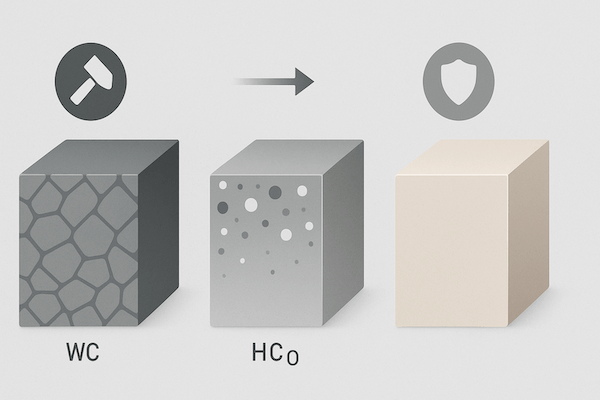
Les outils en carbure de tungstène sont appréciés pour leur extrême dureté, leur grande résistance à l'usure et leur longue durée de vie. Mais comment ces propriétés sont-elles possibles ? La réponse réside dans leur composition en carbure. Ce terme désigne la combinaison spécifique de matériaux utilisés pour la fabrication de l'outil, qui influence directement ses performances mécaniques, chimiques et thermiques.
Cet article explique ce qu'est la composition du carbure, pourquoi elle est importante et comment différents éléments affectent le comportement des outils en carbure cémenté.
Quelle est la composition du carbure ?
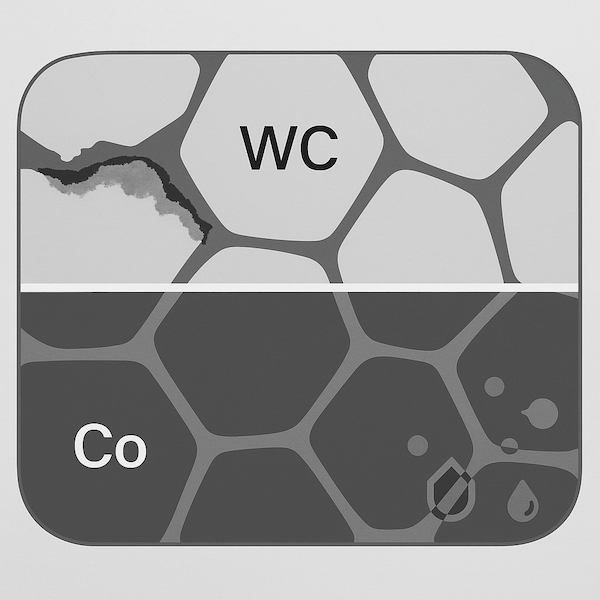
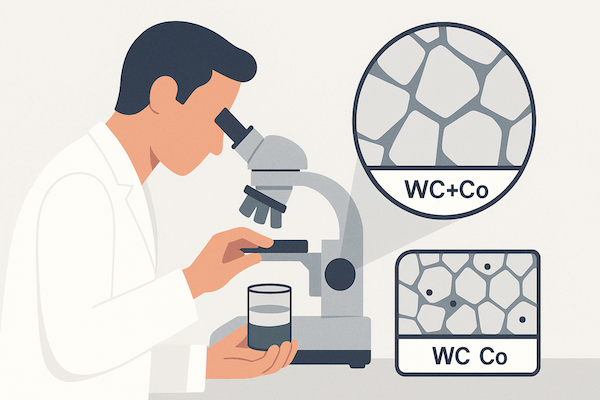
La composition du carbure décrit le rapport et les types de matériaux présents dans un produit en carbure cémentéCes outils ne sont pas fabriqués uniquement à partir de carbure de tungstène pur (WC) ; il s'agit plutôt de composites, fabriqués en mélangeant :
Grains de WC (carbure de tungstène) – la phase dure primaire
liant métallique, généralement du cobalt (Co) ou du nickel (Ni) – qui maintient les grains de WC ensemble
Éléments d'alliage, tels que le vanadium (V), le chrome (Cr), le tantale (Ta) – pour modifier la microstructure et les performances
Les proportions exactes de ces matériaux sont soigneusement conçues pour répondre aux exigences des différents coupe, de formage et d'applications résistantes à l'usure.
