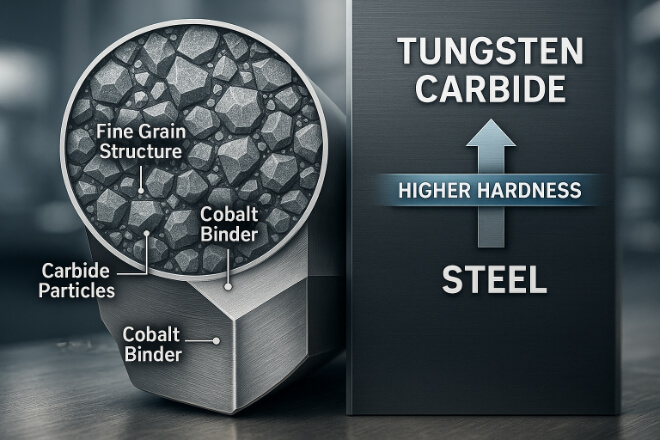
텅스텐 카바이드는 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 재료 중 하나입니다. 절단 도구, 마모 부품및 산업용 부품.
그것은 그것의 가치가있다 경도, 내마모성, 그리고 열에도 성능을 유지하는 능력.
하지만 모든 텅스텐 카바이드 부품이 동일한 것은 아닙니다. 코팅된 부품도 있고 코팅되지 않은 부품도 있습니다. 코팅은 부품의 거동, 수명, 그리고 다양한 환경에서의 성능을 변화시킬 수 있습니다.
제조업의 의사결정권자를 위해 채광, 석유와 가스, 정밀 가공을 위해 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드와 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드 중에서 선택하는 것은 생산성과 비용에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 전략적 결정입니다.
이 글에서는 두 가지 옵션을 비교하여 귀하의 필요에 가장 적합한 선택을 할 수 있도록 도와드리겠습니다.
"코팅된" 텅스텐 카바이드는 무엇을 의미합니까?
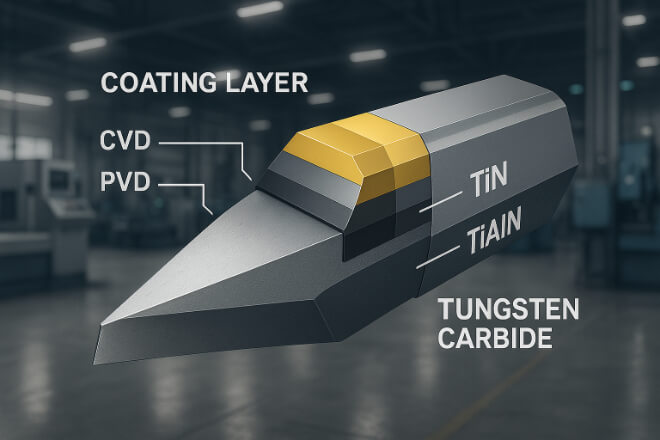
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드는 표면에 다른 물질로 이루어진 얇은 층을 가지고 있습니다. 이 코팅은 일반적으로 화학 기상 증착(CVD)이나 물리 기상 증착(PVD)과 같은 방법을 통해 적용됩니다.
일반적인 코팅 재료:
질화티타늄(TiN) – 금색으로 마찰을 줄여줍니다.
티타늄 카보나이트라이드(TiCN) – 고온에 적합 경도 그리고 적당한 더위.
티타늄 알루미늄 질화물(TiAlN) – 고온 가공에 적합합니다.
알루미늄 티타늄 질화물(AlTiN) – 강한 산화 저항성.
다이아몬드 유사 탄소(DLC) – 비철 재료에 매우 적합합니다.
코팅의 목적은 작동 중 마모를 줄이고, 내열성을 높이고, 표면 마감을 개선하는 것입니다.
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드와 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드의 주요 차이점
| 재산 | 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드 | 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드 |
|---|---|---|
| 표면 경도 | 코팅으로 인해 더 높아짐 | 높지만 코팅된 것보다 낮음 |
| 내마모성 | 우수함 - 코팅으로 마모 감소 | 좋음 - 하지만 연마 조건에서는 더 빨리 마모됨 |
| 내열성 | 더 나은 - 코팅은 열로부터 보호합니다 | 중간 - 고온에서 경도가 더 빨리 떨어질 수 있음 |
| 마찰 | 하단 - 더 부드러운 절단 동작 | 더 높음 - 더 많은 열이 축적될 수 있음 |
| 비용 | 더 높은 선불 | 앞쪽 낮은 |
| 가장 적합한 | 고속, 고열, 연마 조건 | 일반 용도, 부드러운 소재, 저비용 작업 |
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드의 이점
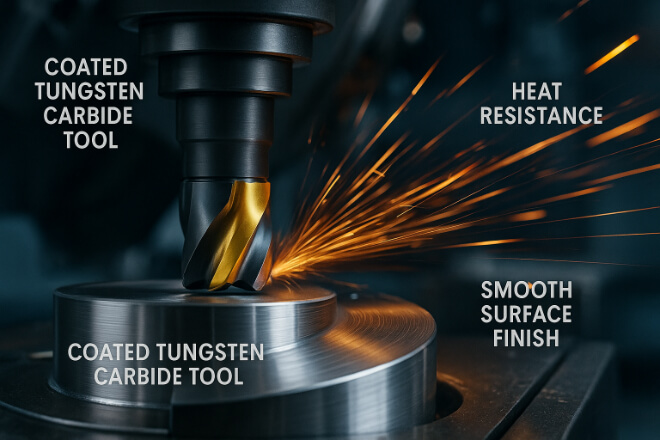
코팅은 단지 겉모습을 꾸미는 것이 아니라 실제 성능상의 이점을 더해줍니다.
