bagues en carbure de tungstène are well-known for their exceptional dureté, résistance à l'usure, et une longue durée de vie.
They are used in critical applications — from pumps and compressors to drilling and automotive systems.
But when these bushings reach the end of their service life, what happens next? Can they be reused or recycled?
The good news is yes — tungsten carbide bushings can be recycled, and doing so brings both economic and environmental benefits.
This article explores how recycling works, why it matters, and how companies can take advantage of tungsten carbide recovery programs.
Why Recycling Tungsten Carbide Matters
Tungsten carbide is made from tungsten (W) and carbon (C), often bonded with cobalt or nickel.
Tungsten is a critical and limited raw material. Mining and refining it require significant energy and resources.
Recycling helps:
Reduce dependence on new tungsten ore.
Lower production costs for tool and component manufacturers.
Save energy compared to mining and refining.
Protect the environment by minimizing waste.
Recycling rates for tungsten carbide are increasing globally because companies realize it’s both sustainable and profitable.
How Tungsten Carbide Bushings Are Recycled
Recycling tungsten carbide involves several steps to recover valuable metal from worn or damaged parts.
The goal is to separate the tungsten and cobalt content for reuse in new carbide production.
| Stage | Process Description | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Collection | Used or broken tungsten carbide bushings are collected from workshops or customers. | Scrap tungsten carbide |
| 2. Sorting and Cleaning | Bushings are sorted by grade, binder type (Co or Ni), and contamination level. | Clean, sorted scrap ready for processing |
| 3. Crushing and Pulverizing | Bushings are broken into fine powder using mechanical crushing and milling. | Tungsten carbide powder with binder metal |
| 4. Chemical Treatment | Powder is treated with chemicals or acids to remove cobalt and impurities. | Pure tungsten oxide (WO₃) |
| 5. Reduction and Refining | WO₃ is reduced in hydrogen atmosphere to recover metallic tungsten. | High-purity tungsten powder |
| 6. Reuse in Production | Recovered tungsten is blended with fresh carbon and cobalt to produce new carbide material. | Recycled tungsten carbide ready for manufacturing |
This process is often managed by specialized carbide recycling companies or tool manufacturers that buy back scrap from customers.
Direct vs. Chemical Recycling
There are two main methods for tungsten carbide recycling: direct recycling and chemical recycling. Each has its benefits and costs.
| Method | Process Type | Avantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Recycling | Mechanical crushing and reprocessing without chemical separation | Low energy use; fast turnaround | Quality depends on scrap purity |
| Chemical Recycling | Full chemical recovery using oxidation and reduction | High purity and flexibility for all grades | More costly and time-consuming |
Many manufacturers use a hybrid approach, combining direct and chemical methods to balance cost, quality, and sustainability.
Environmental Benefits of Recycling

Recycling tungsten carbide reduces the need for new tungsten mining — which involves high energy consumption and generates CO₂ emissions.
Key environmental advantages include:
Up to 70% energy savings compared to primary tungsten production.
Up to 40% reduction in CO₂ emissions.
Less landfill waste, since bushings are reused instead of discarded.
Reduced demand for mining and transportation of raw ores.
For companies focused on sustainability, recycling helps meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals and ISO 14001 standards.
Economic Advantages for Companies
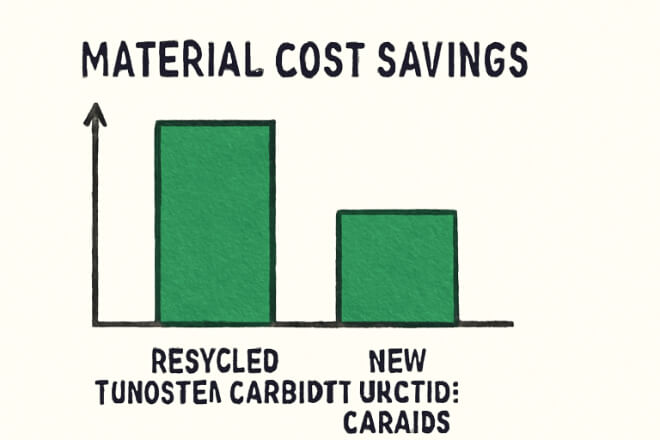
Beyond the environmental impact, recycling also provides economic benefits for manufacturers and end-users.
1). Lower Material Costs
Recyclé poudre de tungstène is significantly cheaper than freshly mined tungsten — helping reduce production expenses.
2). Stable Supply Chain
Recycling creates a local loop of material reuse, reducing dependence on volatile global markets.
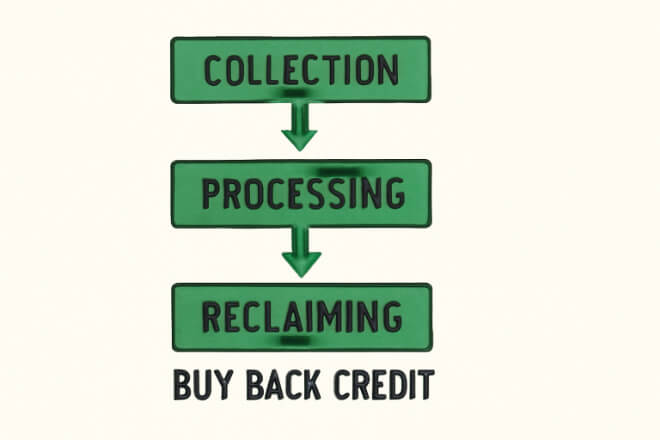
3). Buy-Back Value
Many carbide suppliers offer scrap buy-back programs, where customers receive credit or payment for returned bushings.
4). Branding Advantage
Promoting recycling and sustainability strengthens a company’s brand image and appeals to eco-conscious clients.
Challenges in Recycling Tungsten Carbide Bushings

Despite its benefits, recycling tungsten carbide is not without challenges.
Contamination: Oil, metal, or oxide impurities can reduce powder quality.
Mixed Grades: Sorting different binder types (Co vs Ni) adds complexity.
Transportation: Tungsten scrap is dense and heavy, increasing logistics costs.
Technology Investment: Setting up recycling equipment requires capital.
However, as more industries prioritize sustainability, the return on investment is increasing rapidly.
How Companies Can Start a Recycling Program
For decision-makers looking to integrate recycling into their operations, the process is simple but strategic:
Partner with a certified recycler – Choose suppliers who handle tungsten scrap responsibly.
Collect worn parts – Set up bins or collection points for used bushings.
Clean and label – Remove oil or debris and label parts by grade or binder type.
Track material flow – Keep records for sustainability reports or audits.
Negotiate buy-back terms – Many recyclers pay based on weight and purity.
Working with established tungsten recovery companies ensures your materials are reused efficiently and traceably.
Future Trends in Tungsten Carbide Recycling
With increasing global demand for tungsten, recycling technologies are evolving quickly. Emerging trends include:
Automated sorting systems that identify grades using AI and spectroscopy.
Low-temperature chemical recovery methods with reduced emissions.
Circular supply partnerships between toolmakers and end-users.
Blockchain tracking for verified recycled material origins.
These developments are turning tungsten carbide recycling into a strategic advantage rather than a waste-management task.
Conclusion
Yes, tungsten carbide bushings can absolutely be recycled — and doing so offers both economic and environmental benefits.
By participating in recycling programs, companies not only reduce costs but also demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible resource management.
For decision-makers, investing in recycling is more than a green initiative — it’s a smart long-term business strategy that supports efficiency, resilience, and brand reputation.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
