Ống lót cacbua vonfram are essential components in industries that require high wear resistance and durability, such as ô tô, khai thác mỏ, Và hàng không vũ trụ.
One critical factor in the performance of these bushings is the grain size of the tungsten carbide material used to manufacture them.
In this blog, we will explore the differences between micrograin and submicron tungsten carbide bushings, the benefits of each, and how to select the right one for your specific application.
What is Micrograin Tungsten Carbide?
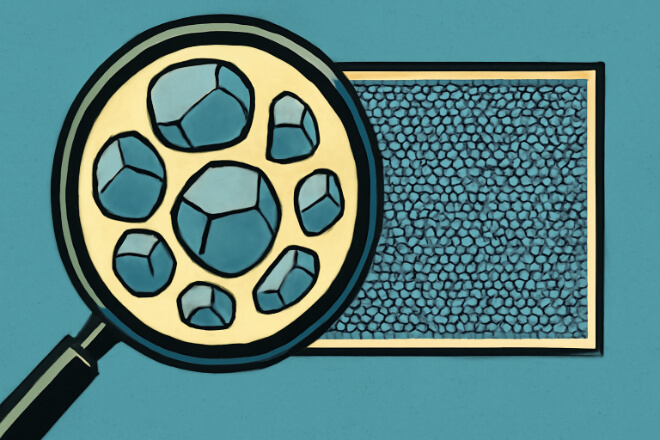
Micrograin tungsten carbide is a material made from tungsten carbide particles that have a relatively larger size compared to submicron tungsten carbide. These grains typically range from 1–5 microns in size.
The micrograin structure gives the material a balance between độ cứng Và độ dẻo dai, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
1). Properties of Micrograin Tungsten Carbide:
Toughness: Micrograin tungsten carbide has excellent impact resistance, which makes it ideal for applications where shock loads are common.
Wear Resistance: While not as wear-resistant as submicron tungsten carbide, micrograin tungsten carbide still provides excellent wear resistance, especially in moderate to heavy-duty applications.
Machinability: The larger grain size of micrograin tungsten carbide makes it easier to machine compared to submicron tungsten carbide.
2). Applications of Micrograin Tungsten Carbide:
Heavy machinery: Micrograin ống lót cacbua vonfram are ideal for heavy-duty applications where toughness is more critical than extreme wear resistance.
Cutting tools: Tools that need to resist impact forces but are not subjected to ultra-high wear can benefit from micrograin tungsten carbide.
What is Submicron Tungsten Carbide?
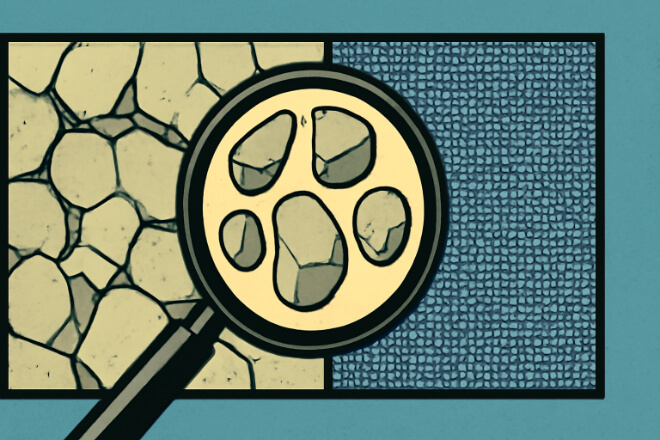
Submicron tungsten carbide is made from tungsten carbide particles that are smaller than 1 micron in size, typically ranging from 0.2–1 micron.
This fine grain structure provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Submicron tungsten carbide bushings are designed for applications that require maximum durability and performance under extreme conditions.
1). Properties of Submicron Tungsten Carbide:
Cao Khả năng chống mài mòn: The smaller grain size increases the material’s surface area, which contributes to better wear resistance. Submicron tungsten carbide is ideal for high-speed or abrasive environments where excessive wear is a concern.
Độ cứng: Submicron tungsten carbide is much harder than micrograin tungsten carbide, making it suitable for precision components that need to maintain a sharp, smooth surface over time.
Brittleness: The fine grain structure of submicron tungsten carbide increases its brittleness. While it offers exceptional hardness, it is more prone to cracking under shock or impact.
2). Applications of Submicron Tungsten Carbide:
Precision machinery: For applications requiring high wear resistance and minimal tolerance variations, submicron tungsten carbide bushings are ideal.
High-speed bearings: In environments where speed and efficiency are crucial, such as pumps or turbochargers, submicron tungsten carbide is often used to reduce friction and improve performance.
