In pumps, compressors, turbines, and marine equipment, seal rings are critical for preventing leakage and protecting machinery.
Choosing the right material for seal rings has a direct impact on equipment life, reliability, and maintenance cost. Two of the most common materials used are tungsten carbide and ceramic.
Both materials have strong advantages, but they are not the same. This article provides a detailed comparison between bagues d'étanchéité en carbure de tungstène and ceramic seal rings, focusing on their properties, performance, and applications.
Que sont les bagues d’étanchéité en carbure de tungstène ?

Tungsten carbide is a compound of tungsten and carbon, bonded with cobalt or nickel. It is widely used in mechanical seals because of its:
Extrême dureté → Wear resistance against friction and abrasive fluids.
Haute résistance à la compression → Ability to handle heavy pressure loads.
Stabilité thermique → Reliability at high operating temperatures.
Résistance à la corrosion → Strong protection in oil, gas, seawater, and chemicals.
Durabilité → Long service life, reducing replacements.
What Are Ceramic Seal Rings?

Ceramic seal rings are made from materials such as alumina or silicon carbide. They are known for:
Fort résistance à la corrosion → Excellent performance in chemical-rich environments.
Lightweight → Inférieur densité compared to metals.
Thermal resistance → Stability in hot applications.
Low cost → Generally cheaper than tungsten carbide.
However, ceramics are more brittle, making them less tolerant to impact or vibration.
Points forts des joints d'étanchéité en carbure de tungstène
Supérieur dureté – Less brittle, can survive shock and vibration.
Longer service life – Especially in abrasive or high-pressure applications.
Mieux résistance à l'usure – Ideal for slurry pumps and oilfield equipment.
Recyclability – Tungsten carbide can be collected and reused.
Weaknesses of Tungsten Carbide Seal Rings
Heavier material – Higher densité ajoute du poids à l'équipement.
Higher upfront cost – More expensive than ceramic alternatives.
Cobalt-bonded grades – Less corrosion resistant in seawater compared to ceramics.
Strengths of Ceramic Seal Rings

Excellent chemical resistance – Strong performance against acids and alkalis.
Lightweight design – Useful in systems where weight matters.
Lower cost – Cheaper initial investment than tungsten carbide.
Non-metallic material – Good for electrically sensitive applications.
Weaknesses of Ceramic Seal Rings
Brittle nature – More likely to crack under mechanical shock or vibration.
Inférieur dureté – Cannot handle sudden pressure spikes as well.
Shorter life in abrasive fluids – Wears faster in slurry or sand-filled environments.
Comparaison côte à côte
| Fonctionnalité | Bagues d'étanchéité en carbure de tungstène | Ceramic Seal Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Résistance à l'usure | Excellent, handles abrasives well | Moderate, weaker in slurry |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Good, nickel-bonded grades excel | Excellent, especially in acids |
| Dureté | High, resists shock and vibration | Low, brittle under impact |
| Durée de vie | Long-lasting in harsh conditions | Shorter in abrasive systems |
| Coût | Higher upfront investment | Coût initial inférieur |
| Recyclabilité | Yes, can be recycled | Limited recyclability |
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Seal Rings
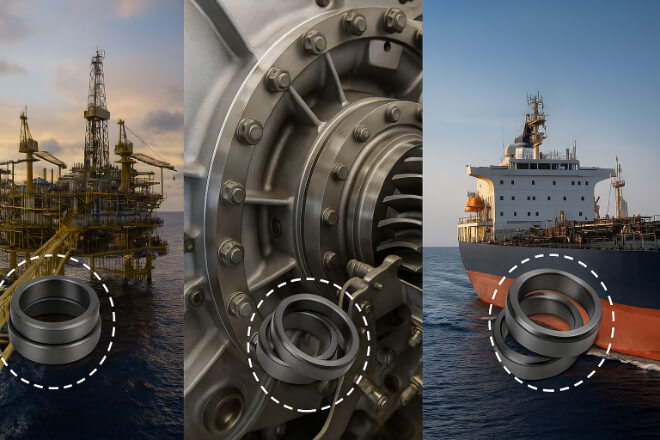

Pétrole et gaz pompes → Withstand pressure, abrasives, and hydrocarbons.
Power generation turbines → Handle heat and stress cycles.
Marine propulsion systems → Resist vibration and seawater.
Chemical plants → Work well in aggressive fluids with the right binder.
Applications of Ceramic Seal Rings
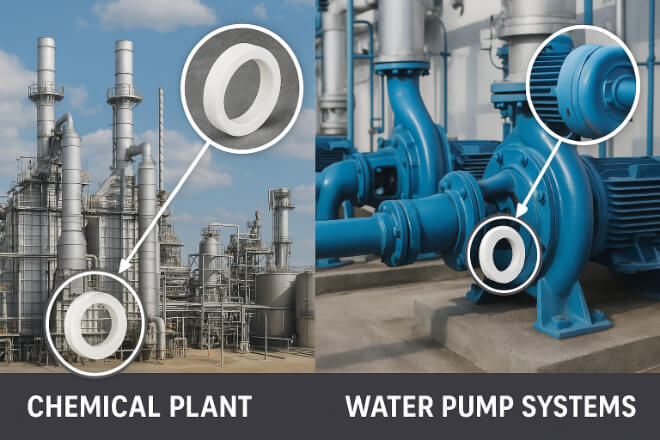
Chemical processing → Resist acids and alkalis.
Water pumps → Cost-effective in less abrasive conditions.
Electronics industry → Suitable for non-metallic sealing applications.
Light-duty marine systems → Work in seawater with low vibration.
Coût vs valeur à long terme
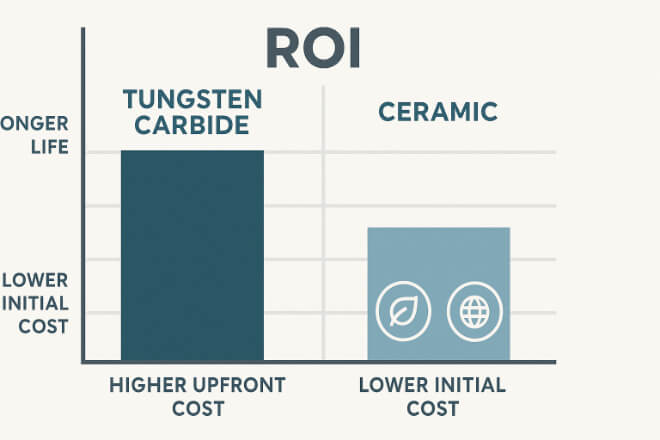
Carbure de tungstène → Higher purchase cost but longer life and fewer replacements → better ROI.
Céramique → Lower purchase cost but shorter life in abrasive or shock-heavy systems → higher maintenance costs.
For decision-makers, the choice often depends on long-term cost savings, not just upfront price.
Points clés à retenir pour les décideurs

Tungsten carbide seal rings are best for abrasive, high-pressure, and high-shock environments.
Ceramic seal rings are best for chemical-rich, lower-shock, and cost-sensitive environments.
The choice depends on operating conditions, fluids handled, and budget priorities.
In many cases, tungsten carbide offers lower life cycle cost, even with higher upfront pricing.
Conclusion
Both tungsten carbide and ceramic seal rings play important roles in industrial sealing systems.
Tungsten carbide provides strength, wear resistance, and durability in tough environments, while ceramics offer excellent chemical resistance and cost benefits.
For decision-makers, the right choice depends on the specific operating conditions.
In abrasive, high-pressure systems, tungsten carbide is usually the better option. In chemical environments with low shock, ceramic seals may be sufficient.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
