Carbide cutting tools have become essential in modern lathe operations. These tools are known for their high hardness, long wear life, and ability to cut tough materials like stainless steel, hardened steel, and cast iron.
For companies aiming to boost machining efficiency and reduce downtime, choosing carbide lathe tools is a smart and strategic move.
In this guide, we’ll explain how carbide tools work on a lathe, explore different types, advantages, performance tips, and how to choose the right carbide tools to improve productivity.
What Are Carbide Cutting Tools?
Carbide cutting tools are made from tungsten carbide, a very hard material that can handle high heat and pressure.
They are stronger than high-speed steel (HSS) and stay sharp longer. This makes them ideal for cutting metal, plastic, and other tough materials on lathes.
Carbide tools can take on continuous cutting jobs, high-speed operations, and materials that would wear out softer tools quickly.
Why Use Carbide Cutting Tools in a Lathe?

Lathe machines work by rotating the workpiece while a tool cuts away material. In this process, tool strength and edge retention are crucial. That’s where carbide tools shine.
Key Benefits of Carbide Lathe Tools:
Longer tool life than HSS
Higher cutting speeds for faster production
Better surface finish on final parts
Reduced downtime from fewer tool changes
Stable performance at high temperatures
By reducing tool wear and rework, carbide lathe tools lower overall production costs.
Types of Carbide Cutting Tools for Lathes
Different turning operations need different tool shapes. Choosing the right geometry helps improve both tool life and part quality.
| Type d'outil | Utilisation courante |
|---|---|
| Plaquettes de tournage | General turning and contour shaping |
| Parting & Grooving Tools | Cutting off parts or making grooves |
| Threading Inserts | Creating internal or external threads |
| Boring Bars | Internal hole enlargement |
| Profiling Tools | Complex shapes and contours |
Each tool type comes in various carbide grades and coatings, tailored for different materials and performance needs.
Choosing the Right Carbide Tool Grade
Tool grade affects dureté, dureté, et résistance à l'usure. You must match the right carbide grade to your machining job.
| Nuance de carbure | Idéal pour | Caractéristiques |
|---|---|---|
| P-grade (Steel) | Cutting steel and alloy steel | High strength and thermal resistance |
| K-grade (Cast Iron) | Cast iron, non-ferrous materials | Hard and wear-resistant |
| M-grade (Stainless Steel) | Stainless steel and alloys | Balanced toughness and wear |
Your carbide tool supplier should guide you in choosing the best grade for your needs.
Coatings That Improve Performance
Tool coatings can dramatically improve cutting speed, reduce wear, and lower friction. Common coatings include:
| Revêtement | Avantage | Utilisation typique |
|---|---|---|
| TiN (nitrure de titane) | Increases hardness and wear resistance | General machining |
| TiAlN (nitrure de titane et d'aluminium) | Haute résistance à la chaleur | Dry cutting, hard steel |
| AlTiN | Thermal stability and oxidation resistance | Stainless steel, high-temp alloys |
| Diamond Coating | Excellent for non-ferrous materials | Graphite, plastics, aluminum |
Coatings help carbide inserts last longer and perform better, especially at high speeds.
Signs It’s Time to Replace Your Carbide Lathe Tool
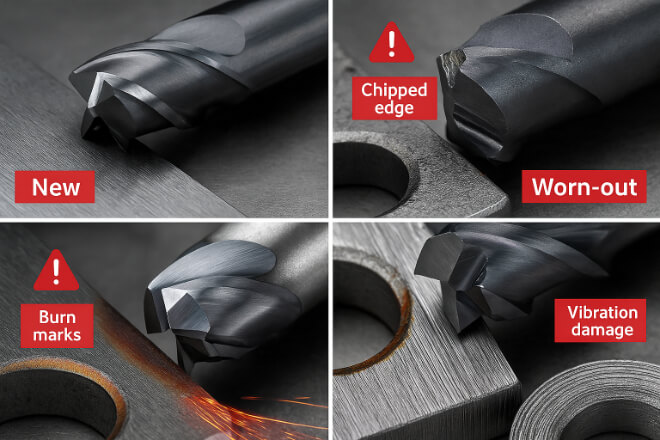

Even high-quality carbide tools will eventually wear out. Using a worn tool affects surface finish and can damage both the machine and the part.
Replace your tool if you notice:
Chipped or broken edges
Burn marks or discoloration
Increased vibration or chatter
More force needed during cutting
Mauvaise finition de surface des pièces
Don’t wait for a tool to break—planned replacement saves time and protects equipment.
Coolant and Cutting Parameters Matter
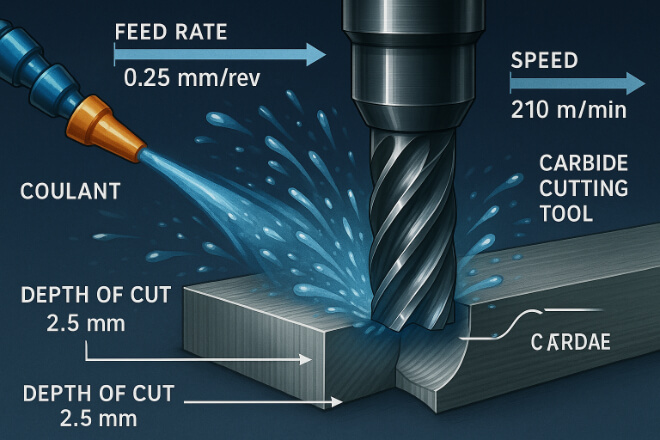
Proper coolant use reduces heat buildup and improves tool life. Similarly, choosing the right cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut is essential.
Tips:
Use water-based coolant for steel and stainless steel.
Use air blast or dry cutting for aluminum (to avoid BUE—built-up edge).
Start with manufacturer-recommended cutting parameters.
Adjust feed/speed based on material and tool wear.
Cost vs. Performance: Is Carbide Worth It?
Carbide tools cost more upfront—but that’s only part of the story. What matters is cost-per-part, not cost-per-tool.
| Facteur | HSS Tools | Outils en carbure |
|---|---|---|
| Durée de vie de l'outil | Court | Long |
| Vitesse de coupe | Ralentissez | Faster |
| Finition de surface | Average | Excellent |
| Tool Change Frequency | Often | Rarely |
| Total Cost Over Time | Plus haut | Inférieur |
With fewer tool changes and better part quality, carbide ends up being the more economical choice for high-production environments.
Choosing the Right Supplier
The quality of your carbide tool also depends on the supplier. A reliable supplier ensures:
High-grade raw materials
Consistent tool geometry
Accurate tolerances
Support technique
Timely delivery
Choosing a trusted supplier helps reduce tool failure, downtime, and part defects.
Réflexions finales
Carbide cutting tools are a powerful investment for lathe machining. From roughing to precision finishing, they outperform traditional tools in speed, durability, and accuracy.
With the right tool geometry, coating, and supplier, your shop can produce better parts—faster and cheaper.
If you’re aiming to improve tool life, cutting speed, and productivity, tungsten carbide tools are the way forward.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