1) 더 긴 공구 수명
코팅은 가공물과 텅스텐 카바이드 기질 사이에 장벽을 형성하여 마모를 늦춥니다.
2) 더 높은 절삭 속도
마찰이 적다는 것은 도구가 과열되지 않고 더 빨리 작동할 수 있다는 것을 의미합니다.
3) 더 나은 표면 마감
마찰이 감소하면 모서리가 쌓이는 것을 방지하고 부품 품질이 향상됩니다.
4) 향상된 내열성
TiAlN과 같은 코팅은 극한의 온도를 견딜 수 있어 건식 가공에 적합합니다.
코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드의 이점

코팅되지 않은 도구와 부품은 여전히 장점이 있습니다. 특히 특정 응용 분야에서는 더욱 그렇습니다.
1) 낮은 비용
코팅되지 않은 카바이드는 생산 및 구매 비용이 저렴합니다.
2) 더욱 날카로운 절단면
코팅층이 없으면 가장자리를 더 날카롭게 갈 수 있어 알루미늄이나 플라스틱과 같은 부드러운 소재를 자르는 데 유용합니다.
3) 코팅 불량 위험 없음
어떤 작업에서는 코팅이 벗겨지거나 깨질 수 있는데, 코팅되지 않은 부품은 이런 문제를 피할 수 있습니다.
4) 재분쇄가 더 쉽습니다.
코팅되지 않은 도구는 코팅층을 제거하지 않고도 다시 연마하여 재사용할 수 있습니다.
적용 적합성
| 애플리케이션 | 추천 옵션 | 이유 |
|---|---|---|
| 기계 가공에서 고속도강 대체 | 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드 | 경도를 잃지 않고 높은 열과 속도를 처리합니다. |
| 알루미늄 또는 연질 플라스틱 절단 | 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드 | 쌓인 모서리를 방지하고 날카로운 모서리를 유지합니다. |
| 경화강의 건식 가공 | 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드 | TiAlN 또는 AlTiN 코팅으로 높은 내열성 |
| 저비용, 단기 일자리 | 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드 | 초기 비용이 낮고 단기 실행에도 내구성이 뛰어납니다. |
| 연마성 암석용 채굴 드릴 비트 | 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드 | 혹독한 환경에서도 뛰어난 마모 보호 기능 |
비용 대 성능
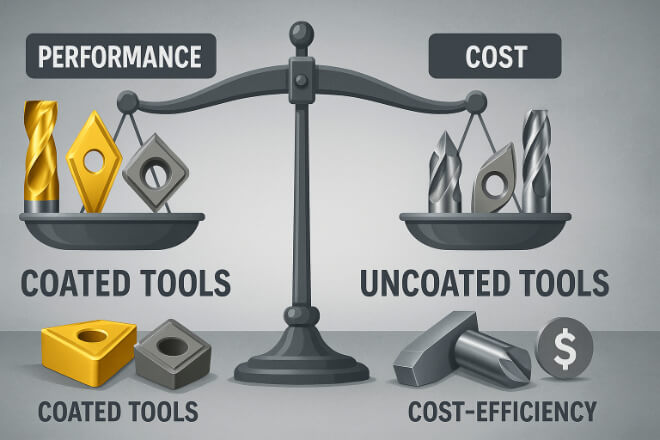
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드 부품은 일반적으로 초기 비용이 많이 들지만 수명이 더 길어 가동 중지 시간과 교체 비용이 줄어듭니다.
코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드는 코팅의 이점이 최소화되는 단기 작업이나 부드러운 소재에 대해 비용 효율적일 수 있습니다.
의사 결정권자에게는 총소유비용(TCO)을 계산하는 것이 중요합니다. 코팅된 부품의 높은 구매 가격은 수명 연장과 성능 향상으로 이어지기도 합니다.
올바른 옵션 선택
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드와 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드를 선택할 때 다음 사항을 고려하세요.
가공 중인 재료(연마재 또는 연질재)
절단 속도 및 온도
예산 및 생산량
가동 중지 비용 대 도구 비용
고속 가공, 연마재 또는 고열이 작업에 관련된 경우 코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드는 일반적으로 투자할 만한 가치가 있습니다.
비용이 적게 드는 작업이나 부드러운 소재 또는 소량 생산의 경우 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드가 더 경제적일 수 있습니다.
결론
코팅된 텅스텐 카바이드와 코팅되지 않은 텅스텐 카바이드는 모두 산업 분야에서 그 자리를 차지하고 있습니다.
코팅된 도구는 까다롭고 빠른 속도와 고온의 환경에서 빛을 발하는 반면, 코팅되지 않은 도구는 날카로움, 낮은 비용, 덜 까다로운 작업에 대한 손쉬운 유지관리를 제공합니다.
비즈니스 리더는 애플리케이션 요구 사항, 비용 효율성, 그리고 예상 성능을 바탕으로 결정을 내려야 합니다. 특정 환경에서 두 가지 옵션을 모두 테스트하는 것이 적절한 균형을 찾는 가장 좋은 방법입니다.
회사에 대한 자세한 내용을 알고 싶으시면 언제든지 문의해 주세요. 문의하세요.