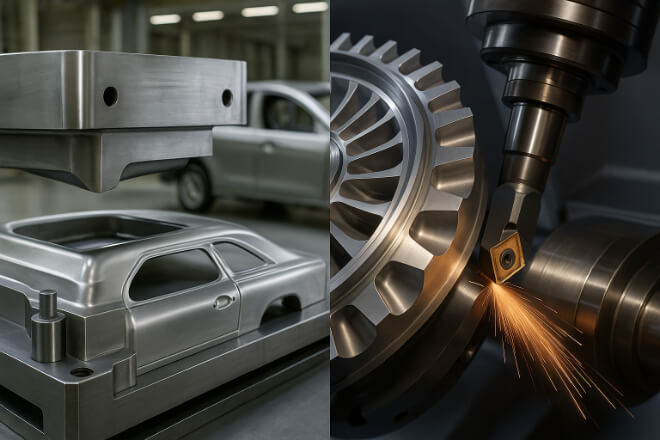

Le automobile L'industrie s'appuie sur le carbure pour les matrices d'emboutissage, les poinçons et les outils de formage.
Le carbure de tungstène garantit que la production à haut volume peut se poursuivre sans réoutillage fréquent.
Dans aérospatialLes pièces d'usure en carbure sont utilisées pour couper le titane, l'Inconel et les matériaux composites.
La résistance élevée et la résistance à l’usure du carbure sont essentielles dans une industrie où la sécurité et la fiabilité ne sont pas négociables.
Applications du papier, du textile et de l'emballage
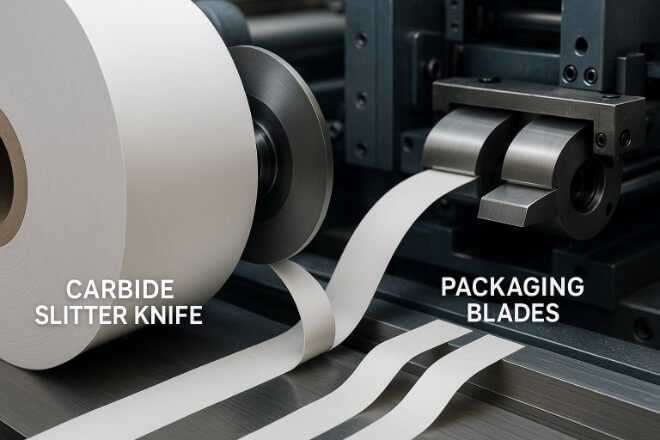
Les pièces d'usure en carbure ne sont pas réservées aux industries lourdes. Elles jouent également un rôle dans les environnements plus tendres mais abrasifs :
Couteaux de découpe dans les usines de papier.
Lames dans les machines de découpe textile.
Rouleaux et coupeurs dans l'emballage.
Ici, le carbure assure la netteté et la conservation des bords, réduisant ainsi les temps d'arrêt dans les lignes de production continues.
Travail du bois et fabrication de meubles
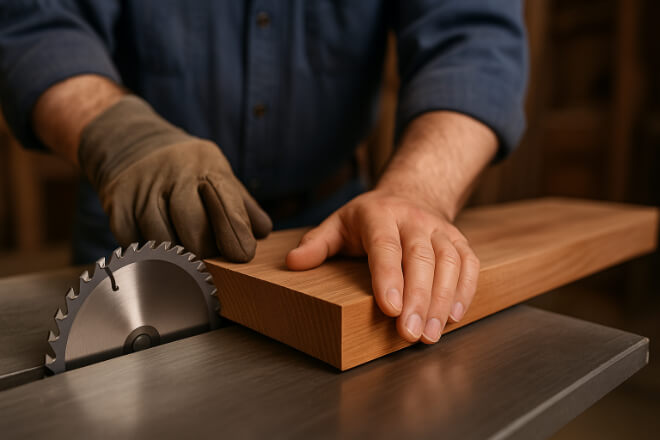

Dans travail du boisLes outils à pointe carbure dominent en raison de leur capacité à couper les bois durs, les stratifiés et les composites. Parmi les applications possibles :
Des lames de scie qui restent affûtées plus longtemps.
Fraises à défoncer pour un façonnage de précision.
Couteaux de rabotage pour des finitions lisses.
Les avantages sont évidents : coupes plus nettes, durée de vie de l'outil prolongée et coûts réduits. Pour les fabricants et les constructeurs de meubles, le carbure garantit efficacité et qualité.
Applications agricoles et agroalimentaires

Le carbure est également utilisé dans l’agriculture et la production alimentaire, où les équipements sont soumis à une usure constante :
Socs de charrue et outils de travail du sol pour l'abrasion du sol.
Mélangeurs et broyeurs d'aliments pour l'élevage.
Lames de coupe dans la transformation des aliments.
La résistance à l'usure et la durabilité du carbure réduisent la fréquence de remplacement et assurent le bon déroulement des opérations.
Comparaison du carbure avec d'autres matériaux
Pour comprendre pourquoi le carbure est préféré, il est utile de le comparer avec des alternatives :
| Matériel | Dureté | Résistance à l'usure | Dureté | Coût |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acier | Moyen | Faible | Haut | Faible |
| Céramique | Très élevé | Haut | Faible | Moyen |
| Carbure de tungstène | Haut | Très élevé | Moyen-élevé | Moyen-élevé |
Conclusion
Les pièces d’usure en carbure sont indispensables dans toutes les industries.
Des foreuses minières et des vannes d'huile aux lames de travail du bois et aux outils de coupe d'aliments, ils offrent une durée de vie plus longue, de meilleures performances et des temps d'arrêt réduits.
Pour les décideurs, investir dans le carbure n’est pas seulement un choix technique : c’est une décision stratégique visant à améliorer l’efficacité et la rentabilité.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
