Tungsten carbide balls are small components with a big impact in modern industry. Known for their 硬度、強さ、そして 耐摩耗性, they are used in many types of equipment where precision and long service life are critical.
From bearings that keep machines running smoothly, to valves that control flow in pipelines, to ball screws that move parts with high accuracy, carbide balls are everywhere in heavy industry.
For decision-makers in 自動車, 石油・ガス, 航空宇宙, and manufacturing, knowing the role of carbide balls helps in choosing the right supplier, reducing downtime, and improving long-term reliability.
This article explains the most important industrial applications of tungsten carbide balls, why they outperform steel in many cases, and what to look for when sourcing them.
Why Tungsten Carbide Balls Are Different
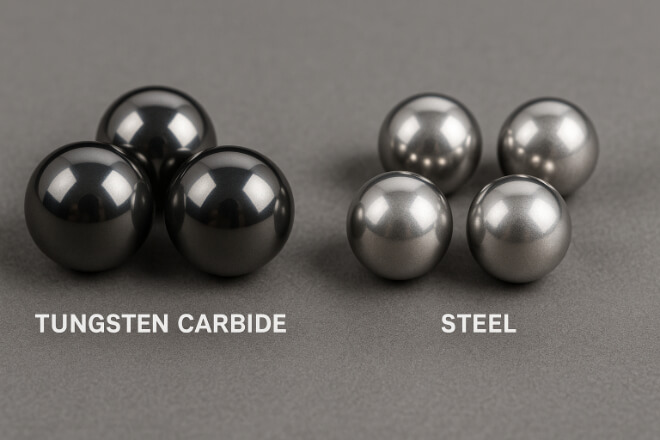

Carbide balls are made from 炭化タングステン粉末 and a binder, usually cobalt.
They are pressed, sintered, and sometimes coated for added performance. Compared to steel balls, they offer:
2–3 times higher 硬度 (88–94 HRA range).
Longer 耐摩耗性 in abrasive or corrosive environments.
High compressive strength, making them suitable for extreme loads.
Stable performance at both low and high temperatures.
These features explain why so many industries are replacing steel or ceramic balls with carbide versions.
Bearings: Precision and Longevity

Bearings are one of the most common uses for tungsten carbide balls.
1). Why carbide is preferred:
Bearings need balls that can roll smoothly under heavy load without deforming.
Steel balls may wear out faster in tough conditions, while carbide balls maintain their shape and polish longer.
2). Applications:
Aerospace bearings where precision is critical.
Mining equipment bearings exposed to dust and high pressure.
Precision instruments where tiny errors can cause failure.
3). Impact for buyers:
By choosing carbide balls, companies can extend maintenance cycles, reduce downtime, and increase machine reliability.
Valves: Sealing and Reliability
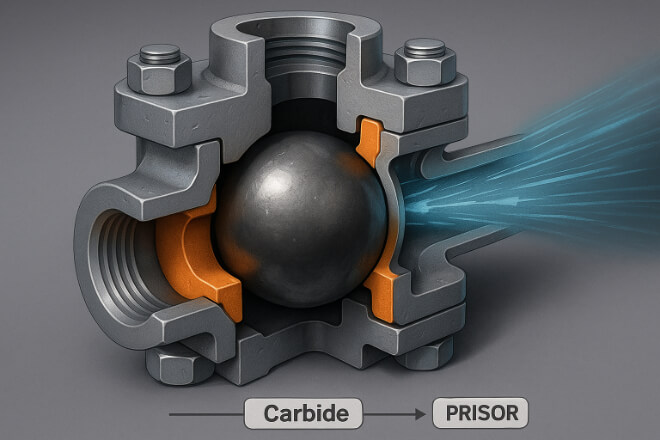
Valves control the flow of liquids and gases, making sealing performance essential.
Tungsten carbide balls are used in check valves, ball valves, and high-pressure regulators.
1). Why carbide is used:
Excellent resistance to erosion from fluids containing sand, chemicals, or high pressure.
Ability to keep a tight seal even after long use.
2). Applications:
石油・ガス pipelines where sand and gas cause rapid wear.
Chemical processing plants handling corrosive fluids.
Water management systems where reliability is critical.
3). Decision-maker’s view:
Using carbide balls in valves reduces leakage, increases service life, and lowers replacement costs.
Ball Screws: Accuracy in Motion Systems
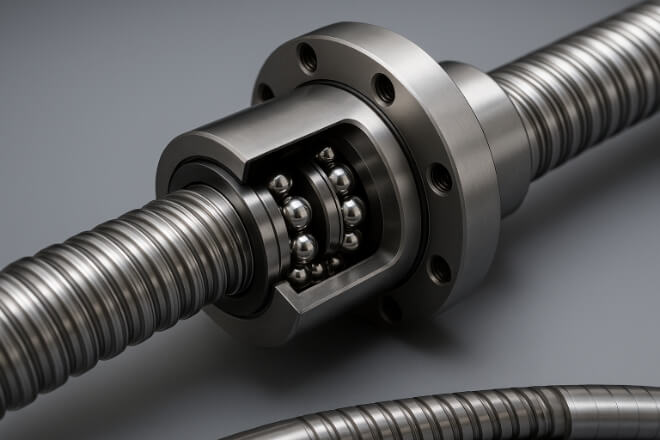

