Dans les industries où les pièces doivent résister à une usure importante, à la chaleur et à la corrosion, le choix du bon matériau est essentiel.
Trois des matériaux les plus populaires pour pièces d'usure Il existe différents matériaux, dont le carbure de tungstène, la céramique et la stellite. Chaque matériau possède des propriétés, des forces et des faiblesses uniques.
Pour les décideurs du secteur manufacturier, exploitation minière, pétrole et gaz, et d'autres industries lourdes, le choix entre ces matériaux peut grandement affecter les coûts de production, les temps d'arrêt et les performances du produit.
Ce guide compare en détail les pièces d'usure en carbure de tungstène, en céramique et en stellite afin que vous puissiez faire des choix éclairés pour vos opérations.
Qu'est-ce que le carbure de tungstène ?

Le carbure de tungstène est un composé composé d’atomes de tungstène et de carbone.
C'est l'un des matériaux les plus durs utilisés dans l'industrie, classé entre 8,5 et 9 sur l'échelle de dureté de Mohs.
Propriétés clés :
Extrêmement élevé dureté — plus dur que l’acier et la plupart des métaux.
Excellent résistance à l'usure — idéal pour les conditions abrasives.
Haute résistance à la chaleur — conserve sa dureté même à des températures élevées.
Modéré dureté — plus cassant que l’acier mais plus résistant que la plupart des céramiques.
Applications courantes : outils de coupe, forets miniers, matrices résistantes à l'usure, composants de pompes et de vannes et buses.
Que sont les pièces d’usure en céramique ?
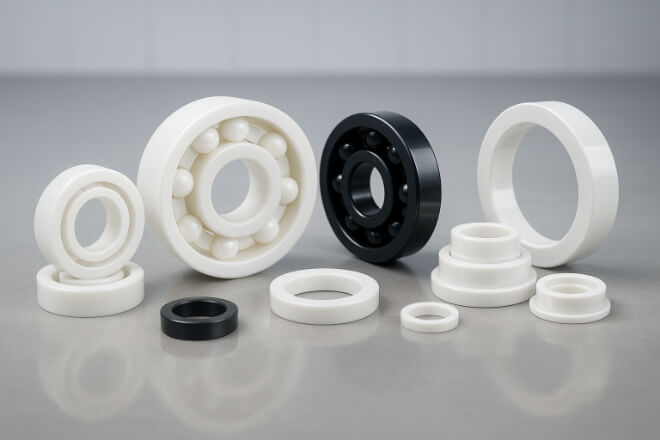

Les céramiques sont des matériaux non métalliques et inorganiques fabriqués à partir de composés tels que l'alumine, la zircone ou le nitrure de silicium.
Propriétés clés :
Très élevé dureté — peut être aussi dur ou plus dur que le carbure de tungstène.
Excellente résistance à la corrosion — ne rouille pas et ne s’oxyde pas.
Léger — moins dense que les pièces d’usure à base de métal.
Faible dureté — très cassant, sujet à la fissuration sous l’impact.
Applications courantes : roulements, joints, lames de coupe pour finitions très fines et composants à haute température dans le traitement chimique.
Qu'est-ce que la stellite ?
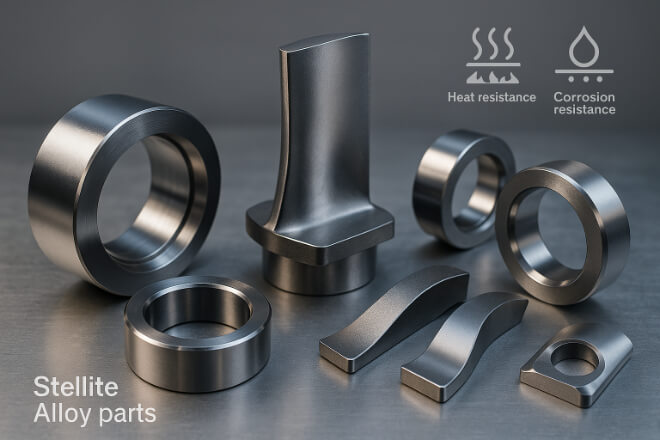

La stellite est un alliage à base de cobalt contenant du chrome, du tungstène et d'autres métaux.
