In modern machinery, reliability often depends on the smallest components.
Bushings, also called bearing sleeves or liners, are one such part. They reduce friction between moving parts and protect shafts or housings from wear.
When high loads, abrasive fluids, or extreme temperatures are involved, standard steel bushings wear out quickly. That’s where tungsten carbide bushings come in.
These bushings are made from one of the hardest engineering materials available — tungsten carbide (WC) — which provides exceptional 耐摩耗性, 硬度, and corrosion protection.
This article explains what タングステンカーバイドブッシング are, how they work, where they are used, and why they are a smart investment for demanding industries.
What Is a Tungsten Carbide Bushing?
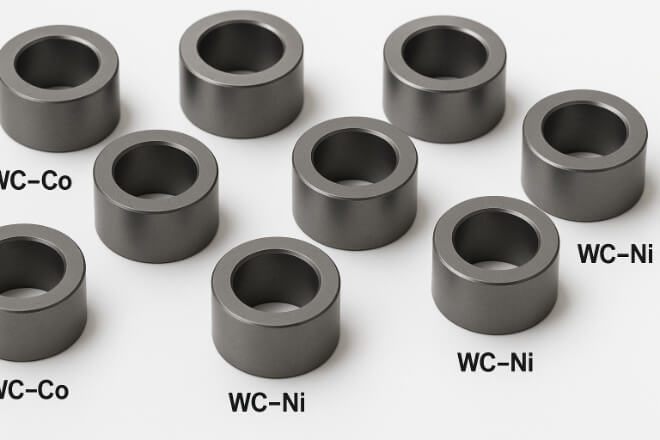

あ tungsten carbide bushing is a precision-machined sleeve made from 炭化タングステン粉末 bonded with cobalt or nickel.
It is designed to support and guide rotating or sliding shafts in pumps, compressors, turbines, and バルブ.
Unlike standard steel or bronze bushings, carbide bushings maintain their shape and dimensions under high pressure, high speed, and abrasive conditions.
Their high 硬度 (around 90 HRA) allows them to last much longer than other materials.
How Tungsten Carbide Bushings Work
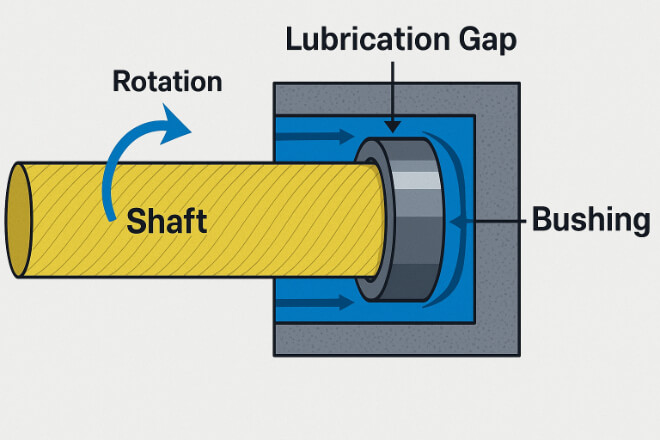
Tungsten carbide bushings function as protective liners or bearing surfaces inside mechanical systems. Their main role is to:
Reduce friction between rotating parts
Absorb radial loads
Prevent shaft wear or misalignment
Provide stable support even in dirty or abrasive environments
A thin film of lubricant (oil, water, or gas) separates the shaft and the bushing, minimizing metal-to-metal contact.
The smooth inner bore of the bushing allows the shaft to rotate with minimal energy loss and maximum durability.
Key Properties of Tungsten Carbide Bushings
| 財産 | 標準値 | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| 硬度 | 88~92 HRA | Resists wear and deformation |
| 密度 | 14.0–15.0 g/cm³ | Provides high strength and impact resistance |
| 圧縮強度 | > 4000 MPa | Handles heavy loads and pressure |
| 熱伝導率 | 80–100 W/m·K | Efficient heat dissipation during operation |
| 耐腐食性 | Excellent in water, oil, and mild chemicals | Ideal for harsh environments |
These properties make tungsten carbide bushings especially suitable for high-speed, abrasive, and corrosive applications where reliability is essential.
Common Grades of Tungsten Carbide Bushings
Different grades of tungsten carbide are selected based on the binder type, grain size, and working environment.
| グレードタイプ | バインダー | アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| WC–Co | Cobalt (6–12%) | General wear and mechanical loads |
| WC–Ni | Nickel (6–10%) | Corrosive and chemical environments |
| Fine-Grain WC | Cobalt (≤6%) | High-precision and high-speed applications |
Nickel-bonded grades are preferred in corrosive chemical or seawater environments, while cobalt-bonded grades are commonly used in oilfield and mechanical wear applications.
Applications of Tungsten Carbide Bushings

