Trong các ngành công nghiệp mà máy móc phải liên tục chịu ma sát, va đập và mài mòn, việc duy trì thiết bị hoạt động hiệu quả là một thách thức hàng ngày.
Một giải pháp đã chuyển đổi hiệu suất trong những môi trường khắc nghiệt này là sử dụng các bộ phận hao mòn cacbua vonfram.
Các bộ phận này được thiết kế để bền hơn, hoạt động mạnh hơn và chống hư hỏng tốt hơn so với các bộ phận bằng thép hoặc hợp kim truyền thống.
Đối với những người ra quyết định, việc hiểu các bộ phận hao mòn cacbua vonfram là gì, chúng được sử dụng ở đâu và cách lựa chọn chúng là chìa khóa để cải thiện năng suất và giảm thời gian chết máy.
Bộ phận mài mòn cacbua vonfram là gì?
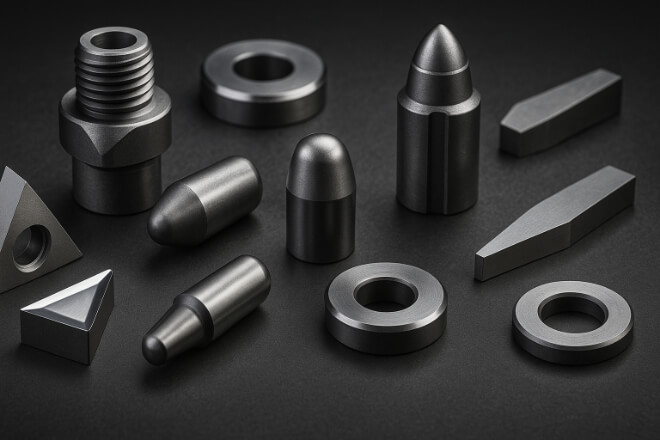

Các bộ phận chịu mài mòn bằng cacbua vonfram là các thành phần máy được làm từ hợp chất của các nguyên tử vonfram và cacbon, liên kết với nhau bằng chất kết dính kim loại (thường là coban hoặc niken).
Sự kết hợp này tạo ra một vật liệu cực kỳ cứng và đặc, có độ cứng chỉ sau kim cương.
Thuật ngữ “bộ phận chịu mài mòn” dùng để chỉ các thành phần chịu mài mòn cơ học trong quá trình hoạt động, chẳng hạn như lưỡi cắt, vòi phun, phớt, ống lót, khuôn và đầu nghiền.
Bằng cách sử dụng cacbua vonfram, các bộ phận này có khả năng chống mài mòn, xói mòn và biến dạng vượt trội.
Tại sao cacbua vonfram được sử dụng cho các bộ phận chịu mài mòn

Có một số lý do khiến các ngành công nghiệp đầu tư vào các bộ phận chịu mài mòn bằng cacbua vonfram thay vì các bộ phận bằng thép hoặc gốm tiêu chuẩn.
Những lợi ích chính bao gồm:
Cao độ cứng – Giữ nguyên hình dạng và độ sắc bén khi chịu tải trọng nặng.
Khả năng chống mài mòn – Giảm tần suất thay thế.
Khả năng chịu nhiệt – Hoạt động tốt ở nhiệt độ cao.
Chống ăn mòn – Chống lại sự tấn công của hóa chất trong môi trường khắc nghiệt.
Hiệu quả về chi phí – Chi phí ban đầu cao hơn nhưng chi phí vận hành trọn đời thấp hơn.
Ứng dụng phổ biến của các bộ phận mài mòn cacbua vonfram

Các chi tiết chịu mài mòn bằng cacbua vonfram được sử dụng trong các ngành công nghiệp đòi hỏi các linh kiện bền bỉ, hiệu suất cao. Một số ví dụ bao gồm:
Khai thác mỏ và khai thác đá – Mũi khoan, búa nghiền và tấm mài mòn.
Dầu khí – Ghế van, phớt bơm và các bộ phận kiểm soát lưu lượng.
Gia công kim loại – Khuôn mẫu, lưỡi cắt và mũi đột.
Xây dựng – Răng phay đường, dụng cụ khoan móng.
Nông nghiệp – Dụng cụ làm đất, lưỡi gặt.
Hàng không vũ trụ – Ống lót và các bộ phận dẫn hướng chống mài mòn.
