Wear parts are critical for industries like mining, oil & gas, construction, metalworking, and manufacturing.
These parts face constant friction, impact, and corrosion. If the material is weak, machines fail, downtime increases, and costs rise.
Tungsten carbide has become the preferred solution because it combines hardness and toughness.
But not all carbides are the same. The difference often comes from the carbide grade—a mix of grain size, binder content, and additives.
This article explains what premium carbide grades are, why they matter for durable wear parts, and how decision-makers can choose the best grade for their business.
What Makes a Premium Carbide Grade?
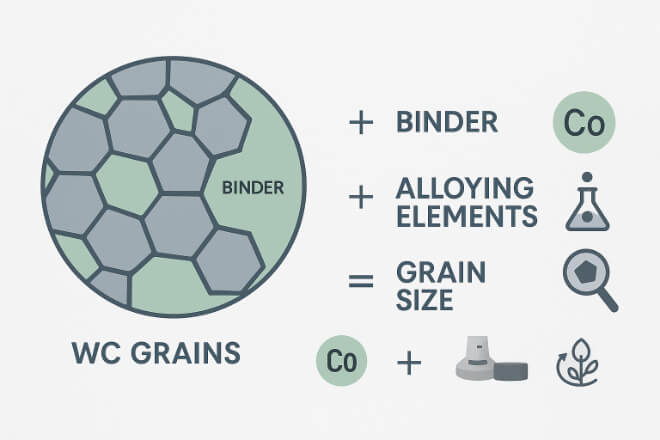
A carbide grade is defined by its microstructure: tungsten carbide grains + metallic binder (usually cobalt or nickel). Premium grades stand out because they offer:
Optimized grain size for balance between hardness and toughness.
High-purity raw materials that reduce weak spots.
Special alloying elements like chromium, vanadium, or tantalum carbides that improve corrosion resistance and control grain growth.
Advanced production methods such as hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to reduce porosity.
Premium carbide grades cost more to produce, but they extend service life and lower downtime—leading to better long-term savings.
The Role of Grain Size
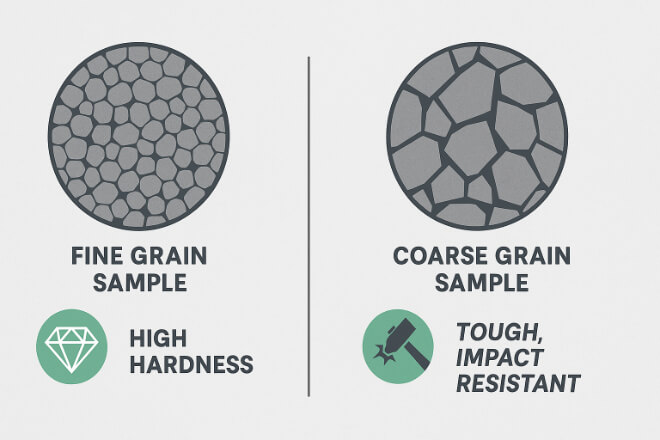
Grain size directly affects performance:
Fine grain carbides (submicron or ultrafine): Extremely hard, excellent for cutting tools and abrasive wear.
Medium grain carbides: Balance between wear resistance and toughness, suitable for general-purpose wear parts.
Coarse grain carbides: More impact-resistant, used in mining picks and drilling tools.
Premium grades often include grain-size control technology to make performance more predictable.
Binder Content and Its Impact
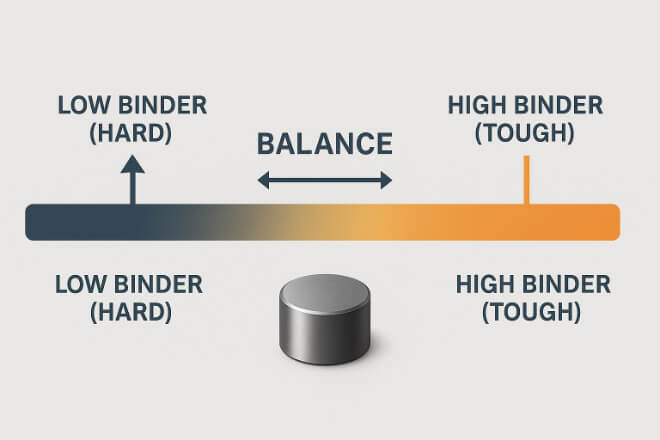
The binder (cobalt or nickel) holds WC grains together. Its percentage defines toughness vs hardness:
Low binder (3–6%): Very hard, best for abrasion but less tough.
Medium binder (6–10%): Balanced properties, common in valves, seals, and nozzles.
High binder (10–20%): More toughness, used for impact-heavy tools like hammers or cutting picks.
Premium grades carefully adjust binder levels for the target application. Nickel-binder grades are especially valued in corrosive environments.
Additives and Alloying Elements
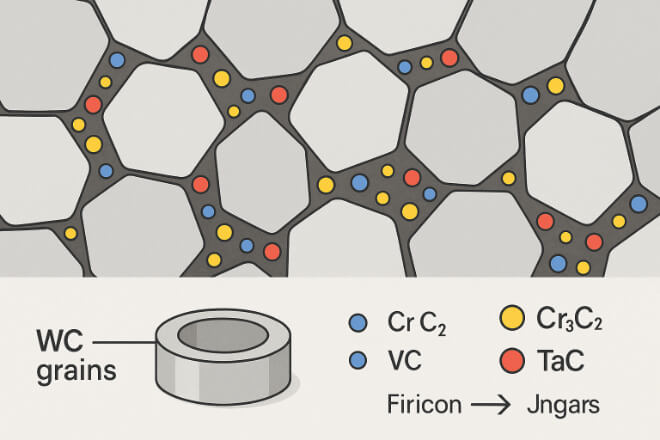
Adding small amounts of secondary carbides makes premium grades stronger:
Chromium carbide (Cr₃C₂): Improves corrosion resistance.
Vanadium carbide (VC): Prevents grain growth, increases hardness stability.
Tantalum carbide (TaC) or Titanium carbide (TiC): Enhances hot hardness.
These additives are why premium grades perform better in specialized industries like aerospace, oil & gas, and high-temperature processing.
Premium Carbide Grades for Abrasive Environments

