In today’s manufacturing world, sustainability is more than just a trend—it’s a responsibility. One important area many businesses overlook is recycling cutting tools, especially those made of tungsten carbide.
If you’re running a machining operation, you’ve probably wondered: Can タングステンカーバイド切削工具 be recycled?
The short answer is yes, and the benefits go far beyond just being eco-friendly. Recycling tungsten carbide tools can help you lower costs, improve your sustainability efforts, and even recover value from worn-out tools.
In this article, we’ll explore how tungsten carbide tool recycling works, why it matters, and how your business can benefit from it.
Why Recycling Tungsten Carbide Tools Matters

Tungsten carbide is a rare and expensive material. It’s known for being extremely hard and 耐摩耗性—perfect for cutting tough metals. But it also takes a lot of energy and raw materials to produce.
Recycling used tools helps to:
Reduce environmental impact
Cut down on mining of natural resources
Save money on raw material costs
Support global sustainability goals
Whether you’re a small machine shop or a large manufacturing facility, recycling should be part of your long-term tooling strategy.
What Makes Tungsten Carbide Recyclable?
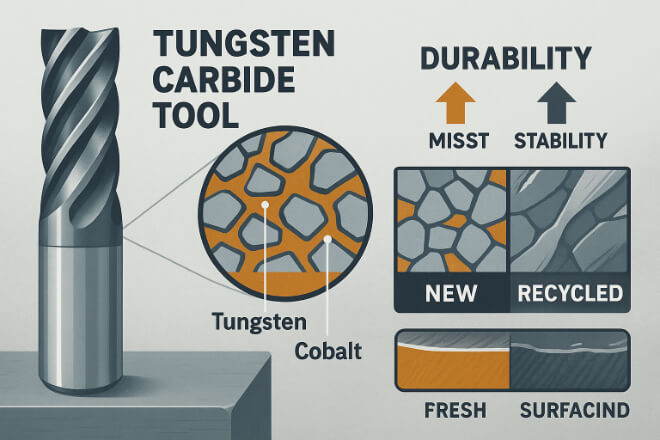
Tungsten carbide is a composite material made from tungsten and a metal binder, usually cobalt.
These elements are highly valuable and don’t degrade easily. Even after tools are worn out, the material can still be recovered and reused.
Key recyclable features:
Durability: Unlike steel, carbide doesn’t lose its core structure after use.
High tungsten content: Typically 70–97% tungsten by weight.
Stable recycling process: Refined through chemical or thermal methods.
Because of its structure, carbide is more recyclable than many other tool materials.
Types of Tools That Can Be Recycled
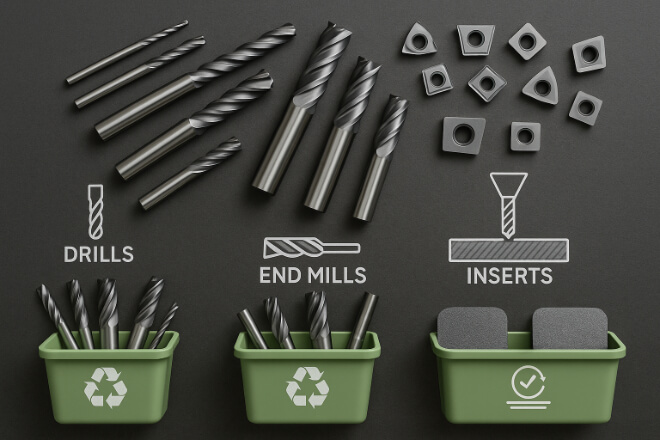
Not all cutting tools are suitable for recycling, but most solid carbide tools and carbide inserts are. These include:
Drills
リーマー
Turning inserts
Milling inserts
Worn-down blanks
Tools with minimal contamination (like coatings or brazed joints) are easier to recycle. Some suppliers will even accept mixed lots for recycling, depending on their process.
How the Recycling Process Works

Here’s a simplified version of how the tungsten carbide recycling process usually works:
Step 1: Collection and Sorting
Used carbide tools are collected and sorted. This includes checking for contamination, separating tool types, and removing any non-carbide material.
Step 2: Crushing and Grinding
Tools are crushed into small particles or powder to prepare for refining.
Step 3: Chemical or Thermal Processing
Two main methods are used:
Zinc recycling process (for direct reuse of tungsten carbide)
Chemical refining (to recover pure tungsten and cobalt)
Step 4: Powder Recovery and Reuse
The final powder can be reused to make new carbide tools with little to no quality loss.
This process allows for up to 95% material recovery and significantly reduces the need for mining new tungsten.
Benefits for Manufacturers

