In pumps, compressors, and mixers, carbide seal rings are vital for preventing leaks and protecting equipment.
The choice between stationary and rotating seal ring designs is critical. Using the wrong type can cause wear, energy loss, and costly downtime.
This guide explains the difference between stationary and rotating carbide seal rings, their strengths and weaknesses, and when each design is the better choice.
Why Seal Ring Design Matters
Leak prevention: Proper selection ensures tight seals under pressure.
Equipment protection: Reduces wear on shafts and housings.
Energy efficiency: Lower friction reduces power loss.
Maintenance savings: Correct design extends service life and reduces repairs.
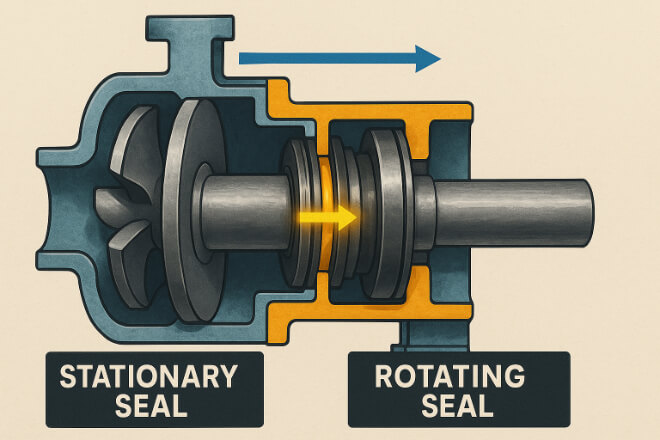
What Are Stationary Carbide Seal Rings?

Stationary seal rings are fixed in the pump or compressor housing. The shaft rotates against them while they remain still.
1). Advantages
Easier to cool because stationary parts are connected to the housing.
Less sensitive to vibration or shaft movement.
Often simpler to install and maintain.
2). Disadvantages
May experience uneven wear if alignment is poor.
Requires precision in shaft movement to avoid leaks.
3). Best Uses
High-speed pumps where shaft vibration is a concern.
Compressors with steady operating conditions.
Applications where maintenance access is limited.
What Are Rotating Carbide Seal Rings?

Rotating seal rings spin with the shaft, while the mating face stays fixed.
1). Advantages
Uniform wear because the ring rotates with the shaft.
Can handle more misalignment or shaft movement.
Better for abrasive or dirty fluids.
2). Disadvantages
Harder to cool since the rotating part does not transfer heat well.
Slightly more complex to install in some systems.
3). Best Uses
Slurry pumps in exploitation minière or pulp and paper industries.
Wastewater or sewage pumps with solid particles.
Systems with high shaft movement or deflection.
Key Differences Between Stationary and Rotating Designs
| Fonctionnalité | Stationary Rings | Rotating Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | Fixed in housing | Spins with shaft |
| Cooling | Better heat transfer | Less efficient cooling |
| Vibration Tolerance | Good for stable shafts | Better for shaft movement |
| Maintenance | Easier access | Slightly more complex |
| Best Fluids | Clean or moderate liquids | Abrasive or dirty fluids |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Design

1). Fluid Type
Dirty or abrasive fluids → Rotating rings.
Clean fluids → Stationary rings.
2). Shaft Stability
Stable shafts → Stationary rings.
Shafts with deflection or runout → Rotating rings.
3). Heat Management
- High heat loads → Stationary rings for better cooling.
4). Maintenance Access
Limited space or frequent inspections → Stationary rings.
Exemples de l'industrie
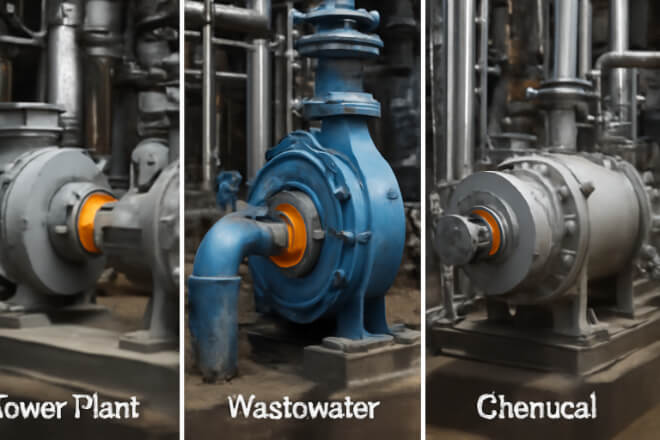

