Chemical processing plants operate in some of the harshest industrial environments.
Pumps, mixers, agitators, and compressors constantly face high pressure, temperature, and corrosive fluids. Every rotating component inside them must perform with precision and reliability.
A small failure in a bearing or bushing can lead to leakage, contamination, or full equipment shutdown.
This is why many engineers and plant operators now rely on tungsten carbide bushings.
These bushings offer superior résistance à l'usure, chemical stability, and long service life—helping chemical facilities run safely, efficiently, and continuously.
Cet article explore comment bagues en carbure de tungstène enhance the performance and durability of chemical processing equipment, and why they are considered an investment in long-term reliability.
Operating Challenges in Chemical Processing
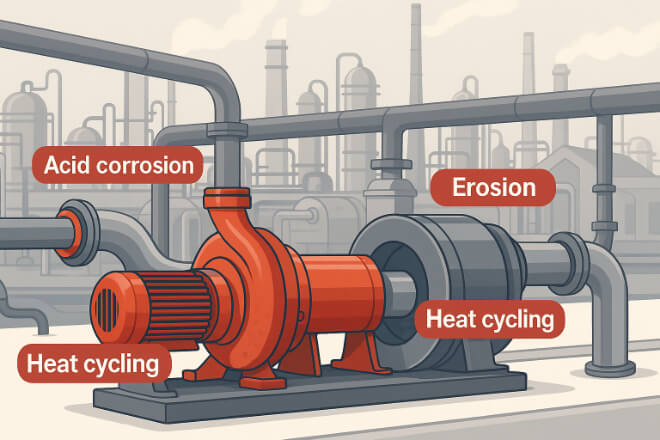
Chemical processing systems are exposed to aggressive conditions that quickly destroy standard metal parts.
Typical problems include:
Corrosion: Acids, alkalis, and chlorides react with metal bushings.
Erosion: Suspended solids cause surface wear.
Thermal cycling: Equipment operates under changing temperature and pressure.
Lubrication failure: Fluids evaporate or degrade under heat.
Contamination: Material transfer or product leakage damages seals and bearings.
When these problems occur, they cause costly downtime and maintenance interruptions.
bagues en carbure de tungstène provide a solution that can handle all these challenges effectively.
Why Tungsten Carbide Is Ideal for Chemical Equipment
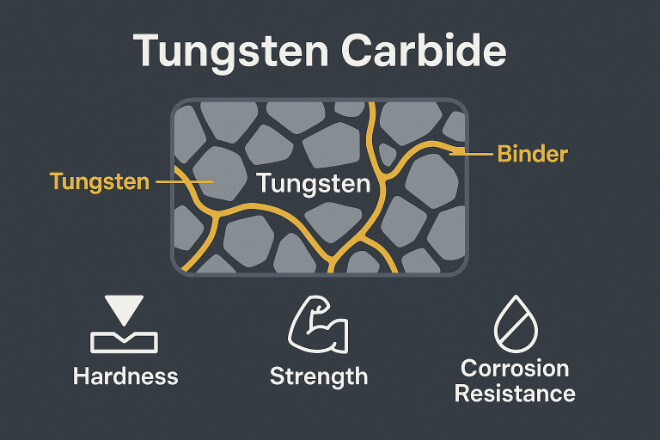
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a compound of tungsten and carbon, usually bonded with a small amount of nickel or cobalt. This creates an extremely hard and chemically stable material.
Propriétés clés :
Dureté up to 92 HRA for résistance à l'usure.
Résistance à la compression > 4000 MPa.
Low coefficient of thermal expansion (~4.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K).
Corrosion resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents.
Excellent dimensional stability under temperature change.
Unlike stainless steel or bronze, tungsten carbide bushings maintain their shape and surface finish even in strong chemical exposure and continuous operation.
Comparaison avec d'autres matériaux de bagues
| Matériel | Résistance à la corrosion | Résistance à l'usure | Temperature Limit (°C) | Durée de vie |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | Low – reacts with acids | Faible | 250 | Court |
| Acier inoxydable | Medium – prone to pitting | Modéré | 400 | Moyen |
| Tungsten Carbide (Ni Binder) | Excellent – resists acids and chlorides | Haut | 800+ | Long |
Tungsten carbide clearly outperforms common materials in terms of wear and résistance à la corrosion, making it the best option for acidic, abrasive, or high-temperature chemical media.
