When it comes to rotating equipment, pumps, and mechanical assemblies, bushings are the unsung heroes.
They ensure smooth shaft movement, reduce vibration, and protect equipment from wear. But not all bushings perform equally under demanding conditions.
Two of the most common materials are tungsten carbide and stainless steel. Both are durable, but their performance in wear, corrosion, and heat resistance differs greatly.
So, which one really lasts longer? This article compares tungsten carbide bushings vs stainless steel bushings, helping engineers choose the right solution for longer service life and better reliability.
Understanding the Basics

Before comparing, it’s important to understand what these bushings are made of and how they work.
Stainless steel bushings are made from alloys that contain iron, chromium, and nickel.
They resist corrosion and are widely used in general machinery and water systems.
Tungsten carbide bushings, on the other hand, are made from tungsten and carbon powder sintered at very high temperature.
The result is a metal-ceramic composite that is much harder and more 耐磨 than metal alloys.
Material Property Comparison
| 财产 | 碳化钨 | 不锈钢 |
|---|---|---|
| 硬度(HRA) | 88–92 | 35–45 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 4000+ | 900–1100 |
| 耐腐蚀 | Excellent (especially with Nickel binder) | 好的 |
| Thermal Stability (°C) | Up to 1000°C | Up to 400°C |
| Cost Level | High (but long life) | 低至中等 |
From 硬度 to strength, tungsten carbide outperforms stainless steel in every area that affects wear and life expectancy.
Wear Resistance in Motion
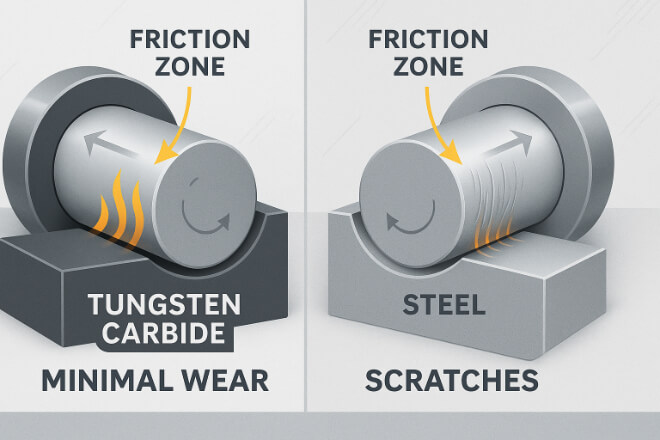
Wear is the main factor that limits the lifespan of a bushing.
In high-speed rotating equipment — such as pumps, compressors, or turbines — friction between the shaft and bushing surface can cause rapid material loss.
Tungsten carbide, with its extremely hard surface, resists both adhesive and abrasive wear.
Even in dry or semi-lubricated conditions, it maintains dimensional accuracy far longer than stainless steel.
Stainless steel bushings are more ductile, which helps absorb shock loads, but they wear much faster when exposed to abrasive media such as sand, slurry, or hard particles in fluids.
Corrosion Resistance and Chemical Stability

In wet or chemical environments, stainless steel can corrode over time, especially if exposed to chlorides, acids, or saltwater.
Tungsten carbide with nickel binder resists these attacks far better. It is chemically inert in many corrosive fluids, including water-glycol, chemical slurries, and oils with additives.
For pumps and mixers used in food, chemical, or offshore environments, tungsten carbide bushings maintain surface smoothness and avoid pitting or rusting — both of which can lead to contamination or seal failure.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
| 健康)状况 | 碳化钨衬套 | Stainless Steel Bushing |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1000°C | Around 400°C |
| Maximum Pressure | Very High (Over 40 MPa) | Moderate (10–20 MPa) |
| Thermal Expansion | Low (Dimensionally Stable) | High (May Expand/Contract) |
Tungsten carbide’s low expansion and high compressive strength make it the better choice for high-pressure, high-temperature machinery.
Cost vs Lifetime: ROI Perspective
While tungsten carbide bushings cost more at the start, they provide much better value over time.
The extended life cycle and reduced maintenance offset the higher purchase price.
| 因素 | 碳化钨 | 不锈钢 |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | 高的 | 低的 |
| Maintenance Frequency | 低的 | 高的 |
| Replacement Interval | 5–10× longer | 短的 |
| Overall ROI | 高的 | 中等的 |
For companies running 24/7 equipment, tungsten carbide bushings can reduce total maintenance costs by 40–60% over several years.
Best Applications for Each Material
| Application Type | Recommended Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Pumps for Slurries or Sand-Laden Fluids | 碳化钨 | Superior abrasion resistance |
| Food or Clean Water Systems | 不锈钢 | Corrosion resistance at lower cost |
| High-Pressure Compressors | 碳化钨 | Handles extreme loads |
| Low-Speed, Non-Critical Assemblies | 不锈钢 | Economical choice |
While both materials have their place, tungsten carbide is the clear winner for abrasive, high-load, and long-duty environments, while stainless steel remains sufficient for general corrosion-resistant 应用程序。
Maintenance and Service Considerations

Tungsten carbide bushings require little to no lubrication once properly installed. Their smooth finish minimizes friction, reducing energy loss and heat generation.
Stainless steel bushings, however, often depend on consistent lubrication. Without it, galling and friction can accelerate wear — especially in dry or high-temperature operation.
Periodic inspection is still important for both types, but tungsten carbide typically allows longer service intervals and less frequent replacements.
Final Verdict: Which Lasts Longer?

When durability is the priority, tungsten carbide bushings clearly last longer.
They can outlast stainless steel by five to ten times, especially under high stress, abrasive, or corrosive conditions.
For low-load, clean environments, stainless steel may still be adequate and cost-effective.
But for heavy-duty industrial machinery, the performance difference is too large to ignore.
结论
The choice between tungsten carbide and stainless steel bushings depends on the working environment, but the evidence is clear:
Tungsten carbide bushings provide superior hardness, wear resistance, and lifespan, making them the long-term solution for companies seeking higher reliability and lower total costs.
By investing in tungsten carbide, manufacturers not only improve equipment uptime but also reduce waste, maintenance effort, and energy loss — all key goals for modern industrial operations.
如果您想了解任何公司的更多详细信息,请随时 联系我们。