Répartition typique de la composition
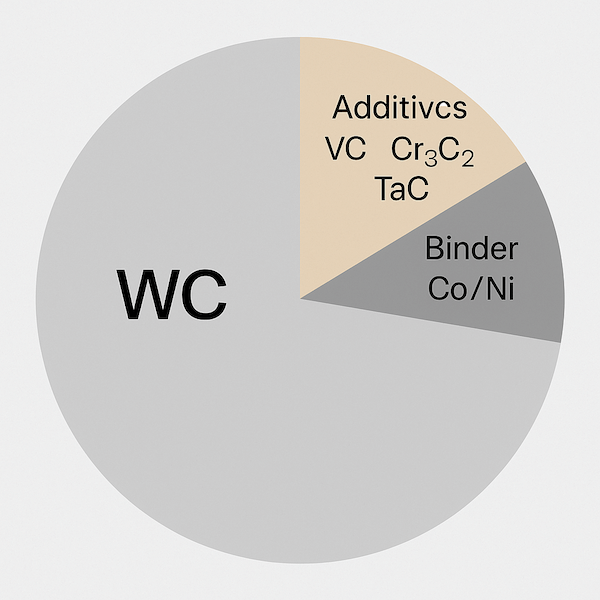
| Composant | Fonction | Contenu typique (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| WC (carbure de tungstène) | Fournit dureté et résistance à l'usure | 70–97% |
| Co ou Ni (liant) | Fournit dureté et maintient les grains ensemble | 3–30% |
| VC, Cr₃C₂, TaC (Additifs) | Contrôle granulométrie, améliorer corrosion/résistance à l'oxydation | 0,1–3% |
Comment la composition affecte les performances des outils
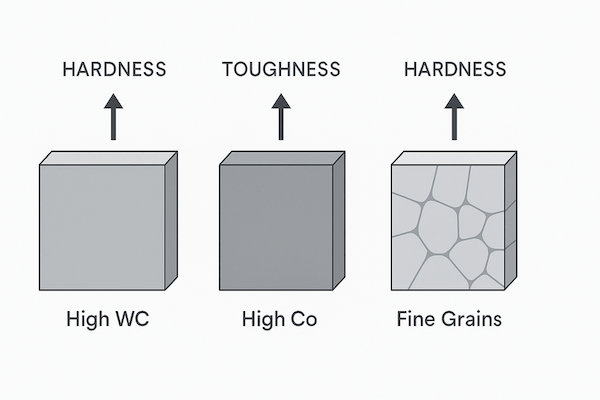
Différentes compositions de carbure donnent des caractéristiques d'outil différentes. Par exemple :
Teneur en WC plus élevée → Dureté et résistance à l'usure supérieures, mais ténacité plus faible
Plus de liant (Co/Ni) → Ténacité accrue, mais dureté réduite
Grains WC plus fins (contrôlés par des additifs) → Stabilité des bords et finition de surface supérieures
Additifs Cr ou Mo → Améliorent la stabilité chimique et empêchent la lixiviation du liant dans les environnements humides ou corrosifs
Chaque application, qu'il s'agisse de découpe d'acier à grande vitesse, de forage pétrolier ou d'usinage de précision, nécessite une composition soigneusement adaptée pour équilibrer la dureté, la ténacité et résistance chimique.
Exemples de composition pour diverses applications

| Application | Focus sur la composition |
|---|---|
| Plaquettes de coupe en métal | Inhibiteurs de grains WC submicroniques, ~6–10% Co |
| Outils miniers | WC grossier, 10–15% Co, haute résistance aux chocs |
| Outils de travail du bois | WC fin, 6–10% Co, résistance à l'usure des bords |
| Médical/Utilisation corrosive | WC avec liant Ni, alliage Cr/Mo pour la stabilité |
Pourquoi le contrôle de la composition est important
Un contrôle précis de la composition du carbure garantit :
Propriétés mécaniques constantes
Durée de vie et performances prévisibles de l'outil
Personnalisation pour différentes industries
Résistance à la fissuration thermique, à l'érosion et à la corrosion
Sans un contrôle de composition approprié, les outils peuvent tomber en panne prématurément ou ne pas être performants dans les tâches critiques.
Conclusion
La composition du carbure est essentielle à la performance de tout outil en carbure de tungstène. Elle détermine sa dureté, sa ténacité, sa stabilité chimique et sa résistance à l'usure. Des trépans miniers robustes aux micro-fraises délicates, comprendre et optimiser la composition du carbure est essentiel pour garantir la fiabilité, l'efficacité et la longévité de l'outil.
Que vous soyez fabricant, ingénieur ou acheteur, connaître le fonctionnement de la composition du carbure vous donne le pouvoir de choisir le bon outil pour le bon travail.
