Carbide-tipped blades are widely used in industries that demand high cutting performance, such as metalworking, woodworking, and construction.
The efficiency and lifespan of these blades depend heavily on the geometry of the blade tips.
Tip geometry, which refers to the shape and angle of the carbide tips, plays a crucial role in determining cutting efficiency, wear resistance, and tool life.
In this blog, we will explore how different tip geometries affect the performance of carbide-tipped blades and why choosing the right geometry is essential for optimizing tool life and cutting efficiency.
1. What Is Tip Geometry in Carbide-Tipped Blades?
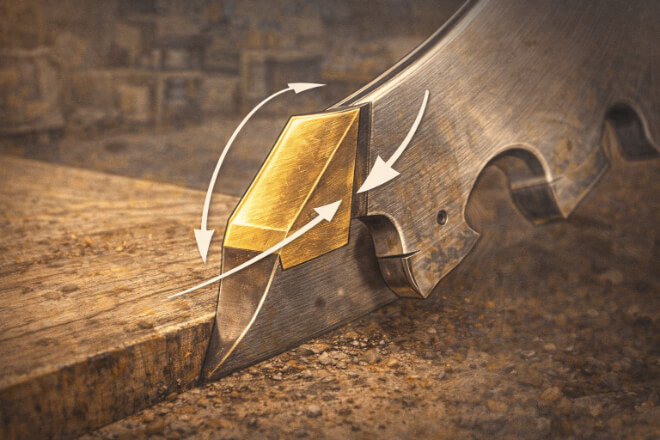

Tip geometry refers to the shape, angle, and design of the cutting edge of a carbide-tipped blade.
These factors influence how the blade interacts with the material being cut, including how much force is required, how clean the cut is, and how quickly the blade wears down.
The key elements of tip geometry include:
Cutting Angle: The angle of the tip relative to the material being cut.
Tip Shape: The overall form of the cutting edge, which can vary from flat to beveled or rounded.
Rake Angle: The angle at which the cutting edge meets the material, affecting how the material is removed.
The right geometry helps ensure that the blade cuts efficiently, lasts longer, and requires less maintenance.
2. How Tip Geometry Affects Cutting Efficiency
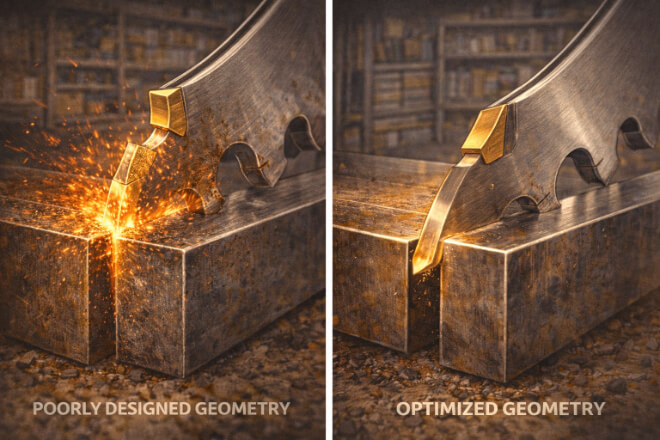
Cutting efficiency refers to how quickly and easily a blade can cut through a material.
Proper tip geometry can significantly improve efficiency by reducing friction, minimizing heat buildup, and optimizing material removal.
Impact of Tip Geometry on Cutting Efficiency:
Lower Cutting Forces:
A well-designed tip geometry reduces the cutting forces required, allowing for faster and smoother cuts.
A sharper cutting edge and an optimized rake angle help reduce resistance during the cutting process.
Reduced Heat Generation:
The geometry of the blade helps manage heat buildup, which can otherwise cause the tool to wear prematurely.
A suitable tip angle helps in better heat distribution, preventing overheating during prolonged cutting operations.
Cleaner Cuts:
The right tip shape can lead to cleaner cuts with less material deformation.
For example, blades with a fine point or sharper edge can create more precise cuts, reducing the need for post-processing.
Optimizing tip geometry results in faster cutting speeds, higher productivity, and cleaner finished products.
3. How Tip Geometry Affects Tool Life
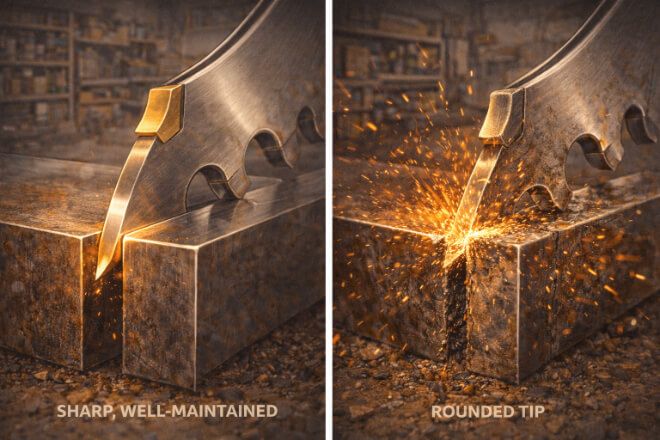

