In many industries, from 採掘 に 航空宇宙, high-stress conditions are part of daily operations. Equipment faces extreme pressure, heat, and wear.
To keep production reliable, decision-makers need materials that can handle these challenges.
Tungsten carbide balls have become a go-to solution because of their 硬度, 耐摩耗性, and ability to perform where steel or ceramics fail.
But using them correctly is just as important as choosing them. This article explains best practices for applying tungsten carbide balls in demanding environments.
By following these guidelines, companies can maximize performance, lower costs, and improve equipment life.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide Balls
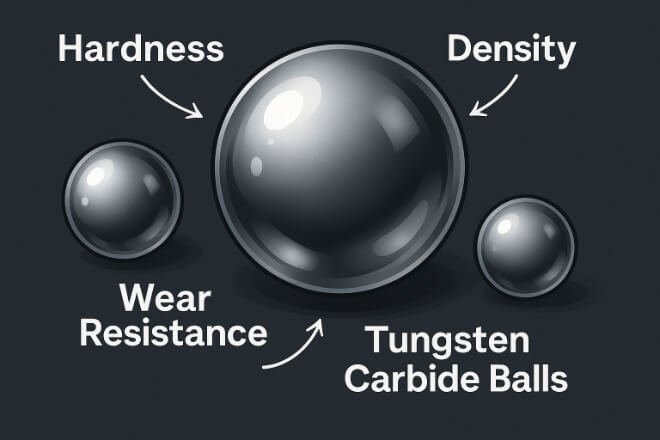
Tungsten carbide is a composite material, made by combining tungsten powder with a metallic binder like cobalt or nickel. The result is a ball that is:
Harder than steel, close to diamond on the Mohs scale.
Very dense, almost twice as heavy as steel.
Highly 耐摩耗性, even under abrasive conditions.
Stable at high temperatures, keeping performance in extreme heat.
These properties explain why tungsten carbide balls are widely used in grinding, milling, バルブ, pumps, and bearings where durability is critical.
Best Practice 1: Select the Right Grade
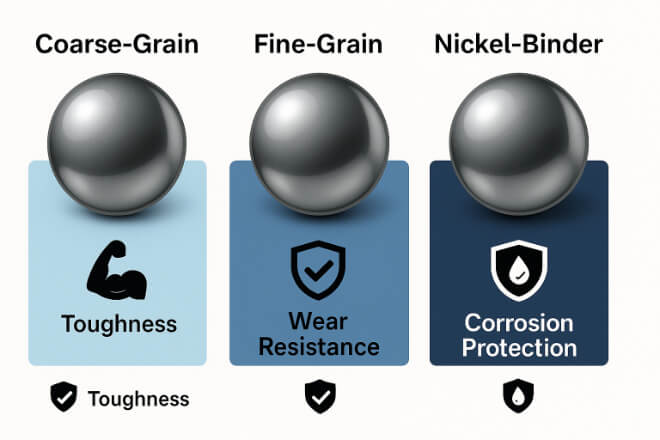
Not all tungsten carbide is the same. The grade depends on the binder type, binder percentage, and grain size.
Coarse-grain carbide works best for impact and shock resistance.
Fine-grain carbide is better for high 耐摩耗性 and precision.
Nickel-binder grades provide higher corrosion resistance compared to cobalt-binder grades.
Decision-makers should match the grade to their specific operating environment.
For example, in corrosive chemical applications, nickel-binder grades are safer, while in mining, cobalt-binder grades are often preferred for toughness.
Best Practice 2: Optimize Operating Conditions
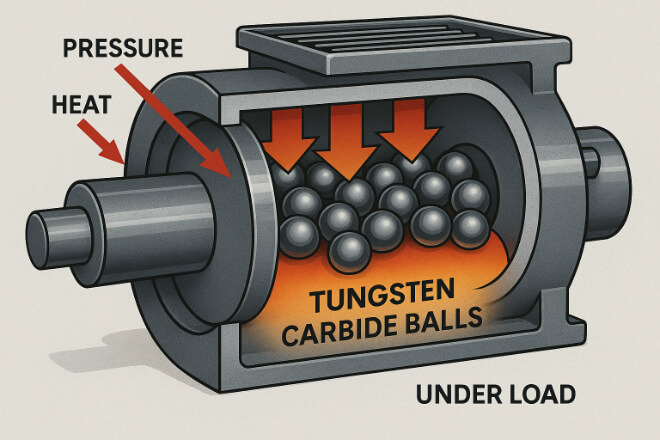
Even the strongest material will fail if misused. To get the most from tungsten carbide balls:
Keep operating temperatures within safe ranges to avoid binder weakening.
Use the correct load and pressure—too much stress may cause cracking.
Avoid sudden shocks where possible, as repeated impact can shorten lifespan.
Monitoring stress levels helps predict when maintenance or replacement will be needed.
Best Practice 3: Ensure Proper Lubrication
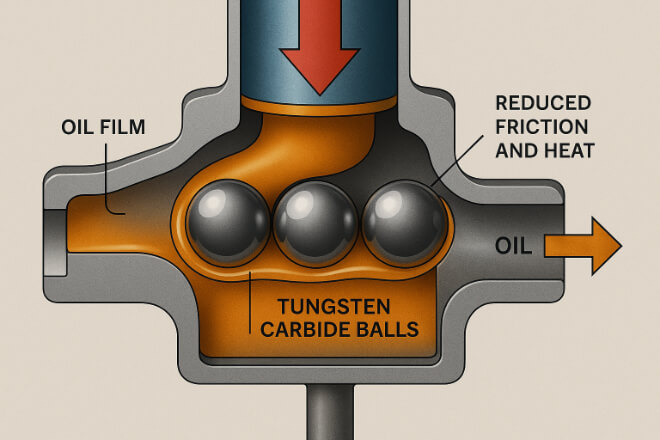
Lubrication reduces friction, prevents overheating, and minimizes wear.
In high-stress applications like pumps and valves, a lack of lubrication can quickly damage carbide balls.
Use lubricants that:
Match the working environment (oil, grease, or dry-film).
Can handle high pressure and heat.
Provide corrosion protection when chemicals are present.
Good lubrication extends service life and keeps equipment stable under extreme stress.
Best Practice 4: Regular Inspection and Maintenance

