The Effect of Temperature on Tungsten Carbide Tips: High-Temperature Performance

Tungsten carbide tips are widely recognized for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them crucial for high-performance industrial applications. However, their performance can be significantly impacted by temperature. In this blog, we will explore how temperature affects tungsten carbide tips. Especially in high-temperature environments, and how industries can optimize their use in such conditions. The Basics of Tungsten Carbide’s Heat Resistance Tungsten carbide is a composite material made from tungsten and carbon. It is widely used in industries that require high-performance materials due to its extreme hardness, wear resistance, and durability. However, tungsten carbide’s performance can be influenced by temperature. At high temperatures, the material can undergo changes that […]
Tungsten Carbide Tips: Cobalt vs Nickel Binders – Which is Better?

Tungsten carbide tips are widely used in industries such as drilling, mining, and machining, thanks to their remarkable hardness and wear resistance. However, the performance of tungsten carbide tips depends not only on the carbide itself but also on the binder material used in its composition. Cobalt and nickel are the two most commonly used binders, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. In this blog, we will explore the differences between cobalt and nickel binders in tungsten carbide tips, helping industrial decision-makers understand which binder is best suited for their specific applications. What Are Tungsten Carbide Binders? Before diving into the comparison, it’s important to understand the role of binders […]
Understanding the Microstructure of Tungsten Carbide Tips

Tungsten carbide tips are essential in many industrial applications, from drilling and cutting to mining and construction. What makes these tips so effective is their microstructure—the arrangement of particles and phases that give the material its unique properties. Understanding the microstructure of tungsten carbide is crucial for optimizing its performance in tough environments. This blog will explore the different components of tungsten carbide’s microstructure and how they influence its properties, particularly its hardness, wear resistance, and overall durability. What is Tungsten Carbide? Tungsten carbide is a compound made from tungsten and carbon. It is known for its exceptional hardness and ability to withstand wear and high temperatures. Tungsten carbide is […]
Tungsten Carbide Tips: The Secret to Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
Tungsten carbide tips are widely known for their exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making them indispensable in various industries, especially in cutting and drilling tools. These tips are designed to perform in the most demanding environments, offering longer tool life and better performance compared to conventional materials. In this blog, we will explore why tungsten carbide tips are considered the secret to superior hardness and wear resistance, highlighting their key advantages and applications. The Role of Tungsten Carbide in Industrial Tools Tungsten carbide, a composite material made from tungsten and carbon, is renowned for its superior hardness. It is one of the hardest materials known, second only to diamond. […]
The Impact of Binder Content on Tungsten Carbide Tips’ Durability
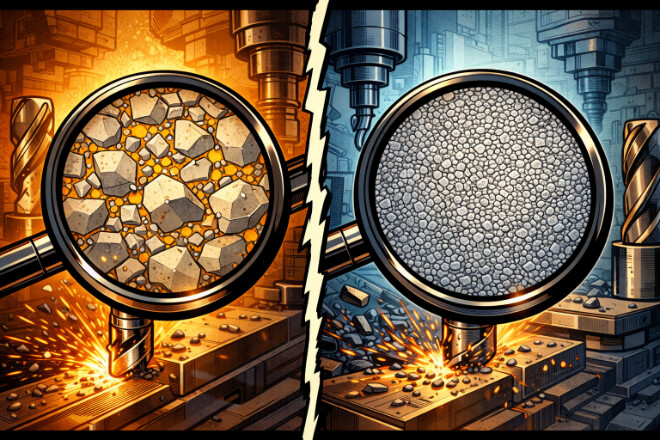
Tungsten carbide tips are known for high hardness and long service life. However, durability does not depend on carbide grains alone. Binder content plays a key role in how strong, tough, and reliable a tungsten carbide tip will be. For decision-makers choosing cutting or wear tools, understanding binder content helps avoid early failure and unnecessary cost. This article explains binder content in simple terms and shows how it affects durability in real applications. What is Binder Content in Tungsten Carbide Tips? Binder content refers to the amount of metal matrix material (such as cobalt or nickel) that is added to the tungsten carbide grains during the manufacturing process. Tungsten carbide, […]