Tool life refers to how long a cutting tool can perform effectively before it needs to be replaced or sharpened.
The geometry of the tip influences the blade’s wear resistance and how quickly the carbide material degrades under continuous use.
How Tip Geometry Impacts Tool Life:
Carbide-tipped blades with properly shaped tips experience less wear due to their optimized geometry.
For example, a flat or slightly beveled tip may wear more evenly and last longer than a tip that is too sharp or poorly angled.
Reduced Tip Chipping:
A well-designed tip geometry reduces the risk of chipping or breaking, especially when cutting hard or abrasive materials.
A proper rake angle ensures that the cutting force is evenly distributed across the blade tip, reducing stress on the edges.
Even Wear Distribution:
Tip geometry also affects how wear is distributed along the blade.
A balanced geometry ensures that the blade wears evenly, which extends its useful life and improves performance over time.
By choosing the right tip geometry, manufacturers can extend the life of their carbide-tipped blades and reduce the frequency of tool replacements, leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
4. Choosing the Right Tip Geometry for Different Materials
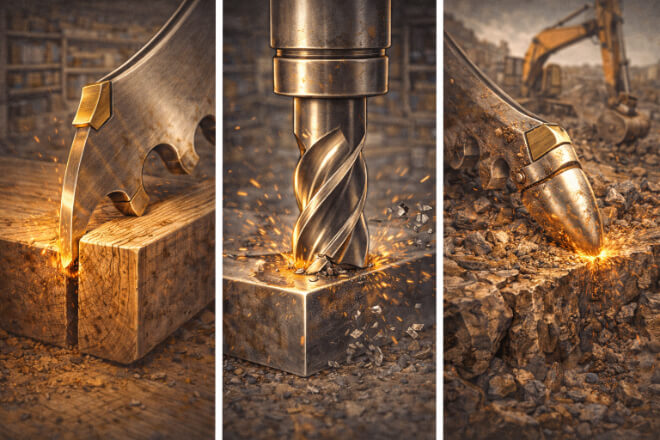

Not all materials are the same, and different materials require different cutting forces and tool geometries.
The material’s hardness, density, and abrasiveness determine the ideal tip geometry for cutting.
Selecting Tip Geometry for Various Applications:
Woodworking: For cutting softwoods, a sharper tip with a moderate rake angle is ideal for clean cuts. The cutting edge should be fine enough to slice through the material without excessive force.
Metalworking: In metalworking, particularly when cutting harder metals like steel, a robust tip geometry with a slightly more rounded edge may be necessary to handle the increased cutting forces and heat.
Stone or Concrete Cutting: For cutting abrasive materials like stone or concrete, a stronger, tougher tip geometry with more substantial angles and thicker edges helps the blade handle impact and wear.
Choosing the right geometry for the material being cut ensures that the blade performs efficiently and has a longer tool life.
5. Rake Angle: The Key to Optimizing Cutting Forces
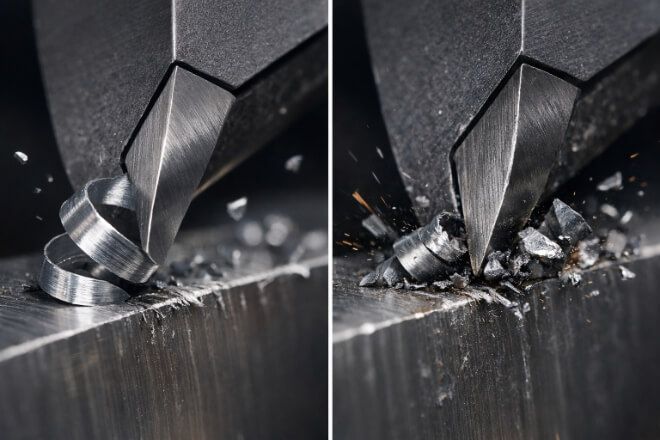

