When we think of cutting tools, mining bits, or industrial wear parts, we often picture strong, solid, high-performance components. But the origins of these incredibly tough tools actually begin with something much finer: carbide powder.
In this article, we’ll explore what carbide powder is, how it’s produced, and why it’s so critical to the manufacturing of cemented carbide tools used in some of the most demanding industrial applications.
What Is Carbide Powder?

Carbide powder typically refers to tungsten carbide (WC) powder, a gray, fine-grained ceramic-like substance made by combining tungsten (W) and carbon (C) at high temperatures.
This powder is not used directly in tooling—it serves as the raw material for making cemented carbide, a composite material where hard WC grains are bonded together with a metallic binder like cobalt (Co) or nickel (Ni).
How Is Carbide Powder Produced?
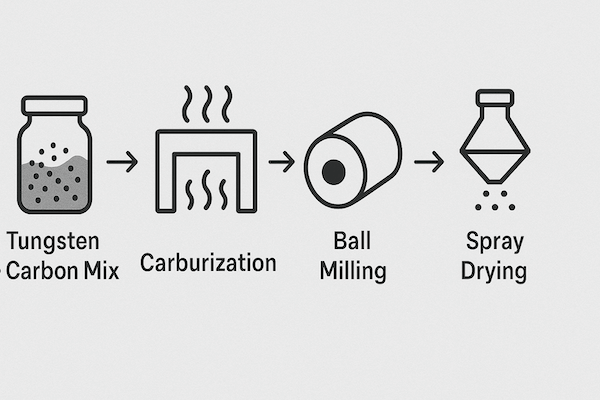
The production of carbide powder involves several precise steps:
Raw Material Preparation: High-purity tungsten and carbon sources are mixed.
Carburization: The mixture is heated in a hydrogen furnace (around 1350–1500°C), allowing tungsten and carbon to chemically bond into WC.
Milling & Particle Control: The resulting WC powder is milled to achieve the desired particle size—ranging from coarse (~5 μm) to ultrafine (<0.5 μm).
Spray Drying: WC is often combined with binder metal powders and spray-dried into granules suitable for pressing and sintering.
The final powder quality (including purity, particle size distribution, and morphology) is crucial to the performance of the finished product.
Why Carbide Powder Quality Matters
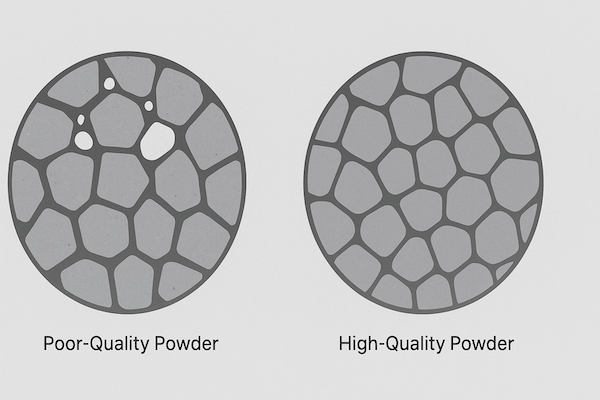
The properties of carbide powder directly affect:
Grain size control after sintering
Porosity levels and densification
Surface finish and edge sharpness
For example, using ultrafine powder allows the production of super-hard micro-grain tools, while coarse powder is better for impact-resistant mining bits.
Applications of Carbide Powder in Tool Manufacturing
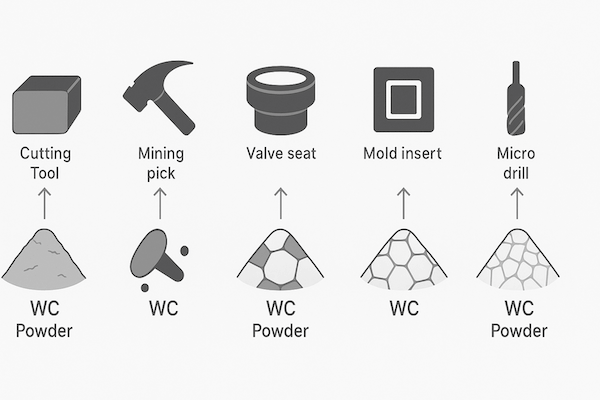
Carbide powder is the foundation of many tungsten carbide products, including:
Mining and construction tools (picks, buttons)
Wear-resistant parts (bushings, sleeves, valve seats)
Each application requires tailored powder grades for optimal results.
Additives in Carbide Powders
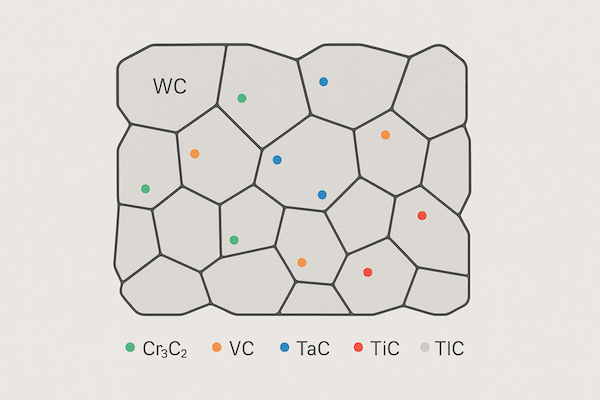
Carbide powders may include alloying elements to improve specific properties:
Vanadium carbide (VC) – grain growth control
Chromium carbide (Cr₃C₂) – corrosion resistance
Tantalum carbide (TaC) – thermal stability
Titanium carbide (TiC) – wear resistance and oxidation protection
These additives are blended into the powder before sintering, forming a more robust and tailored microstructure.
Conclusion
Carbide powder may be small in size, but it plays a huge role in modern industry. It’s the essential building block of high-performance cemented carbide tools that shape, mine, drill, and cut with precision and endurance.
Whether it’s a micro drill for electronics or a heavy-duty drill bit for mining, it all starts with powder—engineered to exact standards, processed with precision, and transformed into tools that drive the world’s most critical applications.