Comparing Micrograin and Submicron Tungsten Carbide Bushings
When choosing between micrograin and submicron tungsten carbide for bushings, several factors must be considered, including the operating conditions, performance requirements, and budget.
| Tài sản | Micrograin Tungsten Carbide | Submicron Tungsten Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Kích thước hạt | 1–5 microns | 0.2–1 micron |
| Khả năng chống mài mòn | High, but lower than submicron | Extremely high, ideal for abrasive conditions |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, suitable for high-impact environments | Lower, more brittle under shock loads |
| Độ cứng | Moderate hardness | Độ cứng rất cao |
| Độ dẻo dai | High, suitable for shock-loading conditions | Lower toughness, prone to cracking |
| Khả năng gia công | Easier to machine due to larger grain size | More difficult to machine due to fine grain structure |
| Ideal Applications | Heavy machinery, cutting tools | Precision machinery, high-speed bearings |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Micrograin and Submicron Tungsten Carbide
1). Application Requirements
Heavy-duty and high-impact environments: Micrograin tungsten carbide is better suited for these applications due to its độ dẻo dai and resistance to impact.
Precision and wear-resistant applications: Submicron tungsten carbide is ideal for high-speed, high-wear conditions where hardness and long-lasting performance are required.
2). Operating Conditions
High-Speed Operations: Submicron tungsten carbide’s superior wear resistance makes it the best choice for high-speed applications where friction reduction and longevity are critical.
Moderate or Low-Speed, High-Impact: Micrograin tungsten carbide is more suited for environments where impact resistance is more important than khả năng chống mài mòn.
3). Cost and Machinability
Micrograin Tungsten Carbide: The lower cost and easier machinability make micrograin tungsten carbide bushings a cost-effective choice for less demanding applications.
Submicron Tungsten Carbide: While submicron tungsten carbide bushings are more expensive and harder to machine, their exceptional performance in high-wear conditions can justify the cost in critical applications.
Comparison of Applications for Micrograin and Submicron Tungsten Carbide
| Ứng dụng | Recommended Tungsten Carbide Type |
|---|---|
| Heavy Machinery | Micrograin Tungsten Carbide |
| Precision Machinery | Submicron Tungsten Carbide |
| Dụng cụ cắt | Micrograin Tungsten Carbide |
| High-Speed Bearings | Submicron Tungsten Carbide |
The Role of Binder Content in Micrograin vs. Submicron Tungsten Carbide
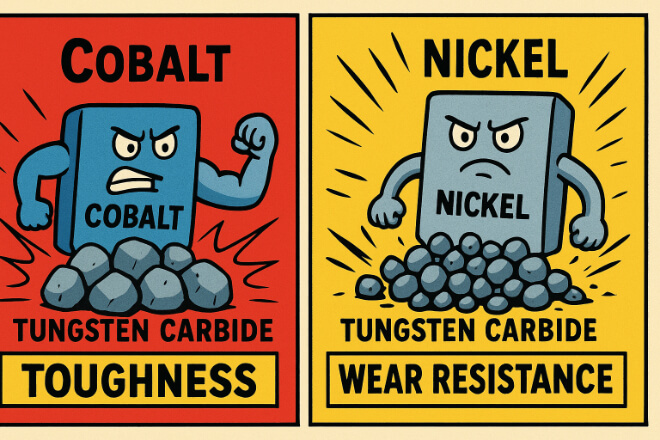
The binder content, typically cobalt or nickel, affects the overall độ dẻo dai Và khả năng chống mài mòn of both micrograin and submicron tungsten carbide.
Higher binder content tends to increase toughness but decrease độ cứng, whereas lower binder content improves hardness but reduces toughness.
Understanding how binder content affects the material’s performance is crucial in choosing the right grade for your application.
Cobalt-Bonded Tungsten Carbide: Typically used in micrograin tungsten carbide, offering a balance between hardness and toughness.
Nickel-Bonded Tungsten Carbide: Often used for submicron tungsten carbide, providing better corrosion resistance and higher thermal stability.
Phần kết luận
Understanding the differences between micrograin and submicron tungsten carbide bushings is essential for selecting the right material for specific industrial applications.
While micrograin tungsten carbide offers superior toughness for high-impact environments, submicron tungsten carbide provides excellent wear resistance and hardness for high-speed and precision applications.
By evaluating the application requirements, operating conditions, and cost considerations, manufacturers can choose the most suitable tungsten carbide bushing to maximize performance and extend the life of their machinery.
Nếu bạn muốn biết thêm chi tiết về bất kỳ công ty nào, vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi.