In mining, construction, and milling, abrasion is the biggest challenge. Premium grades with fine grains and low binder are ideal.
They resist scratches, grooves, and surface wear caused by sand, rock, and hard particles.
Applications: Crusher hammers, wear plates, drill bits.
Benefits: Longer tool life, reduced maintenance, better cost-per-hour performance.
Premium Carbide Grades for Corrosive Environments
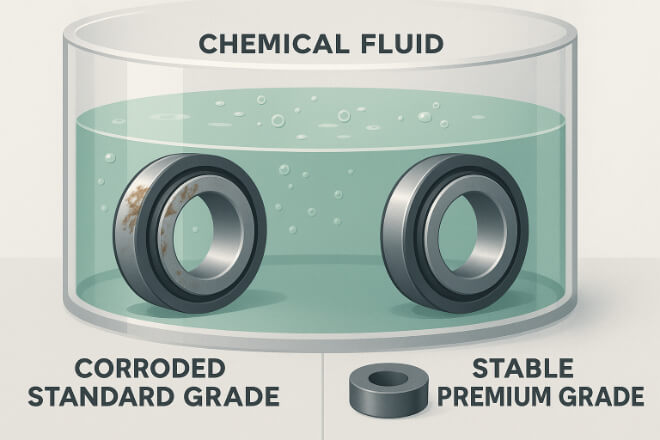
In oil & gas, chemical, and marine industries, wear parts face corrosive fluids. Premium grades with nickel binders and chromium additives last much longer.
Applications: Valves, pump seals, flow control components.
Benefits: Prevent binder leaching, resist acids and brines, ensure stable sealing surfaces.
Premium Carbide Grades for High-Temperature Conditions

