Outils de coupe en carbure de tungstène sont réputés pour leur résistance et leur durabilité. Cependant, même les outils les plus robustes peuvent s'user rapidement dans des conditions extrêmes.
C'est là qu'interviennent les revêtements. Appliquer le bon revêtement peut faire une grande différence dans la durée de vie de votre outil, dans sa qualité de coupe et dans les économies que vous réalisez à long terme.
Dans cet article de blog, nous explorerons comment différents types de revêtements contribuent à améliorer les performances des outils de coupe en carbure de tungstène.
Que vous dirigiez un atelier CNC ou que vous essayiez simplement de réduire les coûts d'outillage, ce guide vous aidera à comprendre l'importance des revêtements.
1. Pourquoi les revêtements sont-ils importants pour les outils de coupe en carbure ?

Le carbure de tungstène est résistant en soi, mais les revêtements le rendent encore plus résistant.
Imaginez vos outils fonctionnant à des vitesses folles, faisant face à des températures extrêmement élevées et meulant des matériaux durs comme l'acier inoxydable.
Même le carbure a besoin d'aide sous pression : c'est là qu'interviennent les revêtements.
Ces revêtements forment un bouclier ultra-fin à la surface de l'outil. Ils permettent à l'outil de rester affûté plus longtemps, de résister à la chaleur et de réduire les frottements.
Vous bénéficiez ainsi d'une durée de vie prolongée de l'outil, de coupes plus régulières et de moins de soucis liés aux pannes. Considérez les revêtements comme une amélioration économique offrant un excellent retour sur investissement.
Ils sont particulièrement utiles pour gérer la chaleur, l'usure et l'accumulation de matériaux collants qui abîment les finitions de surface. Les revêtements protègent l'outil afin que vous puissiez vous concentrer sur la production sans interruption.
2. Principaux avantages des revêtements d'outils
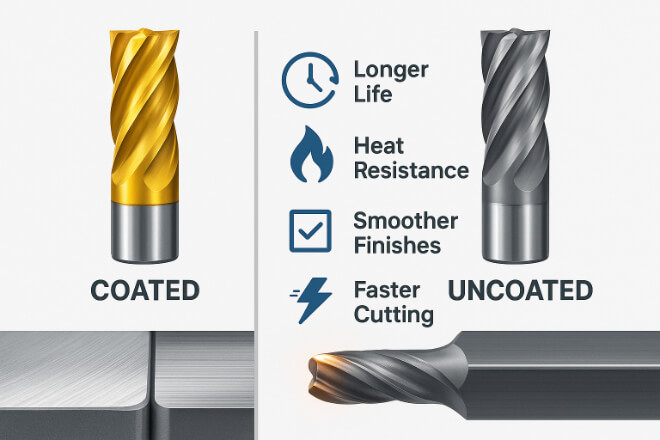
Voici comment les revêtements améliorent les outils en carbure, sans trop compliquer les choses :
1). Durée de vie de l'outil plus longue
Les revêtements d'outils agissent comme une armure. Ils réduisent l'usure directe, ce qui signifie que vos outils ne s'émoussent pas aussi vite.
Cela signifie moins de changements d’outils et un usinage plus cohérent.
Et le bonus ? Moins de temps d'arrêt. Lorsque vous n'avez pas à changer constamment d'outils ou à recalibrer les configurations, votre atelier fonctionne plus facilement et plus efficacement.
2). Meilleure résistance à la chaleur
La découpe à grande vitesse est brûlante, littéralement. Les revêtements permettent aux outils de résister à la chaleur sans perdre leur tranchant.
Ceci est particulièrement utile lorsque vous usinez à sec ou travaillez avec des métaux sensibles à la chaleur.
Certains revêtements supportent des températures extrêmes sans se fissurer ni se ramollir. Cela signifie moins de bords brûlés et de meilleurs résultats.
3). Friction réduite
Les revêtements lisses réduisent la traînée. Votre outil traverse le matériau plus facilement, ce qui se traduit par des copeaux plus propres et moins de vibrations.
Cela améliore non seulement la qualité de coupe, mais contribue également à prolonger la durée de vie de vos machines. Moins de force signifie moins de tension sur tout.