Tungsten carbide bushings are used across industries where long service life, precision, and 耐摩耗性 または 耐腐食性 are critical.
Common Applications
Pumps: For shaft sleeves, impeller liners, and bearing supports.
Compressors: For dynamic sealing and high-speed rotation.
Submersible motors: To handle abrasive water with sand or silt.
Valves and actuators: To prevent metal-to-metal wear in critical assemblies.
石油とガス drilling tools: For stabilizers and mud pump liners.
Chemical process systems: To resist corrosion from acids and solvents.
Advantages Over Steel or Bronze Bushings
| 特徴 | タングステンカーバイドブッシング | Steel / Bronze Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| 硬度 | Extremely high (90 HRA) | Moderate (60–70 HRA) |
| 耐摩耗性 | Outstanding in abrasive media | Poor under abrasive load |
| 耐腐食性 | Excellent (especially Ni-binder) | Limited (requires coatings) |
| Lifespan | 5–10× longer | Shorter under load |
| Operating Cost | Higher initial cost, lower lifecycle cost | Cheaper upfront, frequent replacement |
For companies managing high-wear or corrosive systems, switching to tungsten carbide bushings means lower downtime and fewer replacements — directly improving total cost of ownership.
Design and Manufacturing Considerations

Designing and producing a tungsten carbide bushing requires tight process control:
寸法公差: ±0.005 mm
Surface finish: Ra ≤ 0.2 µm for rotating surfaces
Chamfered edges: Prevent cracking during installation
Lubrication grooves: Custom patterns for oil or water lubrication
Nickel or cobalt binder selection: Based on corrosion risk
Each ring is sintered, machined with diamond tools, and often polished to near mirror finish to reduce friction and enhance longevity.
Maintenance and Handling Tips

Although carbide bushings are durable, proper handling extends their service life:
Avoid impact or dropping — carbide is hard but brittle.
Clean before assembly to remove particles that could scratch the surface.
Use compatible lubricants or seal fluids to prevent dry operation.
Inspect regularly for signs of wear, scoring, or misalignment.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
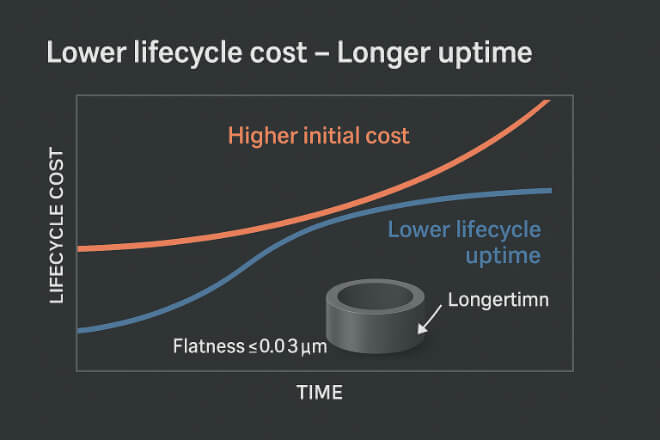
While tungsten carbide bushings cost more upfront, they last significantly longer and perform better in severe conditions.
In applications such as slurry pumps or seawater compressors, their extended lifespan and reduced downtime lead to ROI within 6–12 months.
結論
Tungsten carbide bushings are the backbone of modern industrial sealing and bearing systems.
Their unmatched 硬度, 耐摩耗性, and stability under pressure make them essential for pumps, compressors, and chemical equipment that must run continuously and reliably.
For decision-makers, choosing carbide bushings means fewer replacements, greater uptime, and lower lifecycle costs — all while ensuring safe, efficient performance in harsh environments.
企業の詳細を知りたい場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。 お問い合わせ。