Routine checks help detect small problems before they grow. Inspections should look for:
Surface wear or pitting.
Cracks or micro-fractures.
Signs of corrosion around the binder.
If issues are found, replace or recondition the balls before they fail completely. This prevents downtime and expensive repairs.
Best Practice 5: Avoid Contamination
Foreign particles can scratch surfaces or create micro-cracks in carbide balls. To prevent this:
Keep equipment and work areas clean.
Use seals and filters in pumps and valves.
Store spare balls in dry, dust-free containers.
Contamination control is a simple but powerful way to protect tungsten carbide performance.
Best Practice 6: Partner with Reliable Suppliers

The best results start with quality manufacturing. Choose suppliers who:
Provide certified tungsten carbide grades.
Offer traceability reports for raw materials.
Have experience customizing balls for unique applications.
Low-cost, low-quality products may look attractive but usually lead to premature failure. Trusted suppliers ensure consistency and reliability.
Applications That Benefit Most
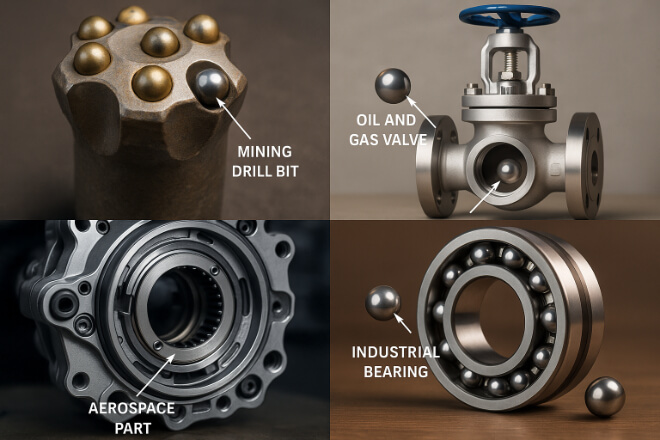

High-stress environments where tungsten carbide balls perform best include:
Mining and drilling equipment exposed to heavy loads and abrasion.
Aerospace components requiring strength under heat and vibration.
Oil and gas valves and pumps facing pressure and corrosive fluids.
Industrial bearings where downtime is very costly.
For decision-makers, the return on investment comes from fewer failures, longer service life, and lower overall costs.
結論
Tungsten carbide balls are not only stronger than steel but also smarter investments for companies working in high-stress environments.
By choosing the right grade, maintaining proper operating conditions, using effective lubrication, and working with reliable suppliers, businesses can get maximum performance and value.
For industries where downtime is expensive, following these best practices means safer operations, better results, and a competitive edge.
企業の詳細を知りたい場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。 お問い合わせ。