4). Finition de surface améliorée
Personne n'aime retravailler une pièce brute. Les outils revêtus offrent une finition plus nette dès la sortie de la machine, réduisant ainsi le polissage et le meulage.
Cela permet d’économiser du temps et de la main-d’œuvre, en particulier dans des secteurs comme aérospatial ou médical, où la qualité de la surface compte beaucoup.
5). Vitesses d'usinage plus rapides
Si vos outils restent plus frais et plus affûtés, vous pouvez pousser vos machines plus loin. Les outils revêtus vous permettent d'augmenter les avances et les vitesses de broche sans endommager l'outil.
Plus de vitesse signifie plus de pièces par heure. Et qui ne souhaite pas ça ?
3. Types de revêtements courants pour les outils en carbure de tungstène
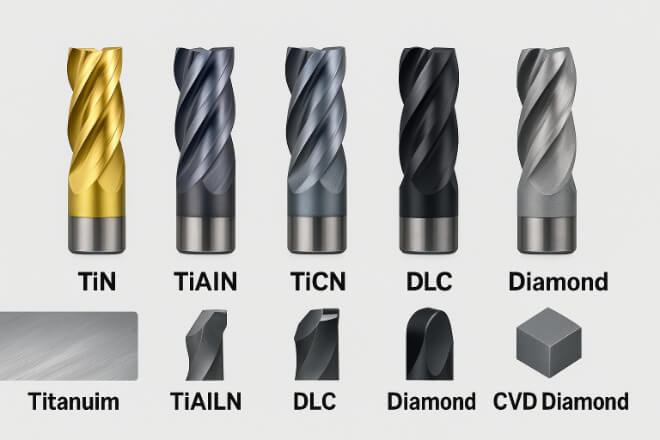

Chaque revêtement a sa propre personnalité. Découvrons les meilleures options :
1). TiN (nitrure de titane)
Couleur or classique. Un produit polyvalent. Réduit les frottements et offre une protection contre l'usure. Convient parfaitement aux aciers doux et aux travaux de base.
2). TiAlN / AlTiN (nitrure de titane et d'aluminium)
Foncé et résistant. Adore les fortes chaleurs. Idéal pour la coupe à sec et les vitesses élevées. Idéal pour l'acier inoxydable et le titane.
3). TiCN (carbonitrure de titane)
Plus résistant que le TiN. Idéal pour les matériaux plus résistants comme la fonte et les aciers plus durs. Idéal lorsque vous avez besoin d'une durabilité accrue sans avoir à opter pour des options plus onéreuses.
4). DLC (carbone de type diamant)
Super lisse et à très faible frottement. Ne colle pas. Parfait pour travailler l'aluminium ou le plastique. Permet un déplacement propre des copeaux.
5). Revêtement diamant CVD
Matériaux rugueux comme les composites et le graphite ? Ce revêtement est fait pour vous. C'est le revêtement le plus résistant du marché, idéal pour la découpe abrasive là où les autres revêtements s'abîment rapidement.
4. PVD vs. CVD : deux méthodes de revêtement courantes

Il existe deux principales méthodes d’application des revêtements : le PVD et le CVD.
1). PVD (dépôt physique en phase vapeur)
Le traitement s'effectue à basse température, évitant ainsi toute déformation de l'outil. Le revêtement est fin et tranchant, idéal pour un travail de précision.
Utilisez-le pour les outils à grande vitesse, les perceuses ou les petits outils de coupe où les détails des bords sont importants.
2). CVD (dépôt chimique en phase vapeur)
Plus épais et ultra-résistant. Résistant aux chocs avec des matériaux abrasifs. Cependant, il peut légèrement émousser les bords tranchants.
Idéal pour les gros travaux de fraisage ou le tournage de la fonte. Plus robuste que le PVD.
Les deux ont leur place. Choisissez en fonction de ce que vous coupez et de votre vitesse.