At high temperatures, regular carbides lose hardness. Premium grades with tantalum or titanium carbides maintain strength.
Premium Carbide Grades for Impact Resistance

Some industries demand toughness over pure hardness. Premium coarse-grain carbides with high binder content absorb shocks without fracturing.
Applications: Mining picks, road milling tools, drilling tools.
Benefits: Reduced chipping, better safety, predictable replacement cycles.
Inspection and Quality Standards

Premium grades are not only about chemistry—they also follow strict inspection standards:
Microstructure analysis to verify uniform binder distribution.
ISO certification and traceability.
Decision-makers should always request inspection certificates to confirm grade quality.
Cost vs Value of Premium Grades
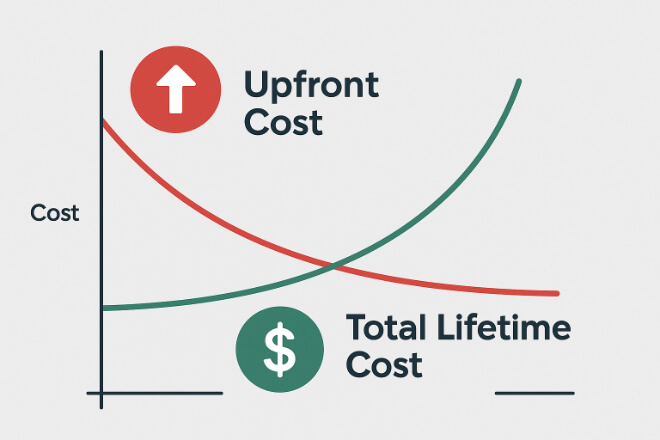
Premium carbide grades are more expensive than standard grades. However, the total cost of ownership tells the real story.
Lower downtime: Fewer breakdowns and replacements.
Higher productivity: Machines run longer at optimal speed.
Better ROI: Premium grades pay back through reduced maintenance and lost production time.
For critical equipment, the extra cost is a smart investment.
How to Choose the Right Premium Grade
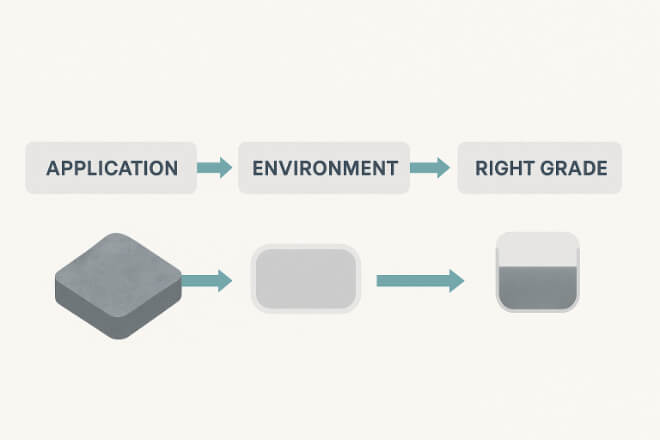
Decision-makers should consider:
Application conditions (abrasion, corrosion, temperature, or impact).
Expected lifetime vs downtime cost.
Supplier capability in producing certified premium grades.
Custom solutions if the standard grade does not meet requirements.
The best choice is the grade that delivers the lowest total cost per operating hour.
Key Takeaways for Decision-Makers

Premium carbide grades improve reliability and cut hidden costs.
Grain size, binder content, and additives define performance.
Match grade to environment: abrasion, corrosion, heat, or impact.
Always verify supplier quality with test reports and certifications.
Think long-term ROI, not just purchase price.
Conclusion
Premium carbide grades are the foundation of durable wear parts. From mining to aerospace, they help machines work longer, safer, and more efficiently.
By understanding grain size, binder levels, additives, and testing standards, decision-makers can make informed choices.
Choosing premium grades is not just about buying better material—it is about ensuring uptime, productivity, and long-term profitability.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