1). Power Plant Boiler Feed Pumps
These pumps operate under high pressure and temperature with stable shafts.
Stationary carbide rings are preferred for heat management and long service intervals.
2). Wastewater Slurry Pumps
Wastewater pumps handle solids and vibration. Rotating carbide rings resist abrasive wear and tolerate shaft movement better.
3). Chemical Transfer Compressors
Compressors moving clean but corrosive chemicals can use stationary rings for easy cooling and maintenance.
Maintenance Tips for Long Seal Life
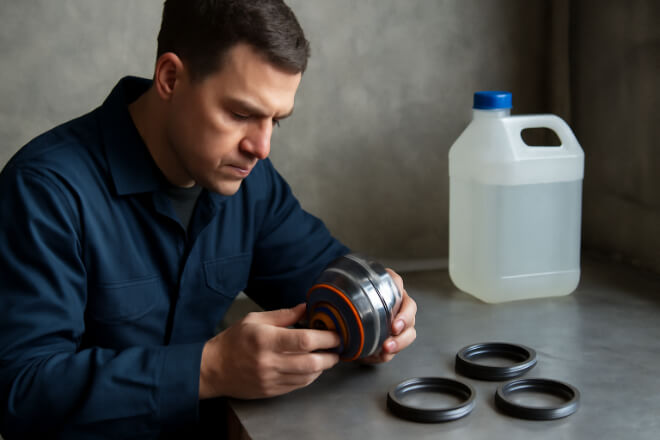

Inspect rings during planned shutdowns for wear or cracks.
Use clean flushing fluids to cool faces and remove particles.
Replace worn rings with matching pairs to avoid leaks.
Keep spare rings ready for critical equipment.
Considérations relatives aux coûts et au retour sur investissement
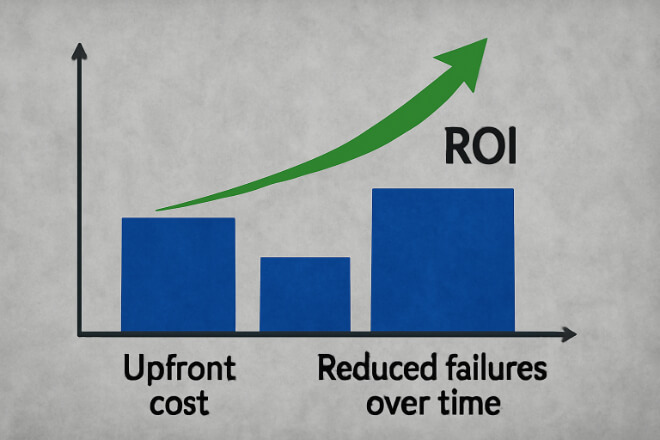
Upfront Cost: Stationary and rotating rings are priced similarly.
Savings: Correct selection reduces breakdowns and downtime.
ROI: Improved uptime and lower maintenance make carbide rings cost-effective.
Avantages environnementaux et de sécurité

Choosing the right ring prevents leaks of harmful fluids, protects workers, and ensures compliance with environmental standards.
Conclusion
Stationary and rotating carbide seal rings each have unique advantages.
Stationary rings excel in stable, high-heat applications, while rotating rings are better for abrasive, dirty, or high-vibration systems.
For decision-makers, selecting the right design improves reliability, extends equipment life, and reduces operational costs.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
