Bushings are essential in machines that involve movement — they reduce friction, guide shafts, and support rotating parts.
The choice of bushing material has a big impact on reliability, performance, and maintenance cost.
Two common materials used in demanding industrial systems are tungsten carbide and bronze.
Both are strong and proven, but their performance characteristics differ greatly.
This article compares tungsten carbide vs bronze bushings, explaining where each one performs best, how long they last, and what factors affect your final choice.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide and Bronze Bushings

Tungsten carbide bushings are made from tungsten and carbon powder, sintered under high temperature and pressure.
The result is a very hard, dense, and wear-resistant material. They are often used in pumps, compressors, and drilling equipment.
Bronze bushings are made from copper alloys mixed with tin or other metals. They are softer and easier to machine, making them popular in general-purpose machinery and moderate-load systems.
The main difference lies in hardness, wear resistance, and cost — tungsten carbide is an investment for longevity, while bronze is ideal for flexibility and repairability.
Material Property Comparison
| Property | Tungsten Carbide | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRA) | 88–92 | 20–40 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 4000+ | 300–500 |
| Friction Coefficient | Very Low (0.15–0.2) | Low (0.2–0.3) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Nickel-bonded grades) | Moderate to Good |
| Cost | High | Low |
Tungsten carbide is clearly stronger and harder, while bronze provides affordability and easier replacement.
Wear and Friction Performance
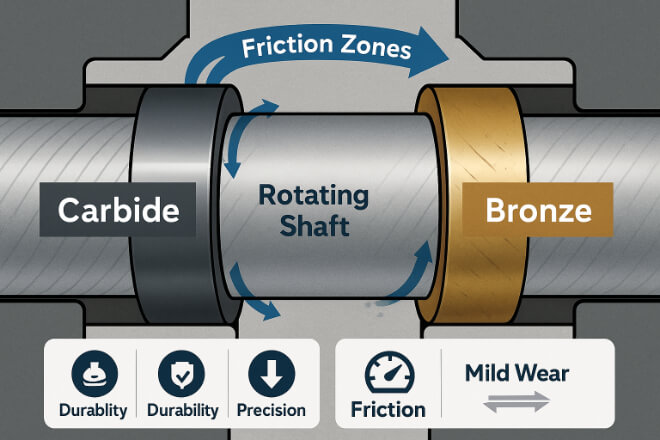
Wear resistance determines how long a bushing lasts under friction and load.
Tungsten carbide has a microstructure of hard particles that resist abrasion, even in slurry, sand, or dry-running conditions.
Bronze bushings, though self-lubricating in some grades (like oil-impregnated bronze), wear much faster when exposed to dust or abrasive fluids.
In real-world terms:
Tungsten carbide lasts 5–10 times longer in heavy-duty pumps.
Bronze is ideal for low-speed, light-load applications, like pivots and linkages.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance

Chemical stability is critical in marine, chemical, and oilfield systems.
Bronze offers moderate protection against fresh water and mild oils, but it corrodes in saltwater, ammonia, and acidic fluids.
Tungsten carbide, especially when nickel-bonded, resists corrosion from most acids and salts, maintaining its surface finish and shape even after long exposure.
For offshore, chemical, or high-moisture environments, tungsten carbide provides a far longer service life with minimal rust or pitting.
Temperature and Pressure Capability
| Condition | Tungsten Carbide | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1000°C | Up to 300°C |
| Max Pressure | 40 MPa or higher | 5–10 MPa |
| Thermal Expansion | Very Low | High |
This makes tungsten carbide suitable for boiler feed pumps, gas compressors, and turbines, while bronze fits better in medium-temperature mechanical assemblies.
Cost vs Lifespan
Upfront, tungsten carbide bushings are more expensive, often costing 4–6 times more than bronze.
However, their lifespan and reliability justify the investment.
| Parameter | Tungsten Carbide | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Price | High | Low |
| Replacement Frequency | Very Low | High |
| Expected Service Life | Up to 10× Longer | Short |
| Total Lifetime Cost | Low | High |
For companies operating 24/7, tungsten carbide bushings reduce total ownership cost by minimizing downtime and part replacement.
Ideal Applications
| Application | Preferred Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Pumps and Compressors | Tungsten Carbide | Handles wear, pressure, and heat |
| Hydraulic Systems | Bronze | Self-lubricating and easy to replace |
| Mining and Drilling Tools | Tungsten Carbide | Superior abrasion resistance |
| General Mechanical Equipment | Bronze | Low cost, simple maintenance |
If your system deals with abrasive slurries, heat, or continuous rotation, choose tungsten carbide.
For low-speed or medium-load systems, bronze offers a cost-effective alternative.
Maintenance and Repair
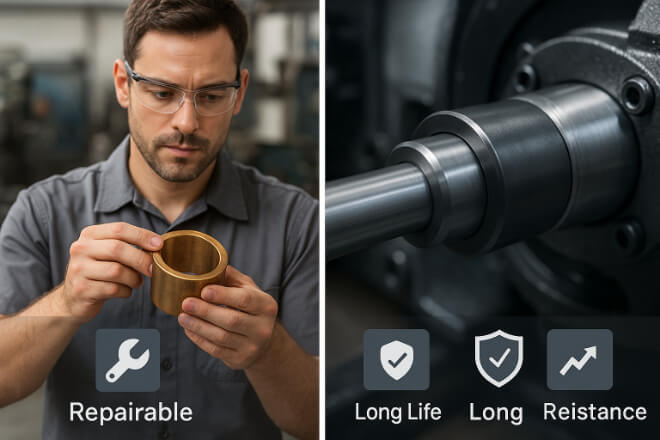

Tungsten carbide bushings are highly wear-resistant but harder to machine.
If damage occurs, they usually require replacement, not rework.
Bronze bushings, being softer, are easy to repair or re-bore. This flexibility suits smaller workshops and industries where downtime is less critical.
However, tungsten carbide’s long-term stability often eliminates the need for frequent maintenance altogether — a key advantage in continuous-process plants.
Final Verdict

If your goal is long lifespan, minimal maintenance, and top wear resistance, tungsten carbide bushings clearly outperform bronze.
If your goal is low cost, easy replacement, and good performance under moderate loads, bronze remains a solid choice.
Ultimately, the decision depends on your operating environment — tungsten carbide wins in harsh, high-load applications, while bronze fits in general-purpose systems.
Conclusion
Both materials have important roles in machinery design. But as industries push for greater uptime, energy savings, and lower maintenance cost, tungsten carbide bushings are becoming the preferred long-term solution.
Choosing the right bushing material can improve reliability, extend machine life, and reduce lifecycle costs — benefits that every decision-maker values.
If you want to know more details about any company, please feel free to contact us.
