강철이란 무엇인가?

강철은 주로 철과 탄소로 만들어진 합금으로, 성능을 향상시키기 위해 크롬, 니켈, 망간과 같은 다른 원소를 첨가하는 경우가 많습니다.
강철은 강하고 튼튼하며 다재다능하기 때문에 인기가 높습니다. 또한 텅스텐 카바이드에 비해 가공과 용접이 쉽고 저렴합니다.
강철의 주요 특성:
높은 강인함 그리고 힘
가공 및 성형이 더 쉽습니다.
대형 부품에 비용 효율적
다양한 용도에 맞는 다양한 등급(예: 공구강, 스테인리스강, 고탄소강)
강철은 기어, 샤프트, 구조 부품, 일반 엔지니어링 구성품에 널리 사용됩니다.
텅스텐 카바이드 대 강철: 특성 비교
| 재산 | 텅스텐 카바이드 | 강철 |
|---|---|---|
| 경도 | 매우 높음(모스 8.5~9) | 하위(등급에 따라 4~8 모스) |
| 내마모성 | 우수하고 연마 조건에 이상적입니다. | 좋은데 마모되면 더 빨리 마모됨 |
| 내열성 | 매우 높음, 고온에서도 경도를 유지합니다. | 중간, 고온에서 경도가 떨어질 수 있음 |
| 부식 저항성 | 특히 코팅의 경우 높음 | 다양함 - 스테인리스 스틸은 부식에 잘 견딥니다. |
| 강인함 | 중간(강한 충격에 깨질 수 있음) | 높음, 충격 하중에 더 좋음 |
| 가공성 | 어렵고 다이아몬드나 카바이드 공구가 필요합니다. | 표준 도구로 쉽게 가공 가능 |
| 비용 | 더 높은 | 낮추다 |
혹독한 환경에서의 내구성

텅스텐 카바이드는 내마모성과 내마모성이 뛰어납니다.
광산이나 금속 가공 시, 텅스텐 카바이드로 제작된 공구와 부품은 강철 소재보다 3~10배 더 오래 사용할 수 있습니다. 이는 가동 중단 시간과 교체 비용을 줄여줍니다.
그러나 부품이 강한 충격이나 굽힘력에 노출될 경우 강철은 텅스텐 카바이드보다 성능이 더 좋을 수 있습니다.
강철의 더 높은 강인함 즉, 균열 없이 충격을 흡수할 수 있어 일부 구조적 용도에 더 적합합니다.
비용 고려 사항

언뜻 보기에 텅스텐 카바이드 부품은 강철보다 비용이 더 많이 듭니다. 하지만 교체, 가동 중단, 유지 보수를 포함한 전체 수명 주기 비용을 고려하면 텅스텐 카바이드가 더 경제적일 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 텅스텐 카바이드 절삭 다이는 강철 다이보다 비용이 2~3배 더 많이 들지만 수명이 5~10배 더 길어 많은 경우 더 나은 투자가 될 수 있습니다.
적용 적합성
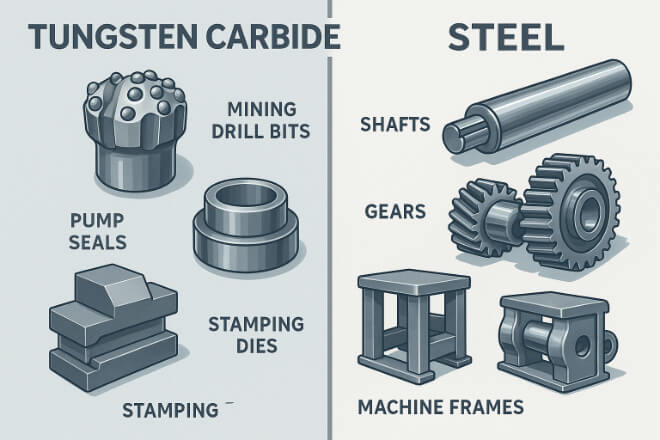
1) 텅스텐 카바이드를 사용하는 경우:
극심한 마모 및 마모
고온
정밀 허용 오차
최소한의 가동 중지 시간으로 연속 작업이 가능합니다.
1.1). 예:
광산 드릴 비트
펌프 씰 석유 및 가스
금속 스탬핑 다이
목공용 칼날
2) 강철을 사용하는 경우:
무거운 충격 하중과 굽힘
낮은 온도 환경
비용이 핵심 요소인 애플리케이션
카바이드에서는 너무 비싼 대형 부품
2.1) 예:
기계 프레임
샤프트와 기어
일반 구조 구성 요소
장단점 요약
| 재료 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| 텅스텐 카바이드 | 우수한 내마모성, 높은 경도, 우수한 내열성 및 내식성, 긴 수명 | 가격이 비싸고, 강한 충격에 취약하며, 기계 가공이 어려움 |
| 강철 | 높은 인성, 낮은 비용, 가공이 쉬움, 다용도 | 내마모성이 낮고 고온에서 경도가 떨어질 수 있으며 유지 관리가 더 필요합니다. |
텅스텐 카바이드와 강철 중 선택

올바른 재료를 선택하는 것은 다음에 따라 달라집니다.
마모 유형 – 연마, 접착, 충격 또는 부식성
작동 온도 - 고온 공정에는 카바이드가 필요할 수 있습니다.
부품 크기 - 대형 부품의 경우 강철이 더 경제적입니다.
서비스 수명 요구 사항 - 카바이드는 종종 교체 횟수가 줄어드는 것을 의미합니다.
예산 – 단기 대 장기 비용 계획
많은 산업에서 가장 좋은 방법은 두 가지를 결합하는 것입니다. 즉, 구조적 지지대에는 강철을 사용하고 마모 표면에는 텅스텐 카바이드를 사용합니다.
성능 극대화를 위한 유지 관리 팁

1) 텅스텐 카바이드의 경우:
갑작스러운 충격을 피하세요
응력 균열을 방지하기 위해 적절한 장착을 사용하십시오.
화학 물질로 인한 부식을 방지하기 위해 정기적으로 청소하십시오.
2) 강철의 경우:
부식 방지를 위해 보호 코팅을 적용하세요
마모를 줄이려면 윤활을 유지하세요
균열이나 변형이 있는지 정기적으로 확인하세요
결론
텅스텐 카바이드와 강철의 논쟁에서 단 하나의 승자는 없습니다. 텅스텐 카바이드는 내마모성과 고온 응용 분야에서 우위를 점하는 반면, 강철은 구조적 및 충격에 강한 용도에서 인성과 비용 이점을 제공합니다.
의사 결정권자는 총소유비용(TCO), 성능 요구 사항, 그리고 운영 조건을 신중하게 고려해야 합니다. 많은 경우, 두 소재를 단일 시스템에 결합하면 내구성과 강인성이라는 두 가지 장점을 모두 얻을 수 있습니다.
회사에 대한 자세한 내용을 알고 싶으시면 언제든지 문의해 주세요. 문의하세요.