Các loại phụ tùng hao mòn cacbua vonfram
Mỗi ngành công nghiệp đòi hỏi thiết kế và cấp độ khác nhau của các chi tiết cacbua vonfram. Sau đây là các loại phổ biến và công dụng chính của chúng:
| Kiểu | Ứng dụng chính |
|---|---|
| Dụng cụ cắt | Gia công kim loại, nhựa và vật liệu composite |
| Mặc tấm | Bảo vệ bề mặt máy chịu tác động mạnh |
| Vòi phun | Phun mài mòn, phun hoặc xử lý chất lỏng |
| Ống lót và Vòng bi | Giảm ma sát ở các bộ phận quay |
| Mẹo nghiền | Thiết bị khai thác và nghiền đá |
Các loại và thành phần của cacbua vonfram
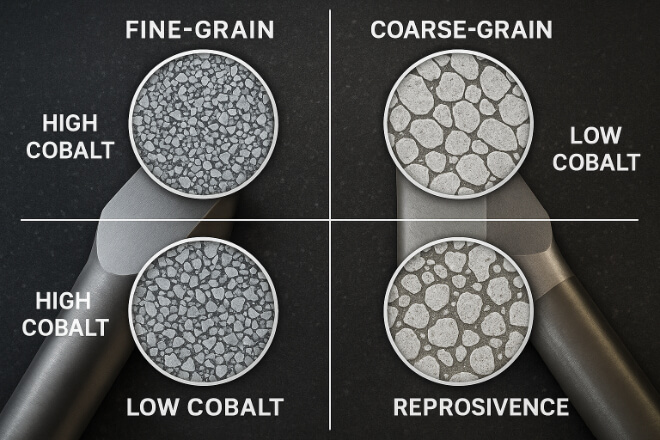
Không phải tất cả cacbua vonfram đều giống nhau. Các nhà sản xuất điều chỉnh kích thước hạt bột cacbua vonfram và hàm lượng kim loại kết dính để phù hợp với các ứng dụng cụ thể.
Cacbua hạt mịn – Tốt nhất cho mục đích cắt chính xác và khả năng chống mài mòn cao.
Cacbua hạt thô – Chịu được va đập mạnh tốt hơn.
Chất kết dính coban cao – Cải thiện độ dẻo dai nhưng giảm độ cứng.
Chất kết dính coban thấp – Tăng độ cứng nhưng có thể giòn hơn.
Việc lựa chọn đúng loại sẽ đảm bảo bộ phận chịu mài mòn hoạt động tối ưu trong môi trường làm việc của nó.
Các bộ phận mài mòn cacbua vonfram được sản xuất như thế nào
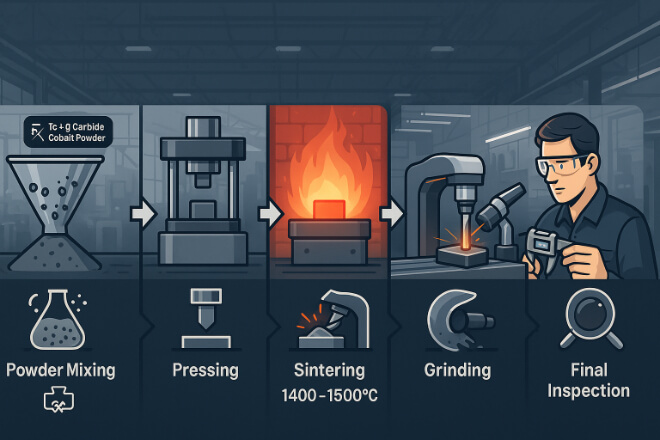
Quá trình sản xuất thường bao gồm các bước sau:
Chuẩn bị bột – Trộn bột cacbua vonfram với một chất kết dính.
Ép – Định hình bột theo hình dạng mong muốn.
Thiêu kết – Nung nóng ở nhiệt độ cao để kết dính các hạt lại với nhau.
Hoàn thiện – Mài, mài hoặc phủ để có kích thước chính xác và chất lượng bề mặt.
Kiểm tra chất lượng – Kiểm tra độ cứng, mật độ và sức mạnh.
Lựa chọn phụ tùng mài mòn cacbua vonfram phù hợp
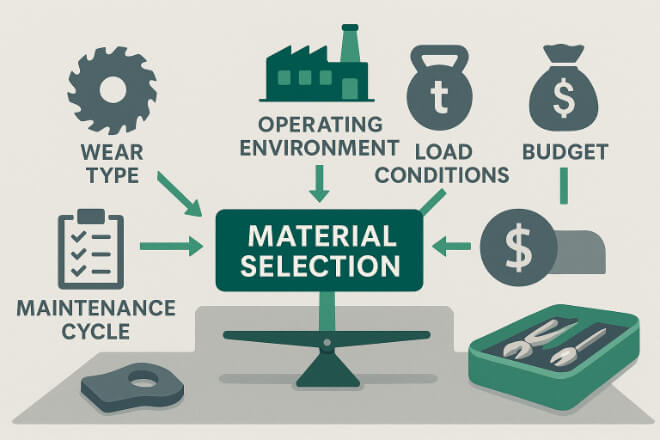
Khi lựa chọn các bộ phận chịu mài mòn cho thiết bị của mình, người ra quyết định nên cân nhắc:
Môi trường hoạt động – Nhiệt độ, độ ẩm, tiếp xúc với hóa chất.