Il a été conçu pour une résistance exceptionnelle à l'usure et à la corrosion, en particulier à des températures élevées.
Propriétés clés :
Haut résistance à l'usure — en particulier dans des conditions de glissement et de grippage.
Bonne résistance à la corrosion — convient aux environnements chimiques et marins.
Haut dureté — résiste mieux aux chocs que le carbure de tungstène et la céramique.
Inférieur dureté que le carbure de tungstène — mais souvent suffisant pour de nombreuses utilisations industrielles.
Applications courantes : sièges de soupape, arêtes de coupe, aubes de turbine et revêtements résistants à l'usure.
Tableau de comparaison des propriétés des matériaux
Voici une comparaison côte à côte des trois matériaux :
| Propriété | Carbure de tungstène | Céramique | Stellite |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dureté | 8,5–9 Mohs | 8–9,5 Mohs | 4–6 Mohs |
| Résistance à l'usure | Excellent | Excellent | Bien |
| Résistance à la chaleur | Très élevé | Très élevé | Haut |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Haut | Excellent | Haut |
| Dureté | Modéré | Faible | Haut |
| Densité | Très élevé | Faible à moyen | Moyen |
| Coût | Haut | Haut | Moyen à élevé |
Forces et faiblesses de chaque matériau
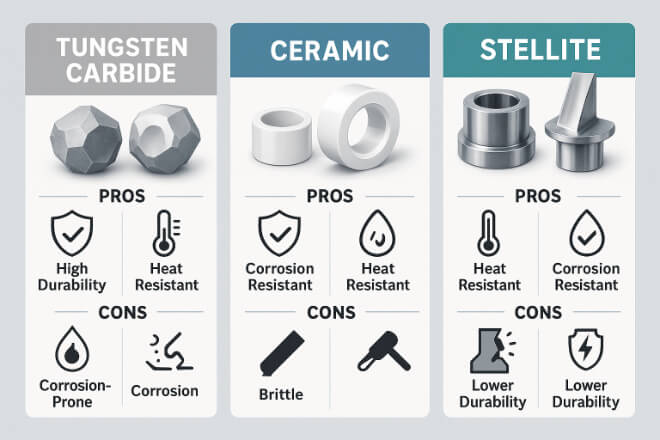
1). Carbure de tungstène
1.1). Avantages :
Excellent résistance à l'usure dans des environnements abrasifs.
Fonctionne bien dans les applications à haute température.
Une longue durée de vie réduit les temps d'arrêt.
1.2). Inconvénients :
Peut s'écailler ou se briser sous un impact très élevé.
Plus cher que de nombreux aciers.
2). Céramique
2.1). Avantages :
Extrêmement dur et résistant à la corrosion.
Léger — idéal pour les applications où le poids est important.
Peut fonctionner à des températures extrêmement élevées.
2.2). Inconvénients :
Fragile — peut se fracturer facilement sous l’effet de chocs ou de charges de flexion.
Peut être coûteux pour les pièces volumineuses ou complexes.
3). Stellite
3.1). Avantages :
Excellent dureté — supporte bien les chocs et les vibrations.
Bonne résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion.
Peut être soudé ou revêtu sur d'autres pièces.
3.2). Inconvénients :
Dureté inférieure par rapport au carbure de tungstène et à la céramique.
Peut s'user plus rapidement dans des environnements abrasifs.
