Qu'est-ce que la résistance à l'usure ?
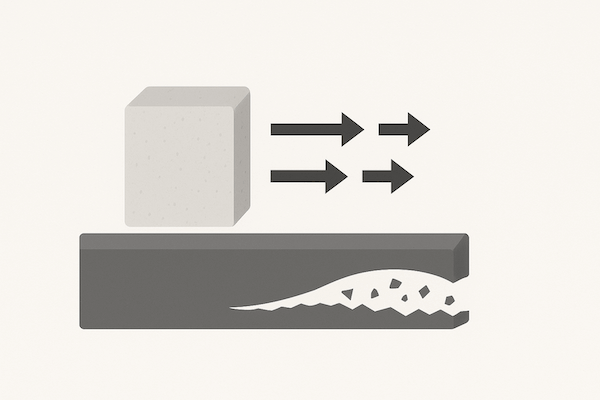
La résistance à l'usure désigne la capacité d'un matériau à résister aux dommages superficiels progressifs causés par le frottement, l'abrasion, l'érosion ou le contact mécanique avec d'autres matériaux. Il s'agit d'une propriété essentielle pour les matériaux utilisés dans des environnements à frottement élevé ou à fortes contraintes, car elle affecte directement la durée de vie et les performances des composants.
Les matériaux à haute résistance à l'usure conservent leur forme, leur intégrité de surface et leurs dimensions même après une utilisation prolongée ou un contact répété avec des surfaces plus dures ou plus rugueuses.
Pourquoi la résistance à l’usure est-elle importante ?
Dans les environnements industriels, de nombreux composants et outils sont soumis à des mouvements, des coupes, des meulages ou des chocs continus. Sans une résistance à l'usure adéquate, les surfaces se dégradent rapidement, entraînant :
Perte de précision
Augmentation des temps d'arrêt
Remplacement fréquent des outils
Des coûts de maintenance plus élevés
Les matériaux résistants à l’usure aident à minimiser cette dégradation, prolongeant la durée de vie des outils et des équipements et améliorant la productivité et les performances globales.
Carbure de tungstène : une référence en matière de résistance à l'usure
Le carbure de tungstène (WC), notamment lorsqu'il est cémenté avec des liants au cobalt ou au nickel, est réputé pour sa résistance exceptionnelle à l'usure. Ceci est dû à :
La dureté extrême des particules de WC (généralement supérieure à 1600 HV)
Une microstructure dense et à grains fins
La phase liante métallique résistante qui aide à absorber le stress et à lier les grains
En raison de ces caractéristiques, le carbure de tungstène est largement utilisé dans outils de coupe, matrices, poinçons, pièces de soupape, plaques d'usure, et composants miniers, où la résistance à l'usure est essentielle.
Types d'usure du carbure de tungstène
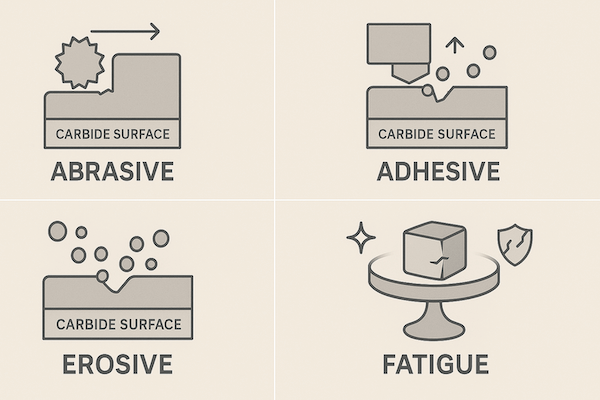
Les outils en carbure de tungstène sont conçus pour résister à plusieurs formes d'usure :
1. Usure par abrasion
Causé par des particules dures ou des surfaces rugueuses glissant sur l'outil (par exemple, lors du perçage ou du meulage).
2. Usure adhésive
Se produit lorsque du matériau est transféré entre des surfaces de contact (par exemple, lors de la découpe ou de l'emboutissage de métaux).
3. Usure érosive
Causé par l'impact d'un fluide ou d'une particule (par exemple, dans une boue) vannes, buses).
4. Usure par fatigue
Se développe à travers des cycles de contraintes répétés conduisant à des microfissures (par exemple, dans les matrices et les outils de formage).
