텅스텐 카바이드 부싱 are widely used in pumps, compressors, and slurry systems because they resist wear better than most materials.
But even tungsten carbide has limits when abrasive particles are present in the fluid. The size, hardness, and concentration of these particles have a major impact on bushing lifespan.
This article explains how abrasive particle size affects wear, what thresholds decision-makers should watch, and how to reduce damage in real applications.
Why Abrasive Particle Size Matters for Tungsten Carbide Bushings

Abrasive wear happens when hard particles slide between the shaft and the bushing surface. Tungsten carbide is extremely hard, but once particles become large enough, they act like cutting tools.
1). Bigger Particles = Faster Wear
Large particles create deeper scratches
They interrupt lubrication film
They increase friction and heat
2). Small Particles Are Still Harmful
Even fine particles can remove material slowly but continuously, especially in high-speed service or boundary lubrication.
How Particle Size Affects Wear Mechanisms
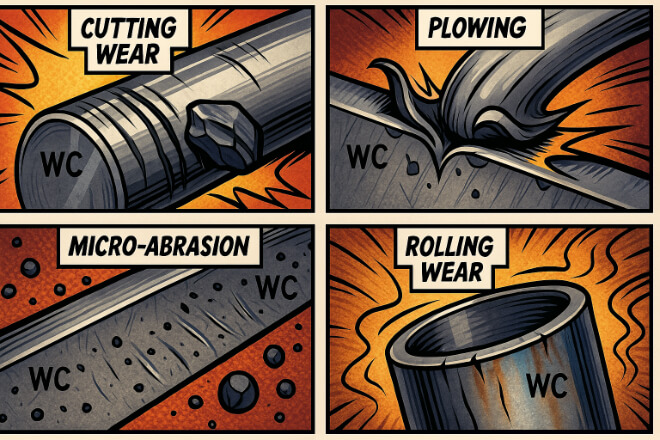
Abrasive wear is not a single mechanism—it changes depending on particle size and 경도. WC bushings typically experience:
Cutting Wear: Large particles cut directly into the surface.
Plowing Wear: Medium particles push material aside, forming ridges.
Micro-Abrasion: Small particles form very fine scratches.
Rolling Wear: Round particles roll instead of cutting, reducing wear rate.
| 입자 크기 | Wear Mechanism | Effect on WC Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| Large (>150 μm) | 절단 | Rapid, severe wear |
| Medium (50–150 μm) | Plowing | Moderate wear, grooves |
| Fine (<50 μm) | Micro-abrasion | Slow but continuous wear |
| Very fine (<10 μm) | Rolling / polishing | Low wear unless high concentration |
Particle Size Thresholds That Impact WC Bushing Lifespan
Different industries operate with different fluid cleanliness levels. Below is a general guideline for tungsten carbide in abrasive service.
| 입자 크기 | Risk Level | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| < 25 μm | 낮은 | Mostly fine polishing wear |
| 25–75 μm | 중간 | Noticeable wear over time |
| 75–150 μm | 높은 | Deep scoring, shorter lifespan |
| > 150 μm | Severe | Rapid wear, early failure |
These thresholds can shift depending on:
System pressure
Particle hardness
Shaft speed
Lubrication quality
Bushing geometry
How Particle Hardness Influences Wear Severity

Particle size is only part of the story. Hardness determines how easily a particle can cut tungsten carbide.
Hardness Comparison (Typical Values)
Silica sand: 1100–1200 HV
Alumina: 1500–2000 HV
Tungsten carbide: 1600–2000 HV
When particles approach or exceed WC 경도, wear becomes much more aggressive.
| Particle Type | Relative Hardness | Wear Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Silica (sand) | Lower than WC | 보통의 |
| Alumina | Equal or higher | 높은 |
| Quartz slurry | Close to WC | High to severe |
| Metal debris | Varies | Can cause scoring or gouging |
Concentration: Why Even Small Particles Become Dangerous in Large Numbers

A single particle may not damage a WC bushing, but millions of particles passing through the gap continuously can act like a sandblasting system.
High Concentration Causes:
More particle impacts per second
Faster breakdown of the lubrication film
Increased surface temperature
Accelerated wear groove development
High-speed pumps and agitators are especially sensitive to particle concentration.
Real-World Wear Patterns Caused by Different Particle Sizes
Every abrasive environment leaves a unique signature on the bushing bore.
Typical Wear Patterns
| 입자 크기 | Typical Wear Pattern | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| < 25 μm | Fine matte surface | Micro-abrasion |
| 25–100 μm | Visible grooves | Plowing wear |
| 100–200 μm | Deep scratches | Cutting wear |
| > 200 μm | Chunk removal, heavy scoring | Severe damage |
How to Reduce Abrasive Wear in Tungsten Carbide Bushings

Reducing wear does not always require redesigning the system. Often, small process improvements make a big difference.
Key Strategies
Install better filtration or sediment traps
Reduce clearance to limit particle ingress
Choose harder grades of tungsten carbide
Use smooth, well-polished shaft surfaces
Improve lubrication flow
Avoid pump cavitation, which pulls particles into the gap
Choosing the Right WC Grade for Abrasive Slurry Service
Different WC grades offer different levels of 내마모성. For abrasive environments, finer grain sizes and higher hardness are usually preferred.
| WC Grade Type | Best Used For | 노트 |
|---|---|---|
| Fine-grain WC-Co | Severe abrasion | 매우 높은 경도 |
| Submicron WC | High-velocity slurry | 우수한 내마모성 |
| WC-Ni | Corrosive slurry | 내식성이 우수하다 |
| Binderless WC | Extreme abrasion | Highest hardness |
결론
Abrasive particle size is one of the most important factors affecting tungsten carbide bushing lifespan.
By understanding how particle size, hardness, and concentration interact, operators can set practical thresholds for filtration, clearance, lubrication, and WC grade selection.
With the right controls, bushing life can be extended significantly even in harsh slurry environments.
회사에 대한 자세한 내용을 알고 싶으시면 언제든지 문의해 주세요. 문의하세요.
