In high-temperature industrial operations, equipment faces extreme thermal stress, friction, and wear.
Pumps, compressors, and rotating machinery often run at elevated temperatures for long periods, and even small material weaknesses can lead to failure.
Tungsten carbide bushings are one of the few components that can perform reliably under such conditions.
They provide excellent thermal stability, hardness, and wear resistance, making them essential in hot environments like power plants, chemical reactors, and metallurgical systems.
This article explains how tungsten carbide bushings function in high-temperature operations, their advantages compared to other materials, and best practices for selection and maintenance.
Challenges of High-Temperature Operations
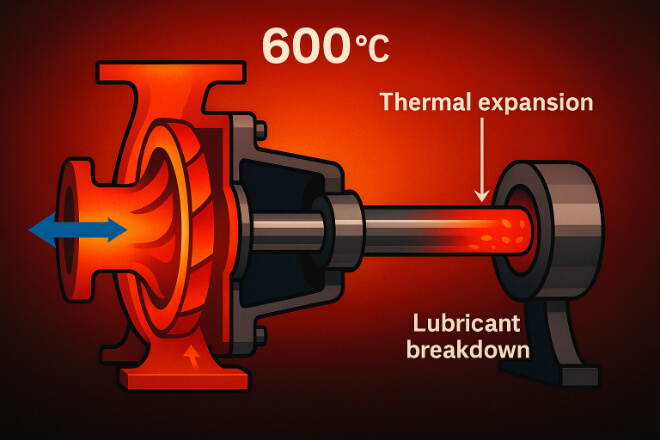
High-temperature environments are among the most demanding conditions for mechanical systems.
When temperatures exceed 300°C (572°F), traditional materials lose strength, expand excessively, or suffer oxidation.
Common Problems:
Loss of hardness – metals soften under heat, leading to deformation.
Thermal expansion – causes shaft misalignment and clearance loss.
Lubricant breakdown – leads to metal-to-metal contact.
Oxidation and corrosion – high heat accelerates chemical attack.
In continuous operations such as turbine lubrication systems or refinery pumps, these problems cause premature failure. Tungsten carbide bushings offer a stable and reliable solution.
Why Tungsten Carbide Excels at High Temperatures
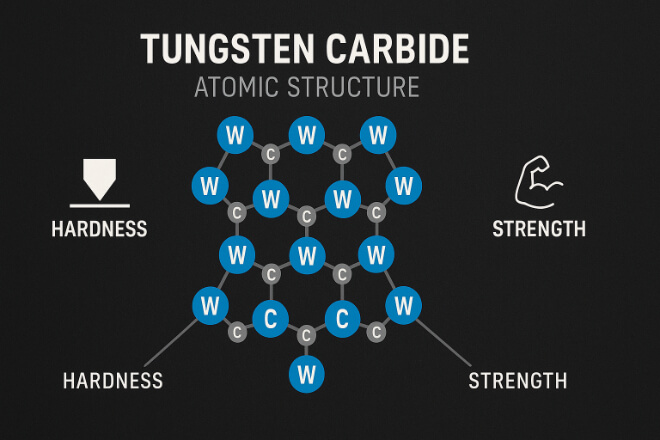
Tungsten carbide (WC) combines tungsten particles and a metallic binder (usually cobalt or nickel).
This structure gives it exceptional mechanical properties even under high heat.
Key Properties:
Hardness up to 92 HRA maintained at high temperature.
Melting point above 2800°C (5070°F).
Low thermal expansion (~4.5 × 10⁻⁶ /K) for dimensional stability.
Compressive strength >4000 MPa.
Resistance to thermal fatigue and resistance oxidation.
These characteristics make tungsten carbide bushings reliable for continuous high-load and high-temperature service.
Comparison with Other Bushing Materials
| Material | Max Operating Temp (°C) | Hardness Retention | Thermal Expansion | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronze | 250 | Low | High | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel | 400 | Medium | Medium | Good |
| Tungsten Carbide | 800+ | Excellent | Low | Excellent (Ni binder) |
As shown above, tungsten carbide maintains superior performance where other materials begin to fail.
This makes it ideal for pumps, compressors, and rotating machinery used in high-heat applications.
Applications in High-Temperature Industries
| Industry | Operating Temperature Range | Typical Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | 300–700°C | Turbine pumps, boiler feed pumps |
| Petrochemical & Refining | 200–600°C | Hot oil circulation pumps, compressors |
| Metallurgy | 400–900°C | Furnace fans, rolling mill drives |
| Chemical Processing | 250–700°C | Catalyst circulation pumps, reactors |
In all these industries, bushings made from tungsten carbide maintain tight clearances and stable operation, even when lubricants evaporate or the system cycles through thermal expansion and cooling.
Binder Selection and Its Effect on Performance
| Binder Type | Max Temp (°C) | Thermal Stability | Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobalt (Co) | 700 | Good | Moderate | High-stress pumps, turbines |
| Nickel (Ni) | 800+ | Excellent | Excellent | Hot oil, steam, corrosive media |
Nickel-bonded tungsten carbide is ideal for environments with both high temperature and corrosive chemicals, while cobalt-bonded grades are better for shock-loaded or impact-prone systems.
Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Strength
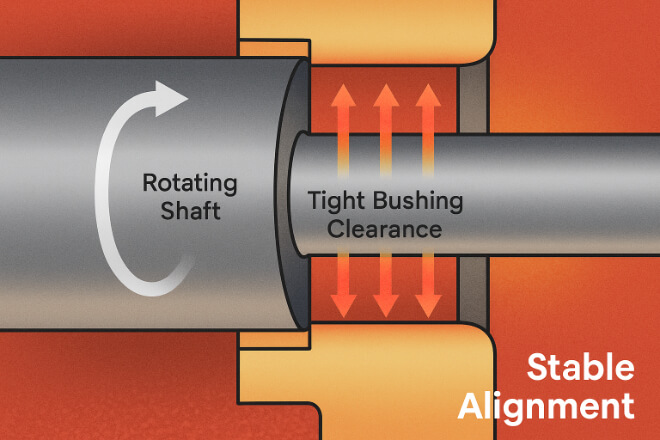
At high temperatures, maintaining the right clearance between rotating parts is critical.
Tungsten carbide’s low expansion coefficient helps prevent shaft distortion and seizure.
Even at 600°C, it retains nearly full compressive strength, avoiding deformation or cracking.
This stability ensures smooth rotation, balanced load distribution, and reduced wear on mating components.
Lubrication and Thermal Fatigue Resistance

Lubricants often lose viscosity or burn off at high temperatures, leaving components unprotected.
Tungsten carbide bushings are capable of running in dry or low-lubrication conditions, thanks to their smooth finish and hardness.
They also resist thermal fatigue, a common cause of cracking in conventional bushings. This property extends service intervals and reduces unplanned maintenance.
Real-World Example
| Industry | Old Material | Service Life (Before) | Service Life (After WC) | Downtime Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petrochemical Pump | Stainless Steel | 10 months | 3 years | ~70% |
| Power Plant Turbine Pump | Bronze | 8 months | 4 years | ~80% |
The results clearly show that tungsten carbide bushings can triple or quadruple service life in high-temperature machinery, offering measurable return on investment.
Conclusion
High-temperature industrial environments demand materials that can handle stress, heat, and wear without failure.
Tungsten carbide bushings provide unmatched durability, dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance, making them the best choice for pumps, compressors, and rotating assemblies exposed to extreme heat.
For decision-makers in energy, chemical, or metallurgical industries, adopting tungsten carbide bushings means longer uptime, lower maintenance, and superior equipment reliability.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
