摩耗部品 are essential in industries like 採掘, 石油とガス, 金属加工, and construction. They face extreme heat, high pressure, and constant friction.
To survive these harsh conditions, manufacturers use advanced processes like sintering, grinding, and coating to produce parts with the right balance of strength, 強靭さ、そして耐久性。
This article explains each of these three key steps in a simple, clear way.
If you are a decision-maker looking to choose the right supplier or understand production quality, this guide will help you.
What Are Wear Parts?
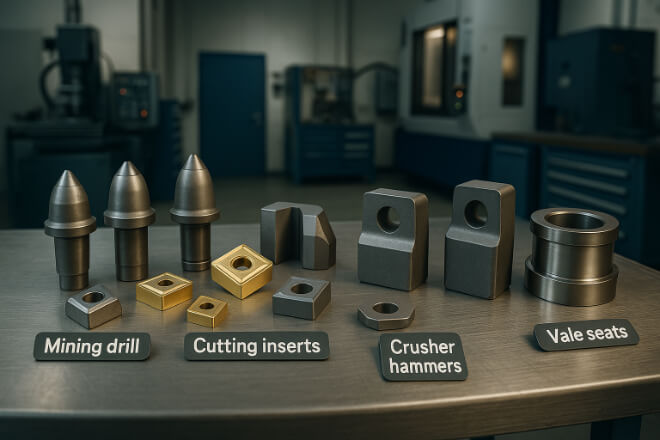
Wear parts are components designed to resist wear and tear in machines and tools. Examples include:
鉱山用ドリルビット
Cutting tool 挿入物
Crusher hammers
バルブシート
Most high-performance wear parts today are made from tungsten carbide — a material that is much harder than steel and can last many times longer.
The Role of Sintering in Wear Part Production
Sintering is the process that turns loose tungsten carbide powder into a solid, high-strength part.
It is done by heating the powder mixture to around 1,450–1,500°C in a furnace without melting the main material.
Why it matters:
Bonds the carbide particles together using a metal binder (like cobalt or nickel).
Removes porosity for higher density and strength.
Improves wear and impact resistance.
Basic Sintering Steps:
| Step | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 粉末の準備 | Tungsten carbide and binder powders are mixed evenly. |
| Compaction | Powder is pressed into the desired shape (green compact). |
| 焼結 | Part is heated in a controlled furnace to bond particles. |
| 冷却 | Part is slowly cooled to avoid cracks and stresses. |
Grinding: Precision Shaping for Performance
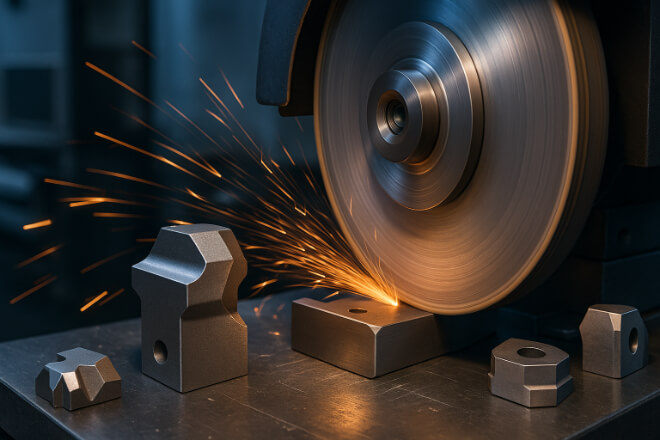

After sintering, the part is extremely hard but may not have the exact final dimensions. This is where grinding comes in.
Why grinding is important:
Achieves precise tolerances.
Creates smooth surfaces for better performance.
Improves fit and assembly with other machine components.
Grinding is done with diamond wheels because tungsten carbide is too hard for normal abrasives.
Grinding applications for wear parts:
Sharpening cutting edges.
Flattening and polishing surfaces.
Shaping complex geometries for specialized tools.
Coating: Extending Service Life
Coating adds a protective layer on top of the tungsten carbide surface. This can:
Reduce friction.
Increase resistance to oxidation and corrosion.
Improve wear resistance in high-speed or high-heat applications.
Common Coating Materials:
TiN (Titanium Nitride) — golden color, excellent wear resistance.
TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) — better heat resistance for high-speed cutting.
Diamond Coating — extreme hardness for non-ferrous materials.
Coating Methods:
| Method | 利点 |
|---|---|
| PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | Thin, hard coating with excellent adhesion. |
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | Thicker coating, very wear-resistant. |
| Electroplating | Cost-effective for corrosion protection. |
Quality Control in Each Stage

A good wear part is only as strong as its weakest step. That’s why sintering, grinding, and coating must be followed by strict quality control.
Typical Tests:
How These Steps Work Together
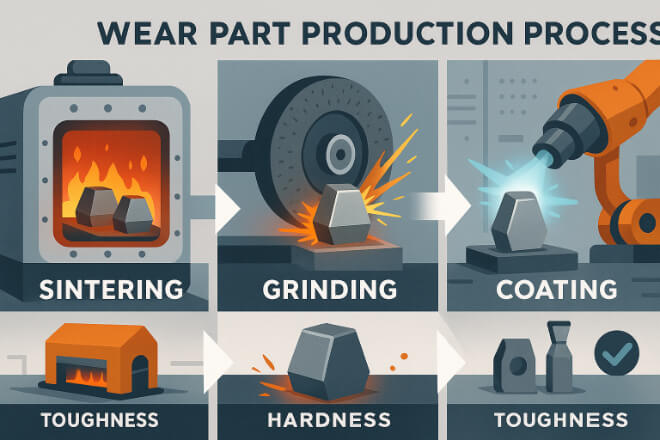
Each process plays a unique role:
Sintering — builds the part’s core strength.
Grinding — gives it precision and fit.
Coating — adds extra life and protection.
When all three are done correctly, the final wear part can last 3–10 times longer than standard steel parts, leading to lower downtime and better return on investment.
意思決定者が気にかけるべき理由

If you are in charge of purchasing or production, knowing these steps helps you:
Choose suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Evaluate part quality beyond just price.
Reduce overall operational costs through longer tool life.
結論
Sintering, grinding, and coating are the three pillars of wear part production. Together, they turn raw tungsten carbide powder into high-performance components ready for the toughest industrial jobs.
By understanding these processes, companies can make smarter sourcing decisions and ensure consistent performance in their machinery.
企業の詳細を知りたい場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。 お問い合わせ。
