Tungsten carbide tips are widely used in industrial applications due to their superior 硬度 和 耐磨性。
Understanding the microstructure of tungsten carbide is key to comprehending how these tips perform in demanding environments.
This blog will explore the essential elements of tungsten carbide’s microstructure, and how it impacts the performance and longevity of carbide tips in various industrial sectors.
什么是碳化钨?
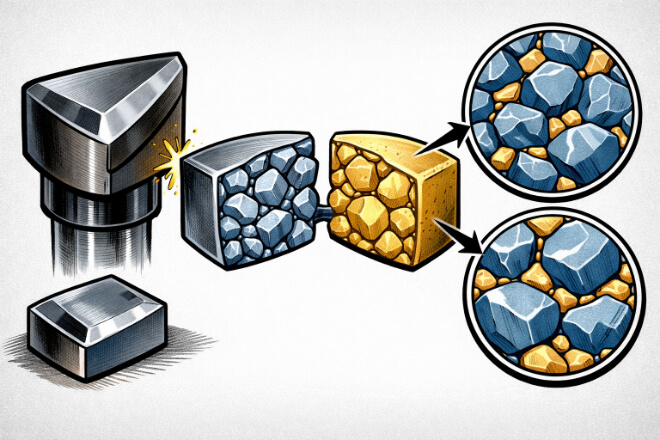
Tungsten carbide (WC) is a compound made from tungsten and carbon. It is well known for its 硬度 和 resistance to wear, making it ideal for cutting tools, 矿业, and other industrial uses.
The microstructure of tungsten carbide is critical to these properties, as it dictates how the material interacts with other surfaces and how well it can withstand extreme conditions.
How the Microstructure of Tungsten Carbide Affects Performance
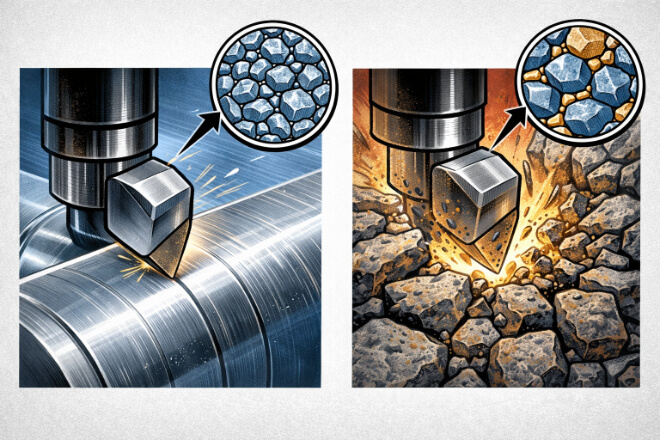
The performance of tungsten carbide tips heavily relies on its microstructure, which consists of tungsten carbide grains bonded together by a metallic binder, typically cobalt.
The distribution and size of these grains influence the material’s toughness, wear resistance, and impact resistance.
A fine-grained structure generally offers better hardness, while a coarser structure provides increased toughness.
The Role of Cobalt in Tungsten Carbide Tips
Cobalt is commonly used as a binder in tungsten carbide tips. It plays a critical role in determining the material’s toughness and durability.
The amount of cobalt used in the mix directly influences the final properties of the tungsten carbide. Higher cobalt content can enhance toughness but may reduce 耐磨性.
Conversely, a lower cobalt content increases hardness but may compromise 韧性。
The Impact of Grain Size on Wear Resistance and Toughness
The grain size in tungsten carbide tips is crucial to its overall performance. Finer grains lead to higher hardness, making the material more resistant to wear.
However, larger grains increase toughness, allowing the material to withstand higher impact forces.
By controlling the 粒度, manufacturers can create tungsten carbide tips optimized for specific applications, balancing 耐磨性 和 韧性.
Manufacturing Process and Its Effect on Microstructure
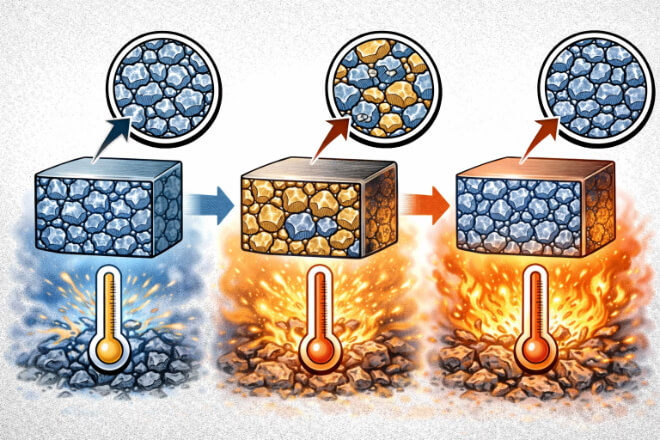
The manufacturing process plays a significant role in shaping the microstructure of tungsten carbide tips.
During sintering, the carbide powder is heated to high temperatures to form a solid mass.
The rate of cooling, temperature, and time spent in the furnace all affect the grain structure and the final properties of the carbide.
Proper control of these factors ensures that the tips have the desired characteristics.
Common Applications of Tungsten Carbide Tips

Tungsten carbide tips are used in a variety of industries, including mining, oil & gas drilling, metalworking, and woodworking.
The specific microstructure of the tips influences how well they perform in these applications. For example:
矿业 tools: Require tungsten carbide tips with a balance of toughness and wear resistance to withstand harsh conditions.
木工 tools: Typically use tips with fine-grain tungsten carbide for superior cutting performance.
钻头: Must have a tough and durable microstructure to handle the high impact and heat generated during drilling.
结论
The microstructure of tungsten carbide is a crucial factor that determines the material’s performance.
By understanding how the grain size, binder content, and manufacturing process affect the properties of tungsten carbide tips, industrial decision-makers can select the right materials for their specific needs.
This knowledge ensures that tungsten carbide tips continue to provide superior performance in even the most demanding applications.
如果您想了解任何公司的更多详细信息,请随时 联系我们。