Meilleur matériau par type d'application
| Application | Meilleur choix | Raison |
|---|---|---|
| Exploitation minière et forage | Carbure de tungstène | Résistance exceptionnelle à l'usure dans les roches et sols abrasifs. |
| Traitement chimique | Céramique | Résistance supérieure à la corrosion et capacité thermique élevée. |
| Sièges de soupapes dans le pétrole et le gaz | Stellite | Haute ténacité pour résister aux chocs et aux vibrations. |
| Outils de coupe à grande vitesse | Carbure de tungstène | Maintient la netteté et la dureté à des vitesses élevées. |
| Roulements haute température | Céramique | Léger et stable sous une chaleur extrême. |
Choisir le bon matériau
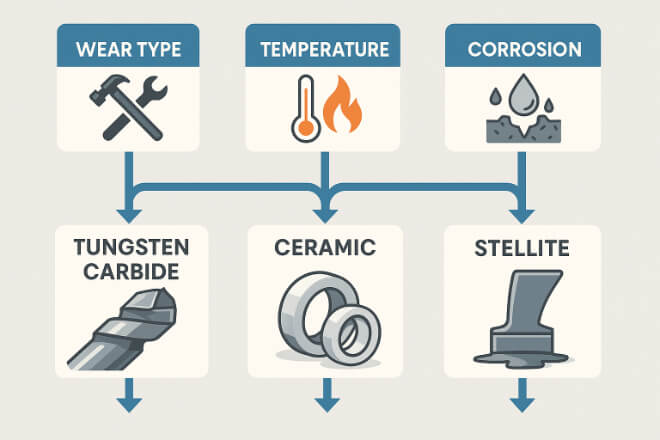
Lorsque vous choisissez entre le carbure de tungstène, la céramique et la Stellite, tenez compte des éléments suivants :
Type d'usure : Pour l'abrasion, le carbure de tungstène et la céramique sont les meilleurs choix. Pour les chocs et le grippage, la Stellite est préférable.
Température de fonctionnement : Les trois supportent bien la chaleur, mais la céramique excelle dans la chaleur extrême.
Risque de corrosion : la céramique offre la meilleure protection contre la corrosion, suivie de la stellite et du carbure de tungstène.
Budget : La stellite coûte souvent moins cher que la céramique et le carbure de tungstène pour des tailles de pièces similaires.
Coût vs. Performance
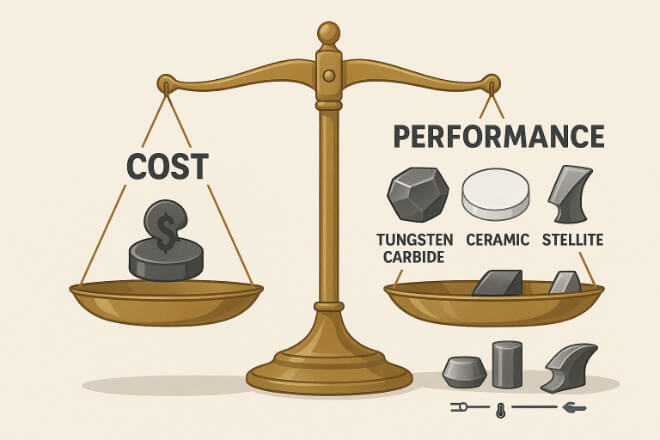
Alors que la céramique et le carbure de tungstène peuvent durer plus longtemps, le Stellite peut être plus rentable pour certains travaux.
Calculez toujours le coût total de possession, et pas seulement le prix d'achat. Des facteurs tels que les temps d'arrêt, les intervalles de remplacement et les coûts d'usinage sont importants.
Conclusion
Le carbure de tungstène, la céramique et la stellite sont tous d’excellents matériaux d’usure, mais ils excellent de différentes manières.
Choisissez le carbure de tungstène pour une résistance extrême à l’abrasion et à la chaleur.
Choisissez la céramique pour des applications résistantes à la corrosion et légères.
Choisissez Stellite lorsque la robustesse et la résistance aux chocs sont les plus importantes.
Pour les décideurs, le bon choix dépend de votre environnement opérationnel, de votre budget et de vos objectifs de performance.
Une comparaison minutieuse de ces matériaux peut permettre à votre entreprise d’économiser de l’argent et d’améliorer la fiabilité de l’équipement.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