The rake angle, which is the angle at which the cutting edge meets the material, plays a major role in determining cutting forces and tool life.
A proper rake angle reduces friction, heat, and cutting forces, enhancing both cutting efficiency and tool durability.
Rake Angle and Its Effect on Performance:
Positive Rake Angle:
A positive rake angle reduces cutting forces and friction, making it ideal for softer materials like wood and some metals.
It allows the material to be sliced off easily with minimal resistance.
Negative Rake Angle:
A negative rake angle is used for tougher materials that require more cutting force, such as hard metals.
This geometry ensures the tip doesn’t dig too deeply into the material, reducing stress on the cutting edge and preventing premature wear.
By adjusting the rake angle to match the material, cutting forces are minimized, improving both efficiency and tool life.
6. Advanced Tip Geometries for Specialized Cutting Applications
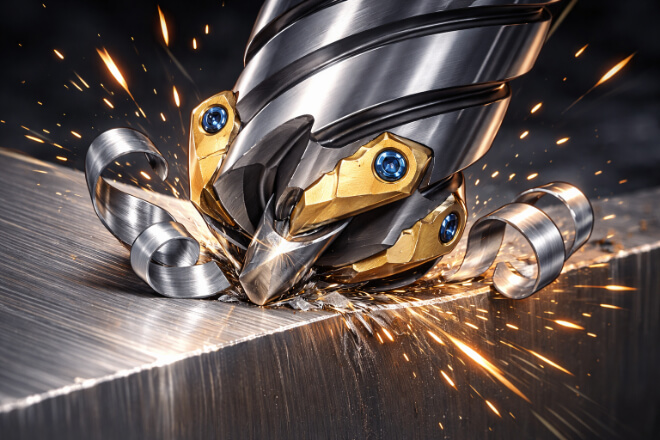

For some specialized applications, such as high-speed machining or precision cutting, advanced tip geometries may be required.
These geometries are designed to provide the best possible balance between cutting efficiency, precision, and durability.
Advanced Geometries Include:
Tungsten Carbide Inserts: Small, replaceable tungsten carbide tips that are welded onto tool bodies, allowing for easy replacement and extended tool life.
Complex Curved Geometries: Used in tools for precision cutting, these geometries ensure smooth, clean cuts with minimal material deformation.
Multi-Tipped Carbide Tools: These tools have multiple carbide tips on the same tool body, providing more cutting edges for faster operations and longer tool life.
These advanced geometries ensure that the tool performs optimally in specialized conditions while maintaining efficiency and durability.
7. Cost Benefits of Optimizing Tip Geometry

Investing in the right tip geometry may involve higher upfront costs, but it can lead to significant long-term savings.
Optimizing tip geometry results in longer tool life, higher cutting speeds, and improved cutting quality, which ultimately reduces the frequency of tool replacements and maintenance costs.
Cost Benefits Include:
Longer Tool Life: Proper tip geometry reduces wear and tear, leading to fewer tool replacements and repairs.
Improved Productivity: Higher cutting speeds and cleaner cuts increase overall production efficiency, reducing operational costs.
Reduced Maintenance: With optimal geometry, carbide-tipped blades require less frequent maintenance, leading to lower labor and downtime costs.
In the long run, selecting the right tip geometry ensures better value and improved return on investment for businesses.
Conclusion
Tip geometry plays a critical role in determining the cutting efficiency and tool life of carbide-tipped blades. Whether you’re cutting through softwoods, metals.
Or hard materials like stone, the right geometry ensures that your tools perform efficiently, last longer, and require less maintenance.
By understanding the impact of rake angles, cutting edge shapes, and other geometry factors, manufacturers can make informed decisions about which carbide tips to use for specific applications.
Ultimately, optimizing tip geometry leads to improved performance, reduced costs, and increased productivity in the long run.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
