In many industries, machine parts face constant wear from friction, impact, heat, and corrosion. When a part wears out too soon, it can cause expensive downtime and lower productivity.
That is why many companies turn to tungsten carbide — a material known for its outstanding 耐磨性 and long service life.
This guide explains what tungsten carbide is, why it is so effective against wear, where it is used, and how decision-makers can get the most value from it.
什么是碳化钨?

Tungsten carbide is a compound made of tungsten and carbon atoms. These atoms are bonded in a way that creates extreme hardness — almost as hard as diamond.
It is usually combined with a metal binder, such as cobalt or nickel, to improve toughness.
最终得到的材料是:
Very hard (resists scratches and dents)
Strong under pressure (handles heavy loads)
Resistant to wear (lasts longer in harsh environments)
This unique combination makes tungsten carbide a preferred choice for parts that need to last under constant mechanical stress.
Why Wear Resistance Matters to Industries
耐磨性 is the ability of a material to keep its shape, size, and performance when in contact with other materials. Poor wear resistance means parts wear out fast, leading to:
Frequent replacements
维护成本更高
Unexpected downtime
Lower productivity
For industries like mining, manufacturing, 石油和天然气, 和 建造, a single equipment breakdown can cost thousands of dollars per hour. Tungsten carbide helps reduce these risks.
Key Properties That Give Tungsten Carbide Superior Wear Resistance

Tungsten carbide’s performance comes from its material properties:
极端 硬度 – Keeps cutting edges sharp and surfaces smooth for longer.
High Compressive Strength – Handles high-pressure contact without deformation.
Excellent Heat Resistance – Maintains hardness even at high temperatures.
Corrosion Resistance – Stands up to chemicals, moisture, and abrasive particles.
Low Friction Coefficient – Reduces material loss during contact.
Common Industrial Applications for Tungsten Carbide Wear Resistance

Tungsten carbide is used anywhere parts face heavy wear. Some examples include:
Comparison: Tungsten Carbide vs. Other Wear-Resistant Materials
| 材料 | Main Strength | Main Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| 碳化钨 | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, heat tolerance | More expensive than steel |
| Tool Steel | Good toughness, easy to machine | Wears faster, less heat resistance |
| 陶瓷 | Excellent hardness, corrosion resistance | More brittle, poor impact resistance |
How Tungsten Carbide Extends Equipment Life

One of the biggest reasons companies choose tungsten carbide is its ability to keep machinery running longer.
By resisting wear, parts maintain their performance for more hours of operation, which means:
Less frequent part changes
Reduced labor costs for maintenance
Lower risk of unplanned downtime
Better return on investment (ROI)
Cost Considerations for Tungsten Carbide

It is true that tungsten carbide components often cost more upfront compared to steel. However, the total cost over the part’s lifetime is often lower because:
They last longer before needing replacement.
They reduce downtime-related losses.
They maintain better performance over time.
For decision-makers, calculating cost per operating hour often shows tungsten carbide as the more economical choice in the long term.
Choosing the Right Tungsten Carbide Grade for Wear Resistance
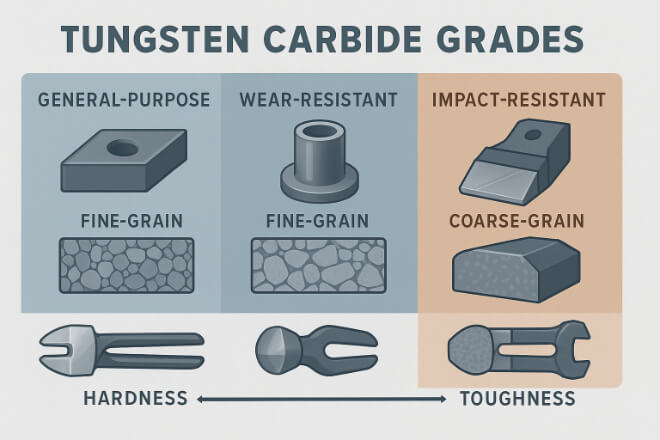
Tungsten carbide comes in different grades, and selecting the right one is essential:
Fine-Grain Grades – Better 耐磨性, ideal for precision cutting.
Coarse-Grain Grades – Better impact resistance for heavy-duty jobs.
Low Cobalt Binder – More hardness, less toughness.
Matching the grade to the application ensures optimal wear resistance and performance.
Maintenance Practices to Maximize Tungsten Carbide Life
Even the hardest material needs care to reach its full potential. Recommended practices include:
| Practice | 益处 |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Identifies wear before it leads to failure |
| Proper Lubrication | Reduces friction and heat buildup |
| Correct Installation | Prevents stress and premature damage |
| Cleaning After Use | Removes debris and chemicals that cause corrosion |
Industries That Benefit Most from Tungsten Carbide

While almost any sector with high-wear machinery can benefit from tungsten carbide, it is especially valuable in:
Mining – Extends the life of expensive drilling and crushing equipment.
Oil & Gas – Protects components in abrasive and corrosive environments.
Manufacturing – Reduces downtime in high-speed production lines.
Construction – Improves durability in roadwork and heavy excavation.
Future Trends: Tungsten Carbide in Advanced Wear Solutions
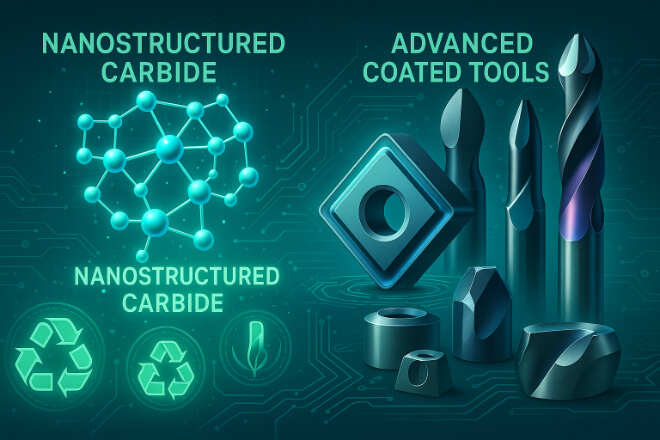
With ongoing advances in powder metallurgy, nanostructured carbides, and coating technologies, tungsten carbide is expected to become even more efficient and versatile in wear applications.
Industries are also moving toward sustainable production, with recycling programs that reclaim tungsten carbide from used parts to reduce waste and material costs.
结论
For industries facing constant mechanical wear, tungsten carbide offers a proven way to extend part life, cut downtime, and improve operational efficiency.
While the initial cost may be higher, the savings in maintenance and the boost in productivity make it a smart choice for many companies.
By understanding the material’s properties, selecting the right grade, and maintaining it properly, decision-makers can maximize the benefits of tungsten carbide in their operations.
如果您想了解任何公司的更多详细信息,请随时 联系我们。