Corrosion Resistance in Aggressive Fluids
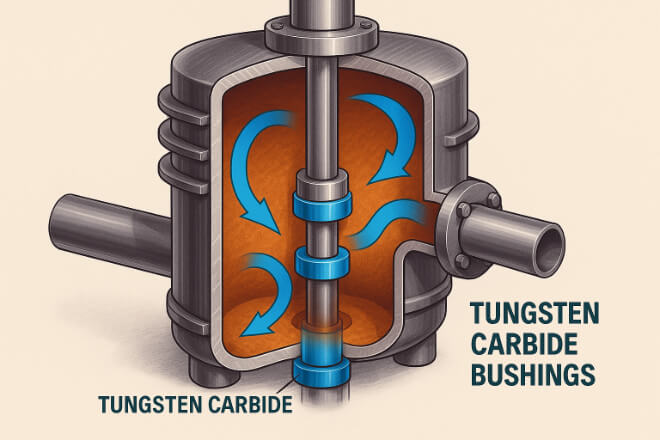
Chemical plants use a wide range of fluids — from sulfuric acid to caustic soda and solvents — that can destroy most metals.
Tungsten carbide, especially when nickel-bonded, resists corrosion in both acidic and basic media.
Even under continuous flow and high pressure, the carbide’s surface remains smooth and chemically inert, preventing pitting or micro-cracks.
This stability ensures long life in acid circulation pumps, chlor-alkali units, and solvent handling systems.
Role in Key Chemical Processing Equipment
| Equipment Type | Function of Bushing | Benefit in Operation |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Supports shaft, maintains alignment | Reduces vibration and leakage |
| Agitator or Reactor Shaft | Provides bearing support under chemical load | Improves stability under heat and pressure |
| Compressor | Reduces friction on rotating parts | Extends component life in gas handling |
| Metering or Dosing Pump | Provides precision movement | Maintains consistent chemical delivery |
Tungsten carbide bushings are found in every major area of a chemical plant—from feed pumps to final filtration—where mechanical stability and safety are critical.
Binder and Microstructure Considerations
| Type de liant | Résistance à la corrosion | Résistance aux chocs | Applications typiques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cobalt (Co) | Bien | Haut | Pumps with low chemical exposure |
| Nickel (Ni) | Excellent | Modéré | Acidic or corrosive chemical pumps |
Nickel-bonded carbide is typically preferred in the chemical industry because it resists chloride and acid attack.
Fine-grain microstructures provide higher dureté and smoother surfaces, reducing friction and wear between rotating components.
Dimensional Stability Under Heat and Pressure
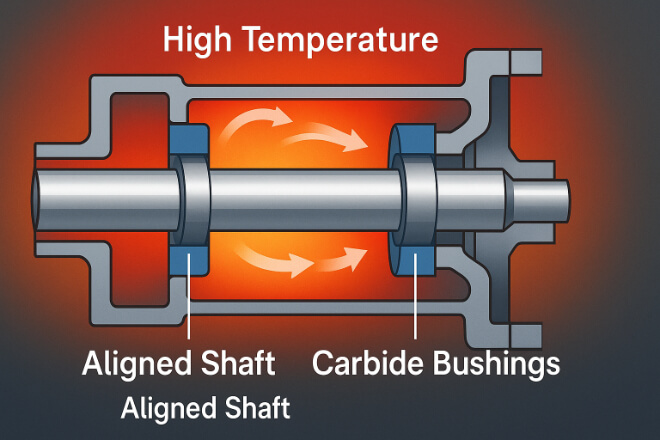
Chemical reactors and pumps often operate at elevated temperatures. Tungsten carbide’s low thermal expansion keeps shaft and housing alignment consistent.
This prevents vibration, misalignment, and premature seal wear — even after thousands of thermal cycles.
As a result, tungsten carbide bushings maintain tight tolerances, enabling pumps and compressors to operate efficiently with minimal leakage.
Maintenance and Cost Efficiency
| Matériel | Durée de vie moyenne | Maintenance Interval | Coût des temps d'arrêt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | 6–12 months | Fréquent | Haut |
| Acier inoxydable | 1–2 years | Modéré | Moyen |
| Carbure de tungstène | 3–5 years | Faible | Faible |
Although tungsten carbide bushings are more expensive initially, their long service life and minimal maintenance lower total costs over time.
In continuous chemical production lines, this reliability translates into reduced downtime and higher process efficiency.
Conclusion
In the demanding world of chemical processing, equipment must resist corrosion, heat, and abrasion without failure.
Tungsten carbide bushings deliver unmatched strength and durability, maintaining performance even in acids, solvents, and high-pressure conditions.
For plant managers and design engineers, upgrading to carbide bushings means longer uptime, fewer replacements, and safer, more efficient operation.
In short, they are a small component with a big impact on plant productivity and safety.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