Ball screws convert rotary motion into linear motion and are found in CNC machines, robotics, and precision positioning equipment.
1). Why carbide balls matter:
They keep smooth motion under heavy loads.
Their hardness prevents flattening, which ensures accuracy over time.
2). Applications:
CNC machining centers requiring micrometer-level accuracy.
Aerospace actuators where safety depends on reliability.
Robotics used in automotive assembly lines.
3). Procurement benefit:
Carbide balls in ball screws mean fewer errors, less vibration, and longer-lasting equipment.
Comparing Carbide Balls to Steel and Ceramic
Decision-makers often ask: why not just use steel or ceramic balls? The answer lies in performance vs. cost.
| 財産 | Steel Balls | Ceramic Balls | タングステンカーバイドボール |
|---|---|---|---|
| 硬度 | 中くらい | 高い | 非常に高い |
| 耐摩耗性 | Low–Medium | 高い | 非常に高い |
| 耐腐食性 | Low–Medium | 高い | 高い |
| Load capacity | 中くらい | 中くらい | 非常に高い |
| 料金 | 低い | 高い | Medium–High |
| Typical applications | Standard bearings | High-speed spindles | Heavy-duty valves, bearings, ball screws |
From the table, it is clear that tungsten carbide balls offer the best balance of performance and cost, especially for industries that value durability.
Quality Control and Standards in Industrial Use
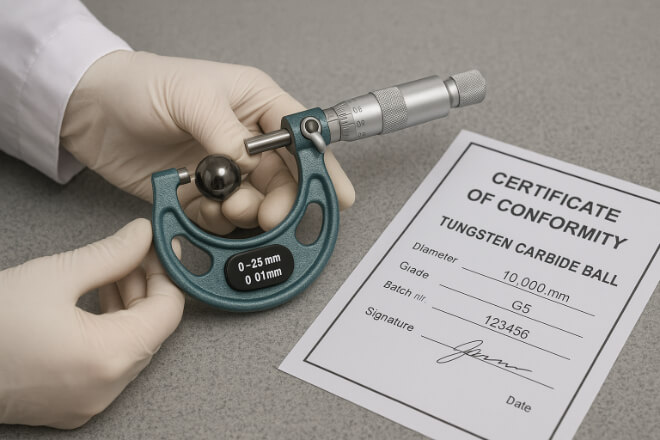
Because carbide balls work in mission-critical systems, suppliers must follow strict tolerance and quality control standards.
ISO 3290 / DIN 5401: Defines grade and roundness.
ISO 9001 certification: Shows supplier quality systems are reliable.
Decision-makers should always check whether suppliers can provide certificates of analysis, inspection reports, and traceability.
This ensures the carbide balls will perform as expected in bearings, valves, and ball screws.
Key Industries That Benefit from Carbide Balls
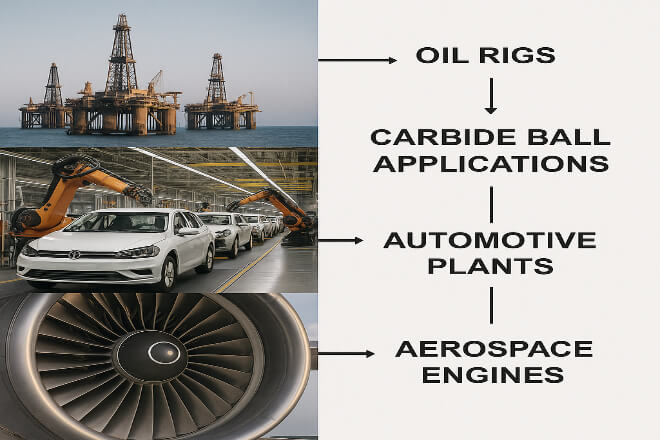
Carbide balls are not limited to one sector—they are widely used across industries:
石油・ガス: Valves and pumps in drilling and refining.
自動車: Bearings and ball screws in precision manufacturing.
航空宇宙: Bearings in engines and actuators.
Industrial Machinery: Heavy-duty valves and high-precision screws.
医療機器: Precision instruments requiring accurate movement.
Each of these industries relies on carbide balls to reduce failure rates and ensure safety.
Cost vs. Value for Decision-Makers

At first glance, carbide balls are more expensive than steel balls. However, the total cost of ownership is lower because:
They last longer, reducing replacement frequency.
They minimize downtime caused by failure.
They improve system reliability, lowering warranty or repair costs.
For decision-makers, the math is clear: carbide balls offer better ROI (return on investment) in demanding applications.
結論
Tungsten carbide balls may be small parts, but they carry great importance in bearings, valves, and ball screws across many industries.
For buyers and decision-makers, understanding their role, standards, and advantages helps make smarter procurement choices.
By choosing high-quality carbide balls from reliable manufacturers, companies can improve equipment life, reduce downtime, and enhance precision.
企業の詳細を知りたい場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。 お問い合わせ。