5. Quand faut-il utiliser des outils avec ou sans revêtement ?
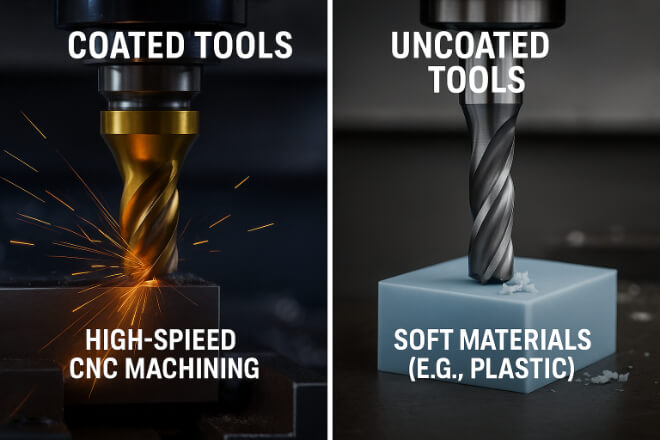
Les outils revêtus sont généralement le meilleur choix. Mais pas toujours. Si vous travaillez avec des matériaux souples comme le plastique ou l'aluminium, les revêtements peuvent parfois devenir collants ou gêner la finition.
Cependant, pour les travaux à grande vitesse et à forte usure, optez pour un revêtement. C'est une évidence.
Les outils non revêtus sont idéaux pour les travaux ultra-précis ou la finition de matériaux tendres. Mais pour la plupart des travaux, les revêtements sont plus performants. Ils durent plus longtemps, sont plus performants et assurent la productivité de votre atelier.
6. Performances réelles : outils revêtus et non revêtus
Pour vous donner une meilleure idée de l’utilité des revêtements, examinons une comparaison concrète :
| Facteur | Carbure non revêtu | Carbure revêtu |
|---|---|---|
| Durée de vie de l'outil | Plus court (souvent 1x) | 2x–5x plus long |
| Résistance à la chaleur | Modéré | Excellent |
| Finition de surface | Plus rugueux, plus de bavures | Des coupes plus lisses et plus nettes |
| Coût au fil du temps | Plus élevé (plus de remplacements) | Inférieur (moins de changements d'outils) |
Ce tableau montre clairement que les revêtements ne constituent pas seulement une petite amélioration : ils constituent un facteur clé de l’efficacité de l’usinage à long terme.
7. Comment choisir le bon revêtement
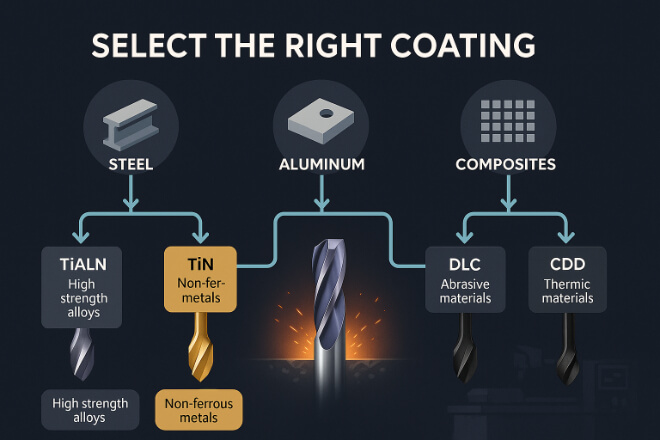
Pour tirer le meilleur parti de vos outils en carbure, choisir le bon revêtement est essentiel. Voici quelques conseils simples :
Pour l'acier et l'acier inoxydable : optez pour TiAlN ou AlTiN
Pour l'aluminium et le cuivre : utiliser des outils DLC ou polis
Pour les matériaux abrasifs : choisissez le revêtement diamant CVD
Pour un usage général : TiN ou TiCN est un bon début
Tenez également compte de votre environnement d'usinage : si vous utilisez des liquides de refroidissement, le type de machine et les temps de cycle souhaités. Ces variables vous aideront à affiner votre choix et à optimiser vos résultats.
Et n'oubliez pas : aucun revêtement n'est parfait pour tous les travaux. Il s'agit d'équilibrer résistance à la chaleur, protection contre l'usure et coût.
Réflexions finales
Les revêtements d'outils sont un petit détail qui fait toute la différence. Ils permettent à vos outils en carbure de durer plus longtemps, de couper plus proprement et de fonctionner plus rapidement. Cela signifie moins de gaspillage et plus de profits.
Que vous usiniez des métaux durs ou que vous cherchiez à atteindre des tolérances plus strictes, un bon revêtement vous simplifie la vie. C'est aussi simple que ça.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
