Ống lót cacbua vonfram are known for their khả năng chống mài mòn, but thermal expansion mismatch with the housing can affect their performance.
Tungsten carbide has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), while materials like steel or aluminum expand more with temperature changes. This mismatch can lead to issues such as excessive wear or mechanical failure.
This article will discuss how thermal expansion mismatch affects tungsten carbide bushings and how to design housings that minimize these issues.
Understanding Thermal Expansion Mismatch
Thermal expansion mismatch occurs when two materials expand at different rates when exposed to temperature changes.
Every material has a specific coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which defines how much it expands or contracts per unit length for each degree of temperature change.
Tungsten carbide, known for its high độ cứng Và khả năng chống mài mòn, has a low CTE, which means it is less prone to expansion or contraction compared to metals like steel or aluminum.
While this makes tungsten carbide ideal for high-wear environments, it can also create challenges when it is used in systems where it interacts with other materials.
Why Thermal Expansion Mismatch Is a Concern
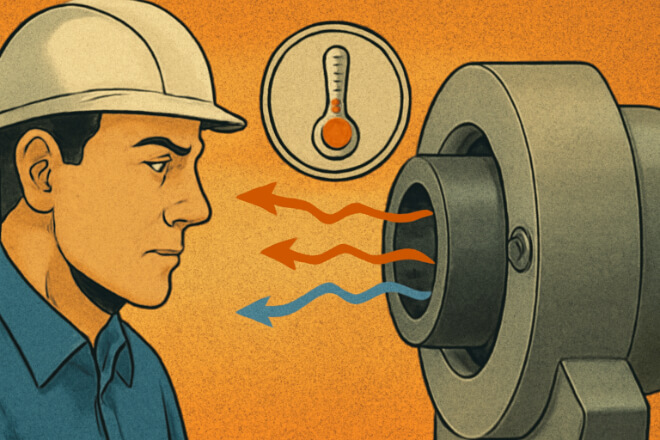
When ống lót cacbua vonfram are fitted into housings made from materials with a higher CTE.
Such as steel or aluminum, temperature changes can create a gap or pressure differential between the bushing and the housing. This can lead to several issues:
Potential Problems:
Excessive wear: If the bushing and housing are under different levels of pressure due to thermal mismatch, it can lead to uneven wear and premature failure of the bushing.
Cracking or fracturing: In extreme cases, thermal expansion mismatch can cause cracking or fracturing of the bushing or housing, especially if the material is exposed to significant temperature fluctuations.
Loss of clearance: When materials expand or contract differently, the clearance between the bushing and housing may decrease, causing the bushing to seize or become misaligned.
How to Design Housing to Accommodate Thermal Expansion

To minimize the effects of thermal expansion mismatch, proper housing design is essential. Here are key considerations for designing housings that work well with tungsten carbide bushings:
Key Design Considerations:
Allow for Expansion:
Ensure that the housing design allows for the thermal expansion of both the tungsten carbide bushing and the material around it.
This can be done by leaving enough clearance around the bushing and designing for controlled thermal expansion.
Use of Materials with Similar CTEs:
When possible, select housing materials with a CTE that closely matches that of tungsten carbide.
Nickel-based alloys or stainless steel can be good options, as their expansion rates are closer to that of tungsten carbide.
Clearance Management:
Proper clearance between the bushing and housing is critical. As temperature changes, the materials will expand or contract.
So the housing should be designed with enough tolerance to accommodate these changes without causing deformation or damage.
Tempercooling systemsorinsulation cature Control:
In some cases, incorporating temperature control measures such asan help maintain the temperature within an optimal range, reducing the effects of thermal expansion mismatch.
Common Housing Materials and Their CTEs
The material used for the housing can have a significant impact on how well it accommodates thermal expansion mismatch.
Below is a comparison of the typical materials used for pump housings and their CTEs:
1). Material CTE Comparison:
| Vật liệu | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (µm/m·°C) |
|---|---|
| Cacbua Vonfram | 4–5 |
| Stainless Steel | 10–16 |
| Aluminum | 22–25 |
| Nickel Alloys | 11–13 |
2). Key Takeaways:
Tungsten carbide has a low CTE, which is beneficial for khả năng chống mài mòn but requires careful material selection for housings.
Stainless steel and nickel alloys have CTEs closer to that of tungsten carbide, making them better options for housing materials.
Aluminum has a much higher CTE, which can lead to more significant thermal expansion mismatch when used with tungsten carbide.
Best Practices for Managing Thermal Expansion Mismatch
In addition to selecting the right housing material and ensuring proper clearance, there are other best practices that can help manage thermal expansion mismatch:
Additional Best Practices:
Preload Mechanism:
A preload mechanism can be used to ensure that the bushing fits securely within the housing even when temperature fluctuations occur.
Thermal Stress Analysis:
Conducting a thermal stress analysis during the design phase can help predict how the housing and bushing will respond to temperature changes, allowing for better design decisions.
Material Coatings:
Applying coatings to either the tungsten carbide bushing or the housing can provide an additional layer of protection against thermal stress and wear caused by temperature fluctuations.
Phần kết luận
Proper housing design is crucial to managing thermal expansion mismatch in tungsten carbide bushings.
By selecting the right materials, ensuring proper clearance, and considering temperature changes, you can prevent wear and damage.
Proper management ensures the longevity and efficiency of both the bushing and the system.
Nếu bạn muốn biết thêm chi tiết về bất kỳ công ty nào, vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi.
