Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a critical quality assurance method used to evaluate the internal and surface integrity of materials and components—without causing damage. In the world of tungsten carbide tools, where reliability, performance, and precision are paramount, NDT plays a key role in ensuring that each part meets stringent quality and safety standards.
What Is Non-Destructive Testing?
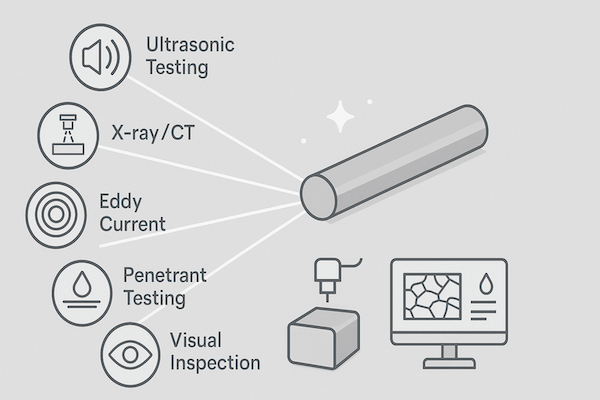
Non-Destructive Testing refers to a group of analysis techniques that allow engineers and manufacturers to inspect, measure, or evaluate a component without altering its usability. This is especially important for tungsten carbide (WC) tools, which are often used in high-precision and high-stress environments such as metal cutting, mining, and mold production.
Common NDT methods used in carbide inspection include:
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
X-ray or Radiographic Testing (RT)
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) (less common for non-ferromagnetic materials like WC)
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Visual Inspection (VT)
Eddy Current Testing (ECT)
3D X-ray CT Scanning
Why NDT Matters in Tungsten Carbide Tooling
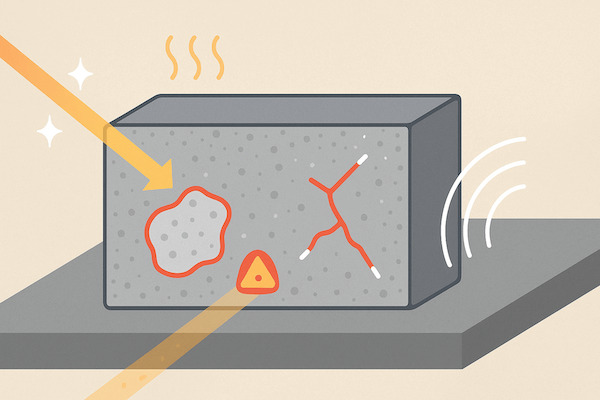
1. Internal Flaw Detection
Tungsten carbide tools can develop internal voids, cracks, or binder separation during sintering. NDT allows detection of:
Microcracks
Inclusions or porosity
Delamination in composite structures
Identifying these flaws before dispatch helps avoid premature tool failure.
2. Surface Integrity Check
High-performance carbide tools often undergo grinding and polishing. Surface-focused NDT methods like liquid penetrant testing and visual inspection under magnification help ensure:
No surface cracks or chips
No grinding burns
No coating delamination (for coated carbide)
3. Quality Assurance Without Sacrificing Inventory
Unlike destructive testing (e.g., breaking a sample), NDT allows 100% inspection of finished carbide tools without wasting parts. This is particularly useful for:
Medical-grade carbide components
Examples of NDT Applications in Carbide Tools
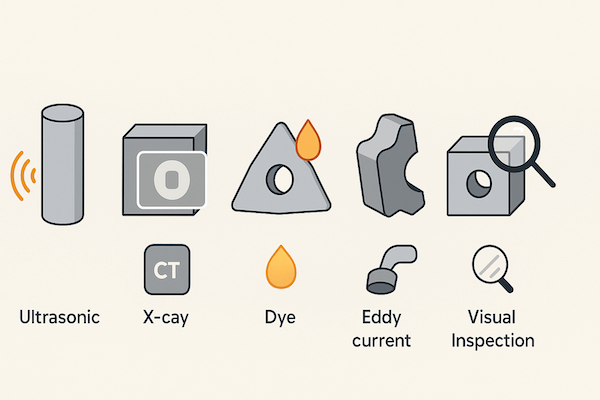
| NDT Method | Use Case in Carbide Tools |
|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Testing | Detecting internal cracks in solid carbide rods |
| X-ray/CT Scan | Revealing voids or porosity in sintered blanks |
| Penetrant Testing | Identifying micro-cracks in ground tool surfaces |
| Eddy Current | Verifying surface integrity in complex geometries |
| Visual Inspection | Checking chamfers, edge chips, and coatings |
NDT and Automation in Modern Carbide Production
Today’s advanced carbide manufacturing lines often include automated NDT stations, where tools are scanned for flaws before moving to packaging. These automated systems:
Reduce manual inspection errors
Speed up throughput
Ensure consistent inspection quality
Some producers even offer digital NDT traceability, where each carbide tool is linked to its inspection report using QR codes or serial numbers.
Conclusion
Non-Destructive Testing is essential for delivering flaw-free, high-performance tungsten carbide tools to demanding industries. By combining surface and volumetric inspection methods, NDT helps manufacturers detect hidden defects, improve process control, and build customer trust. As carbide tools become more advanced and customized, NDT remains a cornerstone of reliable production and long-lasting performance.
