In pumps, compressors, turbines, and mixers, seal rings are small but essential parts.
They prevent leaks, protect systems, and reduce downtime. Choosing the right seal ring material is not only an engineering decision but also a business one.
Among many options, vòng đệm cacbua vonfram are trusted worldwide. But there are two main types: nickel-bonded and cobalt-bonded. Both have unique properties, and the right choice depends on the application.
This article compares the two, explaining their strengths, differences, and best uses, helping decision-makers select the right solution for long-term performance.
Vòng đệm cacbua vonfram là gì?

Tungsten carbide is made by combining tungsten and carbon powder, pressed together with a binder. The binder gives toughness and flexibility.
Cobalt binder → adds strength and độ dẻo dai
Nickel binder → adds khả năng chống ăn mòn
These rings are used in demanding industries where reliability and safety are critical.
Applications include:
Oil & gas pumps and compressors
Chemical plants and refineries
Power generation systems
Marine and offshore pumps
Food and pharmaceutical equipment
The Role of the Binder
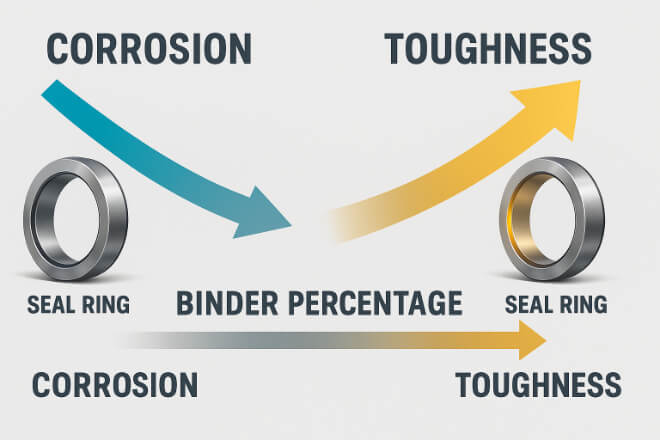
The binder is not just filler. It changes the performance of the ring.
Cobalt: Improves độ dẻo dai, making the ring resist cracking under pressure.
Nickel: Improves khả năng chống ăn mòn, making the ring safer in acids and seawater.
Without the right binder, the seal ring may fail too soon, costing money and time.
Nickel-Bonded Tungsten Carbide Seal Rings
1). Key Properties
Strong resistance to acids, seawater, and chemicals
Stable performance in marine and chemical environments
Slightly lower độ dẻo dai compared with cobalt-bonded types
2). Benefits
Best choice for corrosion-heavy environments
Reduces risk of leaks in chemical and marine systems
Longer service life in pumps exposed to corrosive media
3). Limitations
Higher cost than cobalt-bonded rings
Not as tough for heavy shock loads
Cobalt-Bonded Tungsten Carbide Seal Rings

1). Key Properties
Xuất sắc độ dẻo dai and strength under load
Reliable in dầu, khí đốt, và các ngành công nghiệp khai thác mỏ
Less corrosion resistance compared to nickel-bonded
2). Benefits
Handles pressure and impact better
Lower cost compared with nickel-bonded rings
Performs well in abrasive and high-load systems
3). Limitations
Weaker against acids and seawater
May require more frequent replacement in corrosive applications
So sánh song song
| Tính năng | Nickel-Bonded Rings | Cobalt-Bonded Rings |
|---|---|---|
| Khả năng chống ăn mòn | Excellent (acid, seawater, chemicals) | Moderate (weaker against acids) |
| Độ dẻo dai | Good, lower than cobalt | Rất cao |
| Khả năng chống mài mòn | Mạnh | Mạnh |
| Best Industry | Chemical, marine, pharmaceuticals | Oil, gas, mining, power plants |
| Trị giá | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
Industry Applications

