Tungsten carbide is renowned for its dureté et résistance à l'usure, making it a top choice for cutting tools in various industries.
However, its dureté is just as critical, especially in applications involving high impacts and extreme conditions.
Understanding how tungsten carbide compares to other hard metals, such as steel and ceramics, is essential for choosing the right materials for specific tasks.
In this blog, we’ll explore the toughness of tungsten carbide tips and how they compare to other hard metals, helping industrial decision-makers select the best material for their needs.
What is Toughness in Materials?
Toughness refers to a material’s ability to absorb energy and withstand breaking or cracking under stress or impact. It combines both strength and ductility (the ability to deform without breaking).
For cutting tools, dureté is crucial because tools are often subjected to forces such as bending, impact, and abrasion during operation.
A material with high toughness can absorb these forces without failing, leading to a longer tool life.
In comparison to dureté (which is a material’s ability to resist scratching or indentation), toughness is more about a material’s ability to handle shock and impact without breaking.
For cutting tools like tungsten carbide tips, balancing toughness with hardness is key to ensuring durability in demanding applications.
Toughness of Tungsten Carbide Tips

Tungsten carbide tips are among the hardest materials available, but they are also known for their impressive toughness.
This toughness is primarily due to the material’s microstructure, which consists of tungsten carbide grains bonded together by a metallic binder (usually cobalt).
Tungsten carbide’s dureté:
Despite its extreme dureté, tungsten carbide’s toughness can be influenced by the binder material.
Cobalt, for example, adds some ductility to the material, allowing it to absorb impacts better than pure tungsten carbide would.
This combination of hardness and toughness makes tungsten carbide ideal for cutting tools that need to withstand both abrasion and impact.
While tungsten carbide tips are not as tough as some metals like steel in terms of impact resistance, they are generally superior to other hard metals like ceramics in terms of toughness-to-hardness ratio.
This makes tungsten carbide an excellent choice for high-performance cutting tools in applications where both résistance à l'usure and toughness are required.
Comparing Tungsten Carbide to Other Hard Metals

When evaluating materials for cutting tools, it’s important to compare the toughness of tungsten carbide with other hard metals.
Steel and ceramics are often considered alternatives to tungsten carbide, and each material has its strengths and weaknesses.
1). Tungsten Carbide vs Steel:
Steel is often used in cutting tools due to its dureté and ability to resist impact.
While steel is less hard than tungsten carbide, it offers superior toughness, which makes it ideal for applications that involve heavy impact or shock loading.
Steel tools are more flexible and less prone to cracking under extreme conditions.
Tungsten carbide, on the other hand, is much harder and more wear-resistant, making it better suited for precision cutting and machining tasks.
However, it is more brittle than steel and can fracture under excessive impact.
Therefore, while tungsten carbide tips are ideal for cutting through tough materials, steel tips may be a better option for high-impact applications.
2). Tungsten Carbide vs Ceramics:
Ceramics are harder than tungsten carbide but are typically more brittle.
Ceramic tips can provide exceptional résistance à l'usure, but they lack the toughness required to withstand high-impact forces.
In situations where shock and impact resistance are critical, ceramic tools can easily fracture, making them unsuitable for many industrial applications.
Tungsten carbide, with its combination of hardness and toughness, outperforms ceramics in environments where the material is exposed to both wear and impact.
3). Tungsten Carbide vs High-Speed Steel (HSS):
High-speed steel (HSS) is another common material used for cutting tools.
HSS offers good toughness, especially when compared to carbide, but its hardness and wear resistance are much lower.
In comparison, tungsten carbide tips last much longer and retain their sharpness better under high-friction conditions.
However, HSS tools are more cost-effective and can be a good choice for applications that don’t involve extreme wear or high impact.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Tips

The unique balance of hardness and dureté in tungsten carbide tips makes them ideal for a variety of demanding applications, including:
Outils de coupe:
Tungsten carbide tips are commonly used in drills, milling cutters, and turning tools.
Their excellent résistance à l'usure makes them perfect for high-precision cutting tasks.
Exploitation minière and drilling:
Tungsten carbide tips are widely used in mining and oil drilling tools, where they encounter abrasive materials and high impact forces.
The toughness of tungsten carbide allows these tools to maintain performance under harsh conditions.
In the aerospace and automotive industries, tungsten carbide tips are used for machining components made of tough metals and alloys.
The material’s combination of hardness and toughness ensures a longer tool life in these industries, where precision and durability are critical.
How Toughness Affects Tool Longevity
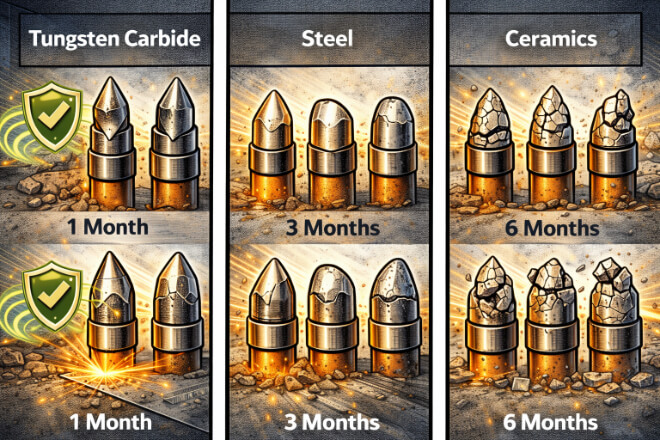

The toughness of a cutting tool plays a significant role in its overall longevity.
In industries where tools are subject to constant wear, shock, or extreme conditions, having a tough material ensures that the tool will last longer and perform better over time.
Increased tool life:
Tools made from tough materials, such as tungsten carbide, can withstand a greater number of cycles before showing signs of wear or damage.
This reduces the need for frequent tool replacements, saving both time and money.
Temps d'arrêt réduits:
Le dureté of tungsten carbide tools reduces the likelihood of breakage or failure during operation, minimizing downtime in manufacturing and machining processes.
This results in increased productivity and fewer interruptions to work.
Balancing Toughness and Hardness for Optimal Performance

While both toughness and hardness are important in cutting tools, the key is finding the right balance for the specific application.
Tungsten carbide offers an optimal combination of both, but in some cases, other materials may be more suitable for particular tasks.
For high-precision, résistant à l'usure applications: Tungsten carbide is the best choice due to its hardness and ability to maintain sharpness over time.
For applications involving high-impact forces: Steel may be the better option due to its superior toughness, even though it may sacrifice some wear resistance.
For general-purpose cutting: High-speed steel (HSS) offers a balance of toughness and cost-effectiveness for less demanding tasks.
Conclusion
Tungsten carbide tips offer a unique combination of hardness and toughness, making them an excellent choice for high-performance cutting tools.
While materials like steel and ceramics may be better suited for specific applications, tungsten carbide remains the best option for tasks that require both wear resistance and toughness.
Understanding the toughness of tungsten carbide and how it compares to other hard metals is essential for selecting the right material for any industrial application.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur une entreprise, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nous.