Loại hao mòn – Mài mòn, xói mòn, ăn mòn hoặc va đập.
Điều kiện tải – Áp suất không đổi hoặc tải trọng va chạm lặp đi lặp lại.
Tần suất thay thế – Chu kỳ bảo trì dự kiến.
Ngân sách và chi phí vòng đời – Cân bằng giữa giá ban đầu và tổng chi phí sở hữu.
Mẹo bảo trì để kéo dài tuổi thọ
Ngay cả những vật liệu cứng nhất cũng có thể hỏng sớm nếu không được bảo trì đúng cách. Các biện pháp tốt nhất bao gồm:
| Bước bảo trì | Lợi ích |
|---|---|
| Kiểm tra thường xuyên | Xác định hao mòn trước khi nó gây hư hỏng cho máy |
| Bôi trơn đúng cách | Giảm ma sát và tích tụ nhiệt |
| Vệ sinh sau khi sử dụng | Ngăn ngừa sự tích tụ hóa chất hoặc mài mòn |
| Thay thế trước khi hỏng | Ngăn ngừa thời gian ngừng hoạt động tốn kém và thiệt hại thứ cấp |
| Sử dụng cài đặt đúng | Đảm bảo các bộ phận phù hợp và hoạt động như thiết kế |
Yếu tố chi phí cho các bộ phận mài mòn cacbua vonfram
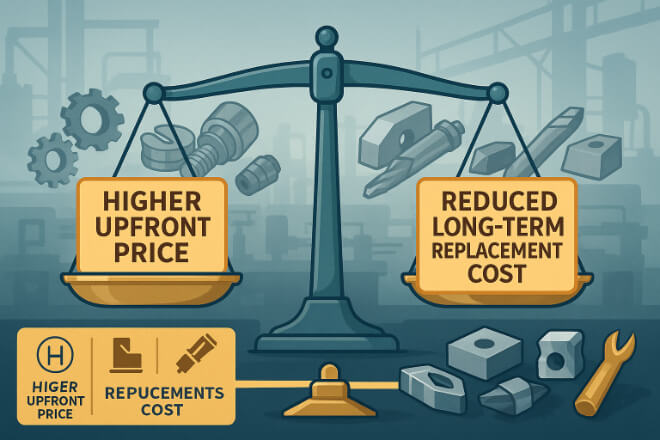
Giá của các bộ phận mài mòn cacbua vonfram phụ thuộc vào một số yếu tố:
Cấp độ vật liệu – Cấp độ cứng cao hơn thường có giá cao hơn.
Độ phức tạp của bộ phận – Hình dạng chính xác và dung sai chặt chẽ làm tăng chi phí.
Số lượng đặt hàng – Đơn hàng số lượng lớn thường làm giảm giá đơn vị.
Lớp phủ – Các phương pháp xử lý bề mặt bổ sung làm tăng chi phí nhưng cải thiện hiệu suất.
Uy tín của nhà cung cấp – Các nhà cung cấp uy tín có thể tính phí cao hơn nhưng cung cấp sự ổn định và hỗ trợ tốt hơn.
Mặc dù khoản đầu tư ban đầu cao hơn so với các bộ phận tiêu chuẩn, nhưng tần suất thay thế giảm thường mang lại khoản tiết kiệm lâu dài.
Phần kết luận
Các bộ phận chịu mài mòn bằng cacbua vonfram là khoản đầu tư quan trọng cho các công ty cần độ bền, độ chính xác và tuổi thọ dài cho máy móc của họ.
Bằng cách hiểu các loại, ứng dụng, cấp độ và yêu cầu bảo trì, người ra quyết định có thể đưa ra những lựa chọn sáng suốt giúp cải thiện hiệu quả hoạt động và giảm chi phí.
Cho dù trong khai thác mỏ, dầu khí, gia công kim loại hay xây dựng, các bộ phận chịu mài mòn cacbua vonfram phù hợp có thể tạo nên sự khác biệt giữa thời gian ngừng hoạt động liên tục và sản xuất trơn tru, có lợi nhuận.
Nếu bạn muốn biết thêm chi tiết về bất kỳ công ty nào, vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi.