1). Dầu khí Ngành công nghiệp
Cobalt-bonded rings are common in drilling pumps and compressors because they handle pressure and shock.
2). Xử lý hóa học
Nickel-bonded rings resist acids and solvents, making them safer and more cost-effective.
3). Marine and Offshore
Nickel-bonded rings last longer in seawater systems compared to cobalt-bonded.
4). Sản xuất điện
Cobalt-bonded rings perform well in turbines where high load strength is more important than corrosion.
How to Select the Right Bonded Seal Ring
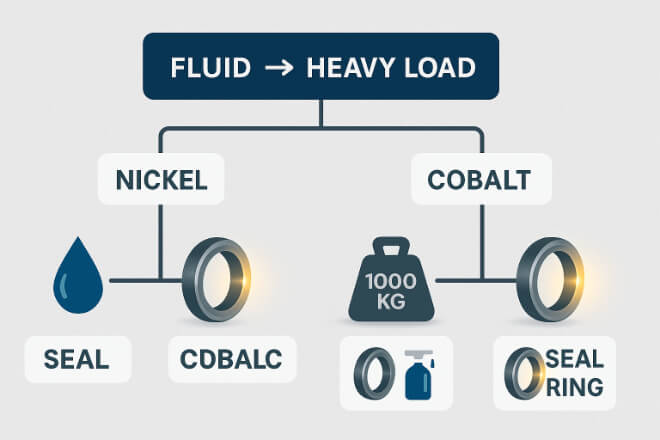
Decision-makers should evaluate:
Fluid Type – Acidic or seawater? Choose nickel. Heavy load and impact? Choose cobalt.
Operating Conditions – High pressure vs high corrosion.
Budget – Nickel-bonded costs more but lasts longer in corrosive environments.
Industry Needs – Follow best practices in your field.
Cân nhắc về chi phí và ROI
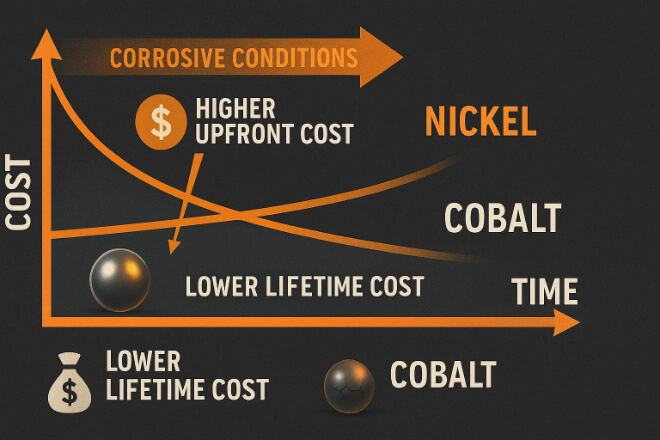
Nickel-bonded: Higher initial cost but lower replacement frequency in corrosive systems.
Cobalt-bonded: Lower cost upfront but shorter life in chemical-heavy environments.
For decision-makers, the goal is to balance initial budget with lifetime value.
Maintenance and Replacement
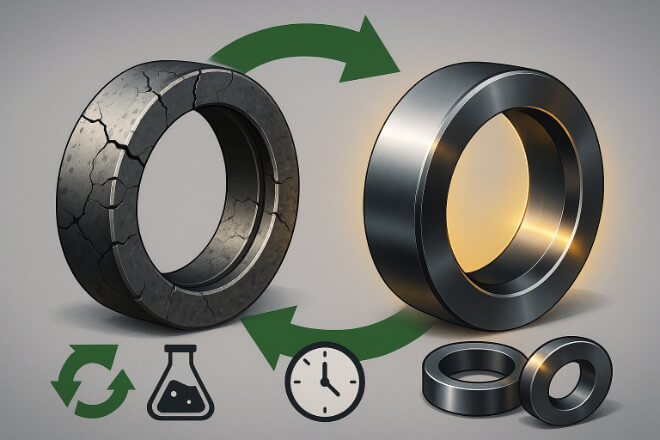

Both nickel- and cobalt-bonded tungsten carbide rings need care:
Inspect regularly for cracks, wear, or corrosion marks
Replace on time before leaks or failures occur
Recycling option: worn tungsten carbide rings can be recycled, lowering cost
Ví dụ trường hợp

1). Marine Pump Manufacturer
Switched to nickel-bonded rings for seawater pumps. Result: longer seal life and reduced warranty claims.
2). Oilfield Compressor
Used cobalt-bonded rings to handle shock and high pressure. Result: stronger performance in drilling operations.
3). Chemical Plant
Nickel-bonded rings replaced stainless steel seals. Result: 50% longer service life and improved safety.
Business Value for Decision-Makers

For company leaders, the binder choice affects:
Machine uptime
Maintenance cost
Safety standards
Long-term ROI
Nickel-bonded → best where corrosion is the biggest risk.
Cobalt-bonded → best where load and toughness are most important.
How to Source Tungsten Carbide Seal Rings

When buying, companies should:
Confirm binder type (nickel or cobalt) with supplier
Check ISO certifications for quality
Ask for case references in your industry
Choose suppliers with local stock for fast delivery
Phần kết luận
Both nickel-bonded and cobalt-bonded tungsten carbide seal rings deliver excellent performance, but they serve different needs.
Nickel-bonded → better for corrosion resistance
Cobalt-bonded → better for toughness and heavy loads
For decision-makers, the key is understanding the environment and matching the right binder type to the system.
This ensures safety, reduces downtime, and improves long-term savings.
Nếu bạn muốn biết thêm chi tiết về bất kỳ công ty nào, vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi.