Facteurs influençant la résistance à l'usure du carbure
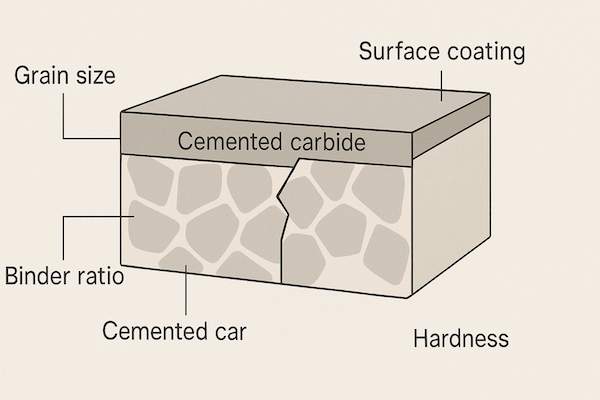
Plusieurs variables affectent la résistance à l’usure du carbure cémenté :
▸ WC Taille des grains
Les structures à grains fins améliorent la dureté et la résistance à l'usure, en particulier dans les applications de coupe.
▸ Contenu du classeur et Composition
Une teneur en liant plus faible augmente la dureté et la résistance à l'usure, mais réduit duretéLe cobalt est couramment utilisé en raison de sa force et propriétés de liaison.
▸ Dureté (HRA)
Il existe une corrélation directe entre la dureté et la résistance à l’usure : des valeurs HRA plus élevées conduisent souvent à de meilleures performances d’usure.
▸ Revêtements
Les revêtements avancés tels que TiAlN, DLC ou CVD diamant améliorent la dureté de la surface et réduisent la friction, améliorant ainsi considérablement la durée de vie.
Applications nécessitant une résistance élevée à l'usure
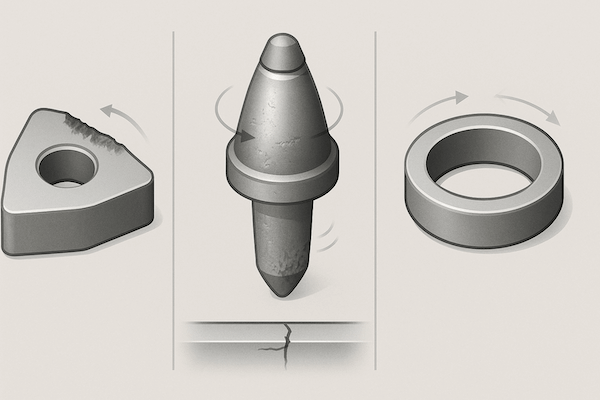
Résistant à l'usure outils en carbure de tungstène sont essentiels dans des secteurs tels que :
Travail des métaux – plaquettes de coupe, fraises en bout, exercices
Exploitation minière et tunneling – pics, boutons, plaques d'usure
Pétrole et gaz – sièges de soupapes, composants de contrôle de flux
Papier et textile – couteaux à refendre, lames de cisaillement
Mouler et mourir – poinçons, matrices de formage, broches d'éjection
Dans toutes ces applications, la défaillance des outils due à l’usure peut entraîner des interruptions coûteuses, ce qui fait de la résistance à l’usure un critère de sélection clé.
Test et mesure de la résistance à l'usure
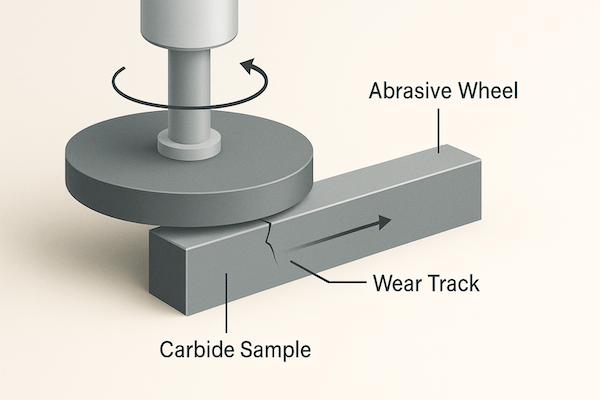
La résistance à l'usure est généralement évaluée par :
Tests de broches sur disque
Essais d'usure par glissement à sec
Essais de meules abrasives
Analyse des performances sur le terrain
Ces méthodes simulent des conditions d’usure réelles et fournissent des comparaisons quantifiables entre différentes nuances de carbure.
Conclusion
La résistance à l'usure est l'un des critères de performance les plus importants pour les outils en carbure de tungstène, notamment dans les environnements industriels exigeants. Grâce à sa combinaison unique de dureté, densitéGrâce à son support liant, le carbure cémenté offre une résistance exceptionnelle à la dégradation de surface. Les ingénieurs et les fabricants doivent sélectionner avec soin la nuance, le liant, la granulométrie et le revêtement adaptés aux exigences d'usure de chaque application, garantissant ainsi des performances supérieures et une fiabilité durable.