Recycling carbide tools isn’t just about being green—it has real benefits for your business:
1). Cost Savings
Used tools can often be sold back to your supplier or recycling partner. You may also receive credit toward future tool purchases.
2). Stable Material Supply
Recycled carbide reduces dependence on raw material mining, which is often impacted by supply chain issues and price spikes.
3). Better ESG Performance
Many companies now track Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics.
Recycling supports goals related to environmental impact and corporate responsibility.
4). Cleaner Workspaces
Regularly collecting and recycling used tools helps keep your workspace more organized and free of scrap.
Choosing a Recycling Partner
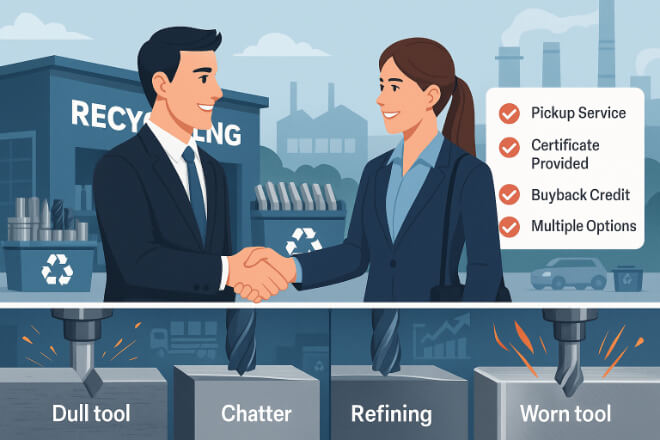
Working with the right recycling partner is essential. Look for companies that:
Specialize in tungsten carbide recycling
Offer pick-up services or drop-off locations
Provide certificates of recycling or material recovery
Offer buyback or credit programs
What About Coated Tools?
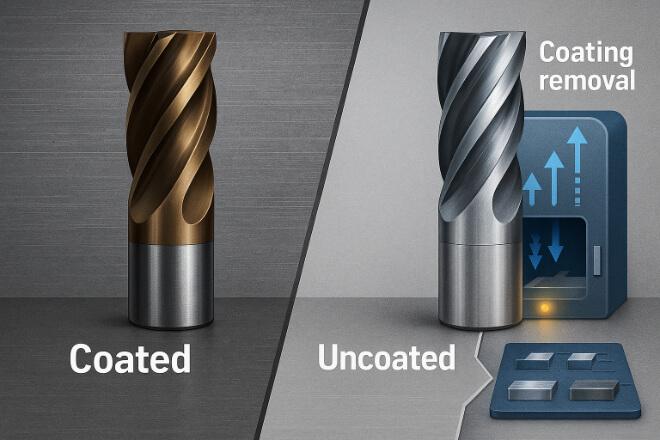

Coated tools—such as those with TiAlN, TiN, or DLC coatings—can still be recycled.
However, the coating may need to be removed before processing, depending on the recycler’s method.
Some recyclers are equipped to handle coatings without extra processing, so it’s worth checking their capabilities.
Common Myths About Tool Recycling
Let’s clear up a few misunderstandings:
吾輩は猫である。名前はまだない。どこで生まれたか頓と見当がつかぬ。
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Recycling is expensive | Most recyclers offer free collection or even pay for scrap |
| Only large companies can recycle | Even small shops can participate |
| Recycled material is lower quality | Modern processes recover high-purity powder used for premium tools |
| It’s not worth the time | Many partners make recycling fast and easy |
Best Practices for Carbide Tool Recycling
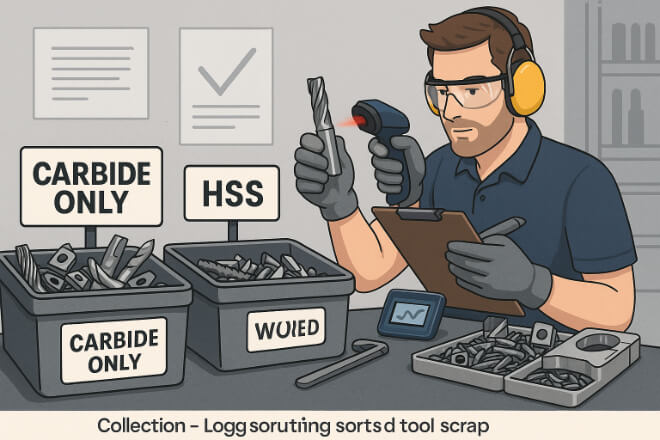
To make the most of your recycling program:
Sort tools by material type (carbide vs. HSS)
Keep tools clean and dry to avoid contamination
Label your scrap containers clearly
Track tool usage and returns for performance insight
Partner with your tool supplier to create a closed-loop process
By building these habits into your workflow, you’ll turn recycling into a routine that boosts both environmental and business results.
Recycling vs. Reconditioning
Recycling is not the only option. Reconditioning—resharpening and re-coating worn tools—is another way to extend tool life.
Many carbide tools can be reconditioned 2–3 times before needing full recycling.
| Option | 最適な用途 | Main Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Reconditioning | Tools still in good shape | Extends tool life at lower cost |
| リサイクル | Worn-out or broken tools | Material recovery and reduced waste |
Tip: Always ask your supplier if a worn tool is a good candidate for reconditioning before you toss it.
Environmental Impact at a Glance
Let’s look at the environmental benefits of recycling 1,000 kg of carbide scrap:
| Impact Area | Estimated Savings |
|---|---|
| Raw material extraction | 60–70% reduction |
| Energy use | 50–60% less energy than mining |
| CO₂ emissions | 30–40% lower emissions |
| Waste reduction | Thousands of tools diverted from landfills |
These numbers show how powerful a small change—like tool recycling—can be.
最後に
Tungsten carbide cutting tools are known for their durability, but they don’t last forever.
When they reach the end of their life, recycling is the smart move—for your business and the environment.
Whether you’re looking to reduce costs, improve sustainability, or simply make smarter use of materials, carbide tool recycling offers real value.
To get started, talk to your cutting tool supplier or recycling partner today. And if you’re looking for a supplier that offers both premium tools and recycling support, visit リトプズ.
