Dans des industries telles que exploitation minière, pétrole et gaz, travail des métaux, and construction, wear parts are critical components.
They face constant friction, impact, heat, and sometimes corrosive environments. Choosing the right material is essential to ensure long life and high performance.
Tungsten carbide is one of the most trusted materials for pièces d'usure because it combines dureté, dureté, et la durabilité.
However, not all tungsten carbide is the same. There are different grades of tungsten carbide, each designed for specific applications.
This article explains how tungsten carbide grades differ, how to select the right grade, and why the right choice can make a big difference for decision-makers in industry.
Quelles sont les nuances de carbure de tungstène ?

A tungsten carbide grade refers to the specific composition and grain size of the carbide and its binder (often cobalt or nickel).
By changing the grain size, binder content, and additives, manufacturers can create grades with different balances of:
Dureté (resistance to wear and abrasion)
Dureté (ability to resist cracking and breakage)
Résistance à la corrosion
Résistance à la chaleur
Different grades perform better in different conditions, so understanding these differences is key to selecting the right one.
Factors That Define a Tungsten Carbide Grade
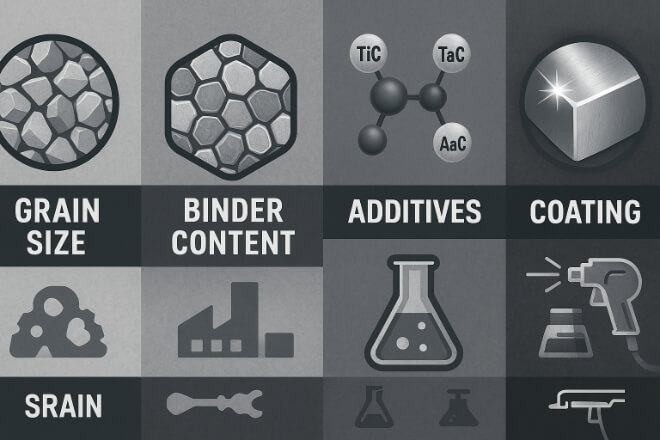
Several factors influence how a tungsten carbide grade will perform:
1). Taille des grains
Fine-grain carbide is harder and gives better résistance à l'usure.
Coarse-grain carbide is tougher and resists impact damage better.
2). Binder Content
Higher cobalt or nickel content increases dureté but reduces hardness.
Lower binder content increases dureté but can make the material more brittle.
3). Additives
Some grades use additives such as titanium carbide (TiC) or tantalum carbide (TaC) to improve heat resistance and reduce chemical wear.
4). Coating
Although not part of the grade itself, coatings like TiN, TiAlN, or diamond can improve life in certain applications.
Common Tungsten Carbide Grades for Wear Parts
| Type de note | Main Features | Applications typiques |
|---|---|---|
| Fine-Grain Carbide (1–2 µm) | High hardness, excellent wear resistance, sharp edges | Cutting tools, precision wear parts, dies |
| Medium-Grain Carbide (2–6 µm) | Balance of hardness and toughness | General-purpose wear parts, metal forming tools |
| Coarse-Grain Carbide (>6 µm) | High toughness, impact resistance | Mining tools, drilling bits, crusher tips |
| Corrosion-Resistant Grade | Nickel binder, high chemical stability | Oil & gas valves, chemical pumps, marine equipment |
| Heat-Resistant Grade | Additives for thermal stability, maintains hardness at high temp | Hot forging dies, high-speed cutting tools |
How to Choose the Right Grade for Wear Parts
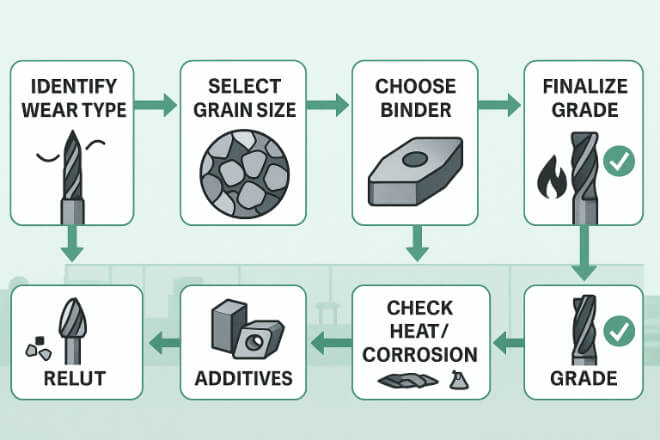
When selecting a tungsten carbide grade, consider the following steps:
1). Define the Wear Type
Is it mainly abrasive wear, impact wear, or corrosion?
For abrasive wear, choose fine-grain, low-binder grades.
For impact wear, choose coarse-grain, high-binder grades.
2). Consider the Operating Temperature
If the wear part works in high heat, use a heat-resistant grade.
For lower temperatures, focus on hardness and résistance à l'usure.
3). Check the Corrosive Environment
For salty, acidic, or chemical exposure, use nickel-binder grades.
4). Look at Cost vs. Performance
The most expensive grade is not always the best choice.
Match grade to actual operating needs to optimize cost.
Example: Tungsten Carbide in Mining Wear Parts
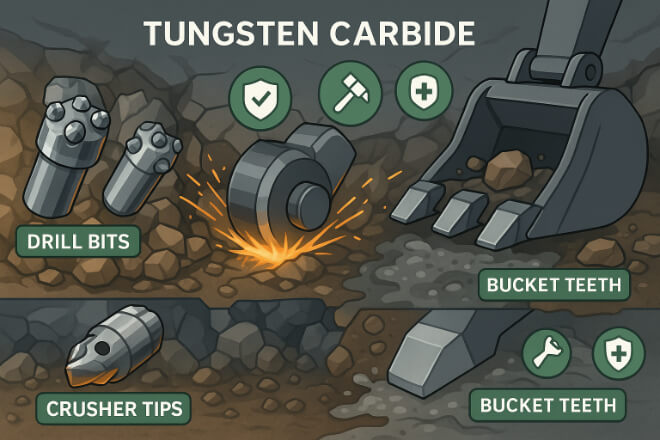
In mining, wear parts like drill bits, crusher tips, and bucket teeth face a combination of abrasion and impact.
For cutting rock, coarse-grain grades with high cobalt content give dureté and prevent breakage.
For slurry pumps or sand handling, corrosion-resistant nickel binder grades prevent rust and pitting.
Choosing the wrong grade can mean faster wear, more downtime, and higher replacement costs.
Benefits of Matching Grade to Application

When the correct tungsten carbide grade is used for a wear part:
Longer service life reduces downtime and replacement costs.
Better performance under the exact operating condition.
Lower total cost of ownership even if the initial price is higher.
Consistent quality for the final product or process.
Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Grades
Manufacturers are developing nano-grain carbides for even higher résistance à l'usure, hybrid binders for better corrosion protection, and advanced coatings to further extend life.
As industries demand more productivity, selecting the right grade will be even more important.
Conclusion
For decision-makers in industries that rely on wear parts, understanding tungsten carbide grades is essential.
Choosing the right grade can extend tool life, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency.
By matching the grade to the actual wear conditions—abrasion, impact, heat, or corrosion—you ensure your investment in tungsten carbide delivers maximum value.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
